
Programs Plus is a retail firm that sells computer programs for home and business use. On December 31, 2019, its general ledger contained the accounts and balances shown below:
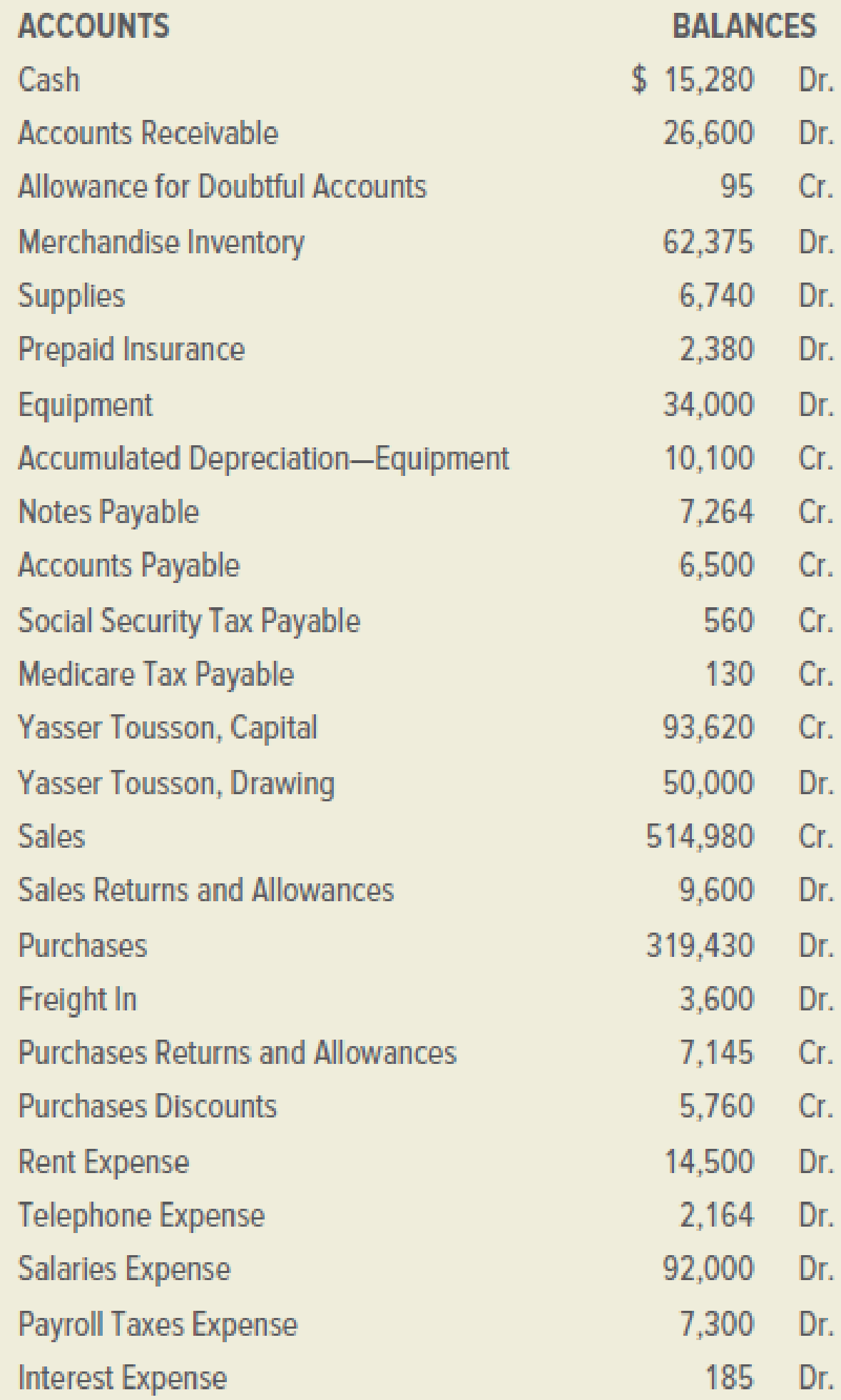
The following accounts had zero balances:

The data needed for the adjustments on December 31 are as follows:
a.–b. Ending merchandise inventory, $67,850.
c. Uncollectible accounts, 0.5 percent of net credit sales of $245,000.
d. Supplies on hand December 31, $1,020.
e. Expired insurance, $1,190.
f.
g. Accrued interest expense on notes payable, $325.
h. Accrued salaries, $2,100.
i. Social Security Tax Payable (6.2 percent) and Medicare Tax Payable (1.45 percent) of accrued salaries.
INSTRUCTIONS
- 1. Prepare a worksheet for the year ended December 31, 2019.
- 2. Prepare a classified income statement. The firm does not divide its operating expenses into selling and administrative expenses.
- 3. Prepare a statement of owner’s equity. No additional investments were made during the period.
- 4. Prepare a classified
balance sheet . All notes payable are due within one year. - 5. Journalize the
adjusting entries . Use 25 as the first journal page number. - 6. Journalize the closing entries.
- 7. Journalize the reversing entries.
Analyze: By what percentage did the owner’s capital account change in the period from January 1, 2019, to December 31, 2019?
1.
Prepare the worksheet and complete the sections of Trial balance, adjustments and compute the changes to the BW Capital that will be shown in the statement of owner's equity.
Explanation of Solution
Worksheet: A worksheet is the used in the preparation of the financial statement. It is a pre-defined form, having multiple columns, used in the adjustment process.
Prepare the worksheet for the year ended December 31, 2019.
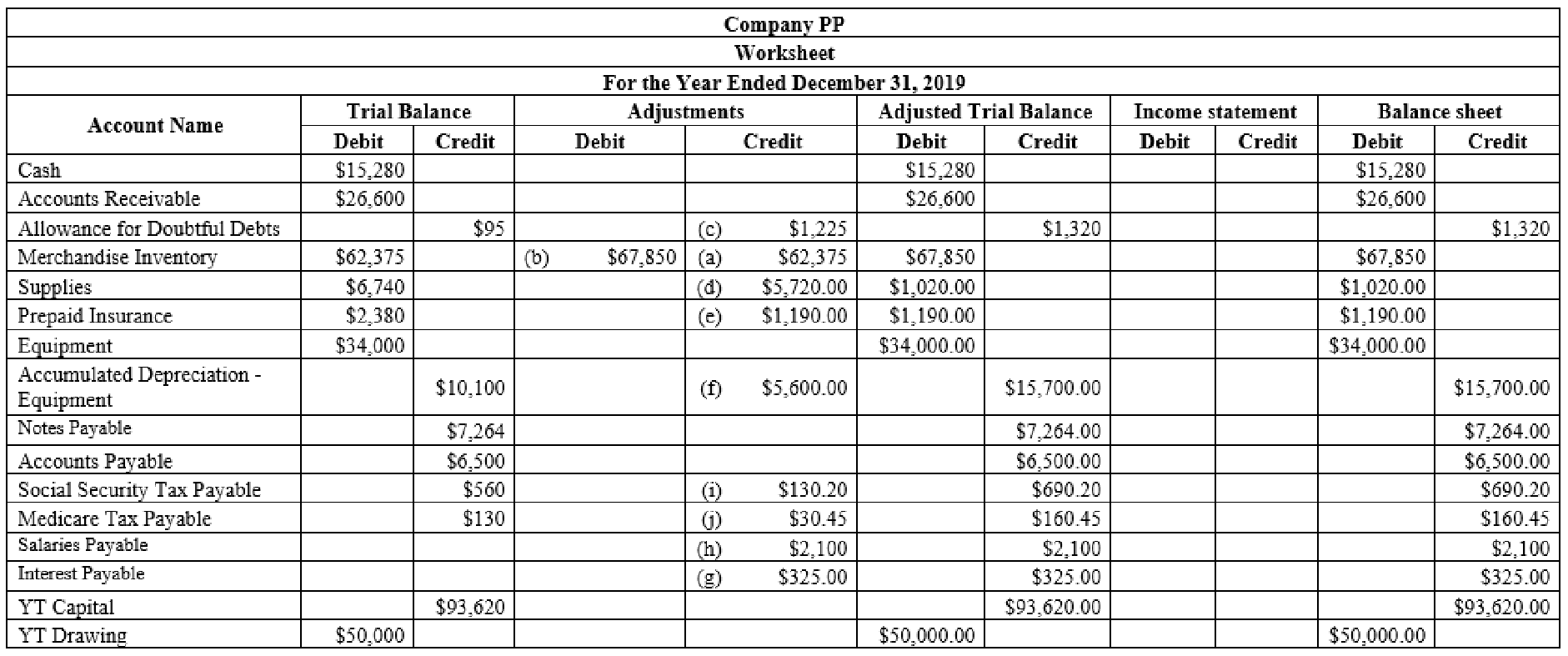
Figure (1)
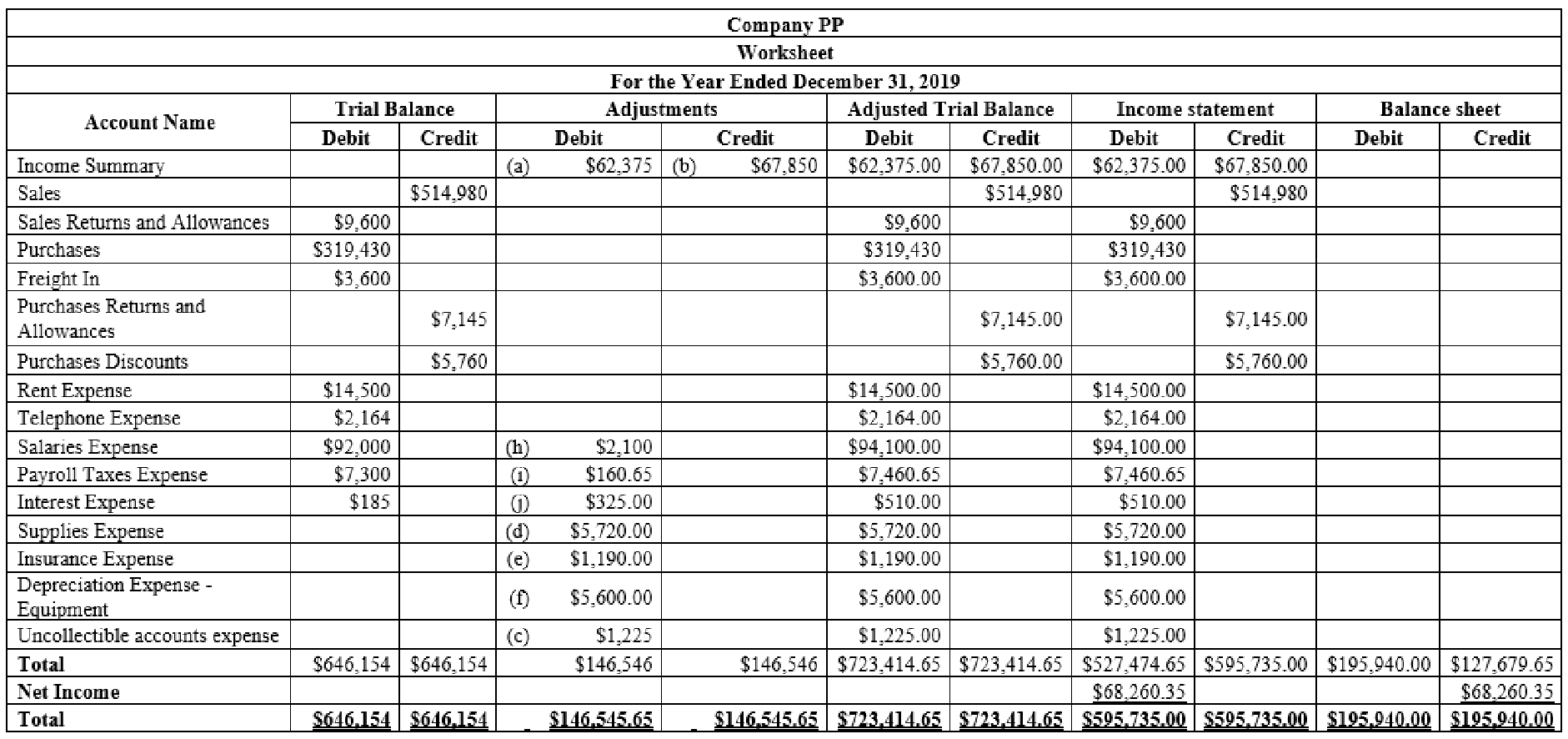
Figure (2)
2.
Show the Classified Income Statement.
Explanation of Solution
Classified Income statement: The classified income statement is a financial statement that shows the revenues, expenses with various classifications and sub-totals. The classified income statement is used for complex income statement as its more easily understandable.
Prepare the classified income statement:
| Company PP | ||||
| Income Statement | ||||
| Year Ended December 31, 2019 | ||||
| Particulars | Amount ($) | Amount ($) | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Operating Revenue | ||||
| Sales | $514,980 | |||
| Less: Sales Returns and Allowances | $9,600 | |||
| Net Sales | $505,380 | |||
| Cost of Goods Sold | ||||
| Merchandise Inventory, January 1, 2019 | $62,375 | |||
| Purchases | $319,430 | |||
| Freight In | $3,600 | |||
| Delivered Cost of Purchases | $323,030 | |||
| Less: Sales Returns and Allowances | $7,145 | |||
| Purchases Discount | $5,760 | $12,905 | ||
| Net Delivered Cost of Purchases | $310,125 | |||
| Total Merchandise Available for sale | $372,500 | |||
| Less: Merchandise Inventory, closing | $67,850 | |||
| Cost of Goods Sold | $304,650 | |||
| Gross Profit on Sales | $200,730 | |||
| Operating Expenses | ||||
| Rent expense | $14,500 | |||
| Telephone Expense | $2,164 | |||
| Salaries Expense | $94,100 | |||
| Payroll Taxes Expense | $7,460.65 | |||
| Supplies Expense | $5,720 | |||
| Insurance Expense | $1,190 | |||
| Depreciation Expense - Equipment | $5,600 | |||
| Uncollectible Accounts Expense | $1,225 | |||
| Total Operating Expenses | $131,959.65 | |||
| Income from Operations | $68,770.35 | |||
| Other Expense | ||||
| Interest Expense | $510.00 | |||
| Net income for the year | $68,260.35 | |||
Table (1)
3.
Show the Statement of Owner's equity.
Explanation of Solution
Statement of owner's’ equity: This statement reports the beginning owner’s equity and all the changes which led to ending owner's’ equity.
Prepare the Statement of owner's’ equity:
| Company PP | ||
| Statement of Owner's Equity | ||
| Year Ended December 31, 2019 | ||
| Particulars | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| YT Capital, January 1, 2019 | $93,620 | |
| Net income for the year | $68,260.35 | |
| Deduct - Withdrawals | $50,000.00 | |
| Increase in Capital | $18,260.35 | |
| YT Capital, December 31, 2019 | $111,880.35 | |
Table (2)
4.
Show the Classified Balance Sheet and compute the percentage change in the owner’s capital in the accounting year 2019.
Explanation of Solution
Classified balance sheet: The main elements of balance sheet assets, liabilities, and stockholders’ equity are categorized or classified further into sections, and sub-sections in a classified balance sheet. Assets are further classified as current assets, long-term investments, property, plant, and equipment (PPE), and intangible assets. Liabilities are classified into two sections current and long-term. Stockholders’ equity comprises of common stock and retained earnings. Thus, the classified balance sheet includes all the elements under different sections.
Prepare the classified balance sheet:
| Company PP | |||
| Balance Sheet | |||
| December 31, 2019 | |||
| Particulars | Amount ($) | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Assets | |||
| Current Assets | |||
| Cash | $15,280 | ||
| Accounts receivable | $26,600 | ||
| Less: Allowance for Doubtful Debts | $1,320 | $25,280 | |
| Merchandise Inventory | $67,850 | ||
| Prepaid expenses | |||
| Supplies | $1,020 | ||
| Prepaid insurance | $1,190 | $2,210 | |
| Total Current Assets | $110,620 | ||
| Plant and Equipment | |||
| Equipment | $34,000 | ||
| Less: Accumulated Depreciation | $15,700 | $18,300 | |
| Total Plant and Equipment | $18,300 | ||
| Total Assets | $128,920 | ||
| Liabilities and Owner's Equity | |||
| Current Liabilities | |||
| Notes Payable | $7,264 | ||
| Accounts payable | $6,500 | ||
| Interest Payable | $325 | ||
| Social Security Tax Payable | $690.20 | ||
| Medicare Tax Payable | $160.45 | ||
| Salaries Payable | $2,100 | ||
| Total Current Liabilities | $17,039.65 | ||
| Owner's Equity | |||
| YT Capital | $111,880.35 | ||
| Total Liabilities and Owner's Equity | $128,920 | ||
Table (3)
Compute the percentage increase in owner’s capital:
The percentage increase in the owner’s capital is 19.5%.
5.
Journalize the adjusting entries as on December 31, 2019.
Explanation of Solution
Adjusting entries: Adjusting entries are those entries which are recorded at the end of the year, to update the income statement accounts (revenue and expenses) and balance sheet accounts (assets, liabilities, and stockholders’ equity) to maintain the records according to accrual basis principle.
Pass the adjusting entry for the given transaction:
| General Journal | Page - 25 | |||
| Date | Description | Post Ref. | Debit | Credit |
| 2019 | ||||
| December 31 | Income Summary | $62,375 | ||
| Merchandise Inventory | $62,375 | |||
| (To record the beginning inventory) | ||||
| December 31 | Merchandise Inventory | $67,850 | ||
| Income Summary | $67,850 | |||
| (To record the closing inventory) | ||||
| December 31 | Uncollectible Accounts Expense | $1,225 | ||
| Allowance for Doubtful Accounts | $1,225 | |||
| (To record the estimated loss on the net credit sale) |
Table (4)
| General Journal | Page - 26 | |||
| Date | Description | Post Ref. | Debit | Credit |
| 2019 | ||||
| December 31 | Supplies Expense | $5,720 | ||
| Supplies | $5,720 | |||
| (To record the Supplies used) | ||||
| December 31 | Insurance expense | $1,190 | ||
| Prepaid Insurance | $1,190 | |||
| (To record the prepaid insurance) | ||||
| December 31 | Depreciation Expense - Equipment | $5,600 | ||
| Accumulated Depreciation - Equipment | $5,600 | |||
| (To record the depreciation on equipment) | ||||
| December 31 | Interest expense | $325 | ||
| Interest Payable | $325 | |||
| (To record the interest payable) | ||||
| December 31 | Salaries Expense | $2,100 | ||
| Salaries Payable | $2,100 | |||
| (To record the salaries payable) | ||||
| December 31 | Payroll Taxes Expense | $160.65 | ||
| Social Security Tax Payable | $130.20 | |||
| Medicare Tax Payable | $30.45 | |||
| (To record the taxes on accrued wages) |
Table (5)
6.
Journalize the closing entries as on December 31, 2019.
Explanation of Solution
Closing entries: The journal entries prepared to close the temporary accounts to Retained Earnings account are referred to as closing entries. The revenue, expense, and dividends accounts are referred to as temporary accounts because the information and figures in these accounts is held temporarily and consequently transferred to permanent account at the end of accounting year.
Pass the closing entries:
| General Journal | Page - 27 | |||
| Date | Description | Post Ref | Debit | Credit |
| 2019 | ||||
| December 31 | Sales | $514,980 | ||
| Purchases Returns and allowances | $7,145 | |||
| Purchases Discounts | $5,760 | |||
| Income Summary | $527,885 | |||
| (To record the closing entry for the income) | ||||
| December 31 | Income Summary | $465,099.65 | ||
| Sales Returns and Allowances | $9,600 | |||
| Purchases | $319,430 | |||
| Freight In | $3,600 | |||
| Rent Expense | $14,500 | |||
| Telephone Expense | $2,164 | |||
| Salaries Expense | $94,100.00 | |||
| Payroll Taxes Expense | $7,460.65 | |||
| Supplies Expense | $5,720 | |||
| Insurance expense | $1,190 | |||
| Depreciation Expense - Warehouse Equipment | $5,600 | |||
| Uncollectible Accounts Expense | $1,225 | |||
| Interest Expense | $510 | |||
| (To record the closing entry for the expenses) |
Table (6)
| General Journal | Page - 28 | |||
| Date | Description | Post Ref | Debit | Credit |
| 2019 | ||||
| December 31 | Income Summary | $68,260.35 | ||
| YT Capital | $68,260.35 | |||
| (To record the closing entry for the capital) | ||||
| December 31 | YT Capital | $50,000 | ||
| YT Drawings | $50,000 | |||
| (To record the closing entry for the capital) |
Table (7)
7.
Journalize the reversing entries as on January 1, 2020.
Explanation of Solution
Reversing entries: Reversing entries are those entries which are recorded at the beginning of the year, to reverse or set right the adjusting entries made in the end of the previous accounting year, in order to maintain the records according to accrual basis principle.
Pass the reversing entries:
| General Journal | Page - 29 | |||
| Date | Description | Post Ref | Debit | Credit |
| 2020 | ||||
| January 1 | Interest Payable | $325 | ||
| Interest Expense | $325 | |||
| (To record the reversing entry for interest payable) | ||||
| January 1 | Salaries Payable | $2,100 | ||
| Salaries Expense - Office | $2,100 | |||
| (To record the reversing entry for salaries payable) | ||||
| January 1 | Social Security Tax Payable | $130.20 | ||
| Medicare Tax Payable | $30.45 | |||
| Payroll Taxes Expense | $160.65 | |||
| (To record the reversing entry for payroll taxes payable) |
Table (8)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
LooseLeaf for College Accounting: A Contemporary Approach
- please don't use AI tool.arrow_forwardincoporate the accounting conceptual frameworksarrow_forwarda) Define research methodology in the context of accounting theory and discuss the importance of selecting appropriate research methodology. Evaluate the strengths and limitations of quantitative and qualitative approaches in accounting research. b) Assess the role of modern accounting theories in guiding research in accounting. Discuss how contemporary theories, such as stakeholder theory, legitimacy theory, and behavioral accounting theory, shape research questions, hypotheses formulation, and empirical analysis. Question 4 Critically analyse the role of financial reporting in investment decision-making, emphasizing the qualitative characteristics that enhance the usefulness of financial statements. Discuss how financial reporting influences both investor confidence and regulatory decisions, using relevant examples.arrow_forward
- Fastarrow_forwardCODE 14 On August 1, 2010, Cheryl Newsome established Titus Realty, which completed the following transactions during the month: a. Cheryl Newsome transferred cash from a personal bank account to an account to be used for the business in exchange for capital stock, $25,000. b. Paid rent on office and equipment for the month, $2,750. c. Purchased supplies on account, $950. d. Paid creditor on account, $400. c. Earned sales commissions, receiving cash, $18,100. f. Paid automobile expenses (including rental charge) for month, $1,000, and miscel- laneous expenses, $600. g. Paid office salaries, $2,150. h. Determined that the cost of supplies used was $575. i. Paid dividends, $2,000. REQUIREMENTS: 1. Determine increase - decrease of each account and new balance 2. Prepare 3 F.S: Income statement; Retained Earnings Statement; Balance Sheet Scanned with CamScannerarrow_forwardAssume that TDW Corporation (calendar-year-end) has 2024 taxable income of $952,000 for purposes of computing the §179 expense. The company acquired the following assets during 2024: (Use MACRS Table 1, Table 2, Table 3, Table 4, and Table 5.) Asset Machinery Computer equipment Furniture Total Placed in Service September 12 February 10 April 2 Basis $ 2,270,250 263,325 880,425 $ 3,414,000 b. What is the maximum total depreciation, including §179 expense, that TDW may deduct in 2024 on the assets it placed in service in 2024, assuming no bonus depreciation? Note: Round your intermediate calculations and final answer to the nearest whole dollar amount. Maximum total depreciation deduction (including §179 expense)arrow_forward
- Evergreen Corporation (calendar-year-end) acquired the following assets during the current year: (Use MACRS Table 1 and Table 2.) Date Placed in Asset Machinery Service October 25 Original Basis $ 120,000 Computer equipment February 3 47,500 Used delivery truck* August 17 Furniture April 22 60,500 212,500 The delivery truck is not a luxury automobile. Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to the nearest whole dollar amount. b. What is the allowable depreciation on Evergreen's property in the current year if Evergreen does not elect out of bonus depreciation and elects out of §179 expense?arrow_forwardLina purchased a new car for use in her business during 2024. The auto was the only business asset she purchased during the year, and her business was extremely profitable. Calculate her maximum depreciation deductions (including §179 expense unless stated otherwise) for the automobile in 2024 and 2025 (Lina doesn't want to take bonus depreciation for 2024) in the following alternative scenarios (assuming half-year convention for all): (Use MACRS Table 1, Table 2, and Exhibit 10-10.) a. The vehicle cost $40,000, and business use is 100 percent (ignore §179 expense). Year Depreciation deduction 2024 2025arrow_forwardEvergreen Corporation (calendar-year-end) acquired the following assets during the current year: (Use MACRS Table 1 and Table 2.) Date Placed in Asset Machinery Service October 25 Original Basis $ 120,000 Computer equipment February 3 47,500 Used delivery truck* August 17 Furniture April 22 60,500 212,500 The delivery truck is not a luxury automobile. Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to the nearest whole dollar amount. a. What is the allowable depreciation on Evergreen's property in the current year, assuming Evergreen does not elect §179 expense and elects out of bonus depreciation?arrow_forward
 Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage LearningCentury 21 Accounting Multicolumn JournalAccountingISBN:9781337679503Author:GilbertsonPublisher:Cengage
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage LearningCentury 21 Accounting Multicolumn JournalAccountingISBN:9781337679503Author:GilbertsonPublisher:Cengage Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning



