
To label:
To label the diagram of the antibody.
Introduction:
The structure of the antibody resembles the alphabet Y and consists of 4 proteins (2 light chains and 2 heavy chains).
Pictorial representation:
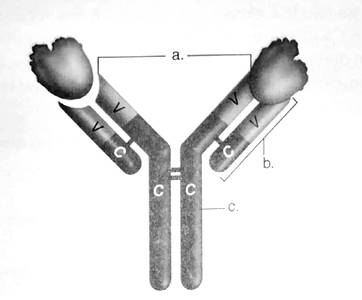
Figure: The structure of an antibody molecule.
The correct answers are:
- Antigen binding sites
- Light chain
- Heavy chain
V stands for the variable region
C stands for the constant region
Explanation for the answers:
- Antigen binding site − These are the sites on the amino-terminal end of both light and heavy chain. It provides a site of attachment for the antigen.
- Light chain − There is 2 identical light chains consisting of polypeptides. They are bound to the heavy chain via disulfide bonds and non-covalent interactions.
- Heavy chain − There are 5 types of heavy chains (accordingly antibodies are named) and attached to each other via the disulfide bonds.
V stands for variable region. The amino-terminal end of both heavy and light chain of about 100-110 amino acids vary considerably among antibodies and hence are called as variable region.
C stands for the constant region. The carboxy-terminalend of both light and heavy chain shows similarity among antibodies and hence is considered as constant regions.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 13 Solutions
BIOL 1010/1020 CLASS ONLY CONNECT
- Which of the following is not true about the life-cycle of Fucus. a. 8 eggs per oogonium b. 64 sperm per antheridium c. eggs are flagellated d. sperm are flagellatedarrow_forwardGreen Algae, as a group, is actually paraphyletic with one subgroup more closely related to higher plants than the other. Which of the following green algae groups is more closely related to higher plants: a. Charophyceans b. Chlorophyceans c. Rhodophyta d. Xanthophyceansarrow_forwardCertain toxic terpenoids in this group is thought to deter herbivory but may also have some anti-tumor activity? a. green algae b. brown algae c. red algae d. golden algae e. none of thesearrow_forward
- In the cellular slime molds, the most common phase is: a. plasmodium b. pseudoplasmodial c. single cells as myxamoebae d. moundingarrow_forwardWhich of the following descriptive terms does not describe Hydrodictyon? a. colonial b. nonmotile c. 1 large reticulated chloroplast in each cell d. all of these describe Hydrodictyonarrow_forwardWhich of the following does not apply to Chara? a. "stoneworts" b. isogamous c. calcified walls d. apical growth with an axis and branchesarrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





