
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
For given solution vapor pressure lowering, freezing point depression, boiling point elevation and osmotic pressures to be calculated.
Concept introduction
Boiling point elevation
Where,
Freezing point depression
Where,
Osmotic pressure is the pressure that is needed to stop osmosis. Osmotic pressure of the solution is directly proportional to the concentration of the solution. We can calculate osmotic pressure by using this formula is given by,
Where,
Vapor pressure lowering: Vapor pressure lowering is one of the colligative properties. Pure solvent has higher vapour pressure than its solution have non-volatile liquid. Thus vapour pressure lowering guide boiling point elevation.
Where,
Answer to Problem 13.79QP
Vapour pressure lowering of the solution = 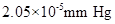
Freezing point elevation = 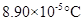
Boiling point elevation = 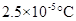
Osmotic pressure = 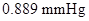
Explanation of Solution
Given data
Molar mass of egg white =
Amount of enzyme which is dissolved in water =
Amount of water =
Vapor pressure of water =
Calculation of number of moles in lysozyme and water
Molecular mass of water =
By plugging in the value of amount of Isozyme and molar mass of egg white, mole of Isozyme has calculated. Similarly, by plugging in the value of amount of water and molar mass of water, mole of water has calculated.
Calculation of vapour pressure lowering of the solution
By plugging in the values of mole fraction of Isozyme and vapour pressure of water, vapour pressure lowering of the solution has calculated.
Calculation freezing point depression of the solution
Molal freezing point depression constant =
By plugging in the values of molal freezing point depression constant and molality of the solution, freezing point depression of the solution has calculated.
Calculation of boiling point elevation of the solution
Boiling point elevation constant =
By plugging in the values of boiling point elevation constant and molality of the solution, boiling point elevation of the solution has calculated.
Calculation of osmotic pressure of the solution
As known above, we assume the density of the solution is
By plugging in the values of molarity of the solution, ideal gas constant and temperature in Kelvin, the osmotic pressure of the solution has calculated.
Vapour pressure lowering of the solution was calculated as
Freezing point elevation has calculated as
Boiling point elevation has calculated as
Osmotic pressure has calculated as
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
General Chemistry
- Calculate the pH and the pOH of each of the following solutions at 25 °C for which the substances ionize completely: (a) 0.200 M HClarrow_forwardCalculate the pH and the pOH of each of the following solutions at 25 °C for which the substances ionize completely: (a) 0.000259 M HClO4arrow_forwardWhat is the pH of a 1.0 L buffer made with 0.300 mol of HF (Ka = 6.8 × 10⁻⁴) and 0.200 mol of NaF to which 0.160 mol of NaOH were added?arrow_forward
- Determine if the following salt is neutral, acidic or basic. If acidic or basic, write the appropriate equilibrium equation for the acid or base that exists when the salt is dissolved in aqueous solution. If neutral, simply write only NR. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. NaN₃arrow_forwardCan I please get help with this?arrow_forwardCan I please get help with this?arrow_forward
- Use the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation to calculate pH of a buffer containing 0.050M benzoic acidand 0.150M sodium benzoate. The Ka of benzoic acid is 6.5 x 10-5arrow_forwardA. Draw the structure of each of the following alcohols. Then draw and name the product you would expect to produce by the oxidation of each. a. 4-Methyl-2-heptanol b. 3,4-Dimethyl-1-pentanol c. 4-Ethyl-2-heptanol d. 5,7-Dichloro-3-heptanolarrow_forwardWhat is the pH of a 1.0 L buffer made with 0.300 mol of HF (Ka = 6.8 × 10⁻⁴) and 0.200 mol of NaF to which 0.160 mol of NaOH were added?arrow_forward
- Can I please get help with this.arrow_forwardDetermine if the following salt is neutral, acidic or basic. If acidic or basic, write the appropriate equilibrium equation for the acid or base that exists when the salt is dissolved in aqueous solution. If neutral, simply write only NR. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. N₂H₅ClO₄arrow_forwardPlease help me with identifying these.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





