
Concept explainers
To explain: The following,
'a'If isomaltose is a mono-, di-, or polysaccharide?
Answer to Problem 13.55UTC
Solution:
'a'Isomaltose is a disaccharide.
Given: Structure of isomaltose in Haworth projection
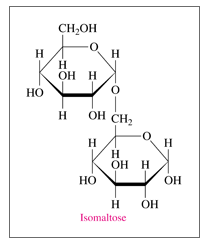
a.
Explanation of Solution
Isomaltose is a disaccharide as it contains two monosaccharides i.e.sugar units which are obtained after hydrolysis.
Therefore isomaltose is a disaccharide
b. The monosaccharides in isomaltose are two glucose units.
c. There is C1-C6 (a-a) O-glycosidic link in isomaltose.
Glycosidic link is the bond which connects two monosaccharides through anomeric carbon (a carbon which is coming from carbonyl group and attached with two oxygen atoms). In case of isomaltose, the anomeric carbon i.e. hemiacetal is linked with another sugar moiety through O atom. Thus this is a C1-C6 (a-a) O-glycosidic link.
Therefore, the monosaccharides in isomaltose are two glucose units and there is C1-C6 O-glycosidic link.
d. The given structure is an a-isomer of isomaltose.
As the OH group in the anomeric carbon is downward i.e. below the plane, so it is a-anomer (a-isomer of isomaltose).
Therefore the given structure is an a-isomer of isomaltose
e. Isomaltose is a reducing sugar
Isomaltose is a reducing sugar as it is capable of reducing Tollen’s reagent and Fehling solution. All the monosaccharides (aldoses) are reducing sugars along with some disaccharides. A disaccharide (as for example isomaltose) which has one anomeric carbon involved in glycosidic linkage but other anomeric carbon is free then it is able to reduce Tollen’s and Fehling solution.
Thus, isomaltose though a disaccharide is a reducing sugar.
- Isomaltose is a disaccharide.
- The monosaccharides in isomaltose are glucose units.
- The glycosidic link in isomaltose is C1-C6 (a-a) O-glycosidic link.
- The given structure is an a-isomer of isomaltose
- Isomaltose is a reducing sugar.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
CHEMISTRY: AN INTRODUCTION TO GENERAL, O
- What I Have Learned Directions: Given the following reaction and the stress applied in each reaction, answer the question below. A. H2(g) + Cl2(g) 2 HCl(g) Stress applied: Decreasing the pressure 1. What is the Keq expression? 2. What will be the effect in the number of moles of HCl(g)? 3. What will be the Equilibrium Shift or the reaction? B. Fe3O4(s) + 4 H2(g) + heat 53 Fe(s) + 4 H₂O(g) Stress applied: Increasing the temperature 1. What is the Keq expression?. 2. What will be the effect in the volume of water vapor collected? 3. What will be the Equilibrium Shift or the reaction? C. 4 NH3(g) + 5 O2(g) 4 NO(g) + 6 H2O(g) + heat Stress applied: Increasing the volume of the container 1. What is the Keq expression?. 2. What will be the effect in the amount of H₂O? 3. What will be the Equilibrium Shift or the reaction?arrow_forwardConsider the solubility products (Ksp values) for the following compounds:SrSO4 (Ksp = 7.6 x 10−7), BaSO4 (Ksp = 1.5 x 10−9), SrCO3 (Ksp = 7.0 x 10−10), BaCO3 (Ksp = 1.6 x 10−9)Which anion is the harder base, CO32− or SO42−? Justify your answer.arrow_forwardQ1: a) Arrange the compounds in order of decreasing pKa, highest first. ОН ΟΗ ῸΗ дон ОН ОН CI Brarrow_forward
- (4 pts - 2 pts each part) A route that can be taken to prepare a hydrophobic (water-repellent) aerogel is to start with trichloromethylsilane, CH3SiCl3 as the silicon source. a. What is the chemical reaction that this undergoes to form a product with Si-OH groups? Write as complete of a chemical equation as you can. CI CI-SI-CH3 CI b. The formation of a byproduct is what drives this reaction - what is the byproduct (if you didn't already answer it in part (a)) and how/why does it form?arrow_forwardb) Circle the substrate that would not efficiently generate a Grignard reagent upon reaction with Mg in ether. CI Br ד c) Circle the Grignard reagents that contain incompatible functional groups. MgBr HO MgBr MgBr MgBr MgBr HO MgBrarrow_forwardQ2: Predict all organic product(s), including stereoisomers when applicable. PCC OH a) CH2Cl2 Page 2 of 5 Chem 0310 Organic Chemistry 1 HW Problem Sets b) .OH Na2Cr2O7, H+ OH PCC CH2Cl2 c) OHarrow_forward
- d) Circle the substrates that will give an achiral product after a Grignard reaction with CH3MgBr. Harrow_forwardQ4: Predict the organic products for the following reactions. Then draw curved arrow electron- pushing mechanism for the reactions. a) NaBH4 EtOH Page 4 of 5 Chem 0310 Organic Chemistry 1 HW Problem Sets b) 요 1. Et₂O H MgBr 2. H+, H₂Oarrow_forward5Helparrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





