
(a)
Interpretation:
The bubble point temperature for any one of the given binary systems in table
Concept Introduction:
Antoine equation is used to determine the vapor pressure of any substance at the given temperature by the equation:
Here,
Equation
to be used for Modified Raoult’s law is:
The Bubble point pressure for a binary system in vapor/liquid equilibrium is defined as the pressure where first bubble of vapor appears which is in equilibrium with the liquid present in the system. The equation which defines this pressure at this point is:
Wilson equations to be used are:
Here, the parameters
are calculated by the formula:
Where,
(a)
Answer to Problem 13.49P
The bubble point temperature for
using Wilson equation is:
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The pressure at which the bubble point temperature is to be calculated is
Wilson equation parameters are given in Table 13.10 as shown below:
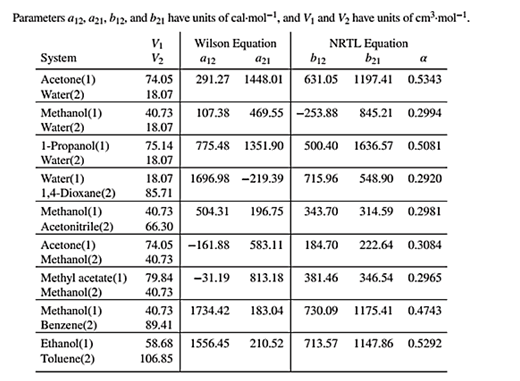
The binary system for which the bubble point temperature will be calculated is
. The liquid phase composition is:
From table B.2 of appendix B, the Antoine equation constants for
are:
Now, use equation (1) to calculate the vapor pressure of
as:
From table
to be used in Wilson equation are:
The value of universal gas constant to be used is,
Now, use equation (5) to calculate the values of
as:
Now, use these values of
using equations set (4) as:
Now, use the Modified Raoult’s law equation to calculate the pressure at the given value of
using the below mentioned formula as:
At
Make an initial guess for
as:
(b)
Interpretation:
The dew point temperature for any one of the given binary systems in table
Concept Introduction:
Equation
to be used for Modified Raoult’s law is:
Wilson equations to be used are:
Here, the parameters
are calculated by the formula:
Where,
The Dew point pressure for a binary system in vapor/liquid equilibrium is defined as the pressure where first drop of liquid appears which is in equilibrium with the vapor present in the system at a particular temperature. The equation that defines this pressure at this point is:
(b)
Answer to Problem 13.49P
The dew point temperature for
using Wilson equation is:
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The pressure at which the bubble point temperature is to be calculated is
Wilson equation parameters are given in Table 13.10 as shown below:
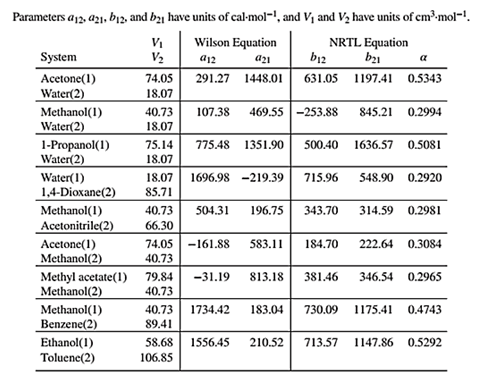
Use the values of
as calculated in part (a) as:
The vapor phase composition is:
From table
to be used in Wilson equation are:
The value of universal gas constant to be used is,
Now, use the values of
as calculated in part (a) as:
Now, use these values of
using equations set (4) as:
Now, use the Modified Raoult’s law equation to calculate the pressure at the guessed value of
using the below mentioned formula as:
Make an initial guess for
as:
(c)
Interpretation:
Concept Introduction:
Equation
to be used for Modified Raoult’s law is:
The Bubble point pressure for a binary system in vapor/liquid equilibrium is defined as the pressure where first bubble of vapor appears which is in equilibrium with the liquid present in the system. The equation which defines this pressure at this point is:
The Dew point pressure for a binary system in vapor/liquid equilibrium is defined as the pressure where first drop of liquid appears which is in equilibrium with the vapor present in the system at a particular temperature. The equation that defines this pressure at this point is:
The equation for equilibrium ratio,
also known as K-value is:
Here,
The equations for flash calculations to be used are:
Here,
In terms of
is:
Here,
(c)
Answer to Problem 13.49P
The result of the
flash calculations is:
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The flash pressure at which the
The condition for the flash temperature for this system is,
Wilson equation parameters are given in Table 13.10 as shown below:
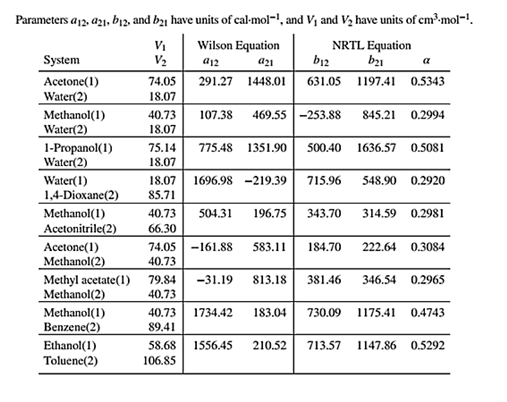
Use the values of
as calculated in part (a) as:
To perform
To calculate bubble point temperature, let
Since, the given conditions are same as in part (a), the calculated value of
as in part (a) is:
To calculate dew point temperature, let
Since, the given conditions are same as in part (a), the calculated value of
as in part (a) is:
From the given condition of the flash temperature, it is calculated as:
Use this temperature to get the values of
as:
Now, use the values of
as calculated in part (a) as:
Now, use these values of
using equations set (4) as:
Now, using the modified Raoult’s law, calculate the values of equilibrium ratio of component 1 and 2 using equations (2) and (7) as:
Now, use equation (9) and write it for both the component, 1 and 2 as shown below:
Since,
as:
Now, use equation (8) to calculate the value of
as:
Also, use the calculated value of
Using these values and the calculated values of
by equation (7) as:
Again, substitute these calculated values of
flash calculations is:
(d)
Interpretation:
The values of the azeotropic temperature and composition of the system is to be calculated if it exists for the given binary system.
Concept Introduction:
Antoine equation is used to determine the vapor pressure of any substance at the given temperature by the equation:
Here,
Equation
to be used for Modified Raoult’s law is:
Wilson equations to be used are:
Here, the parameters
are calculated by the formula:
Where,
Relative volatility is defined by,
When
At the azeotropic point,
(d)
Answer to Problem 13.49P
The azeotropic values of temperature and composition for the binary system is calculated as:
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The pressure at which the azeotrope of the system may exists is
Wilson equation parameters are given in Table 13.10 as shown below:
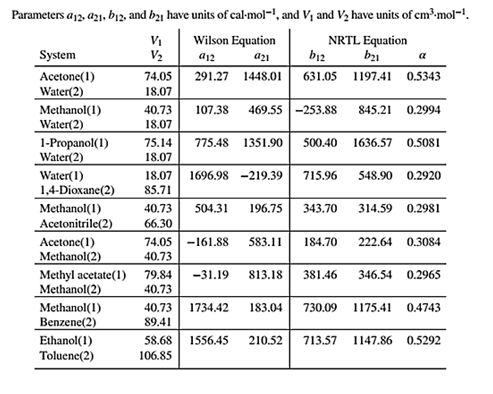
Use the given value of
as:
From table
to be used in Wilson equation are:
The value of universal gas constant to be used is,
Now, use equation (5) to calculate the values of
as:
Now, use these values of
using equations set (4) as:
Calculate
using equation (1) as:
Using equation (11) along with the modified Raoult’s law, calculate the value of relative volatility at
as:
For
using equations set (4) as:
Using equation (11) along with the modified Raoult’s law, calculate the value of relative volatility at
as:
Since
To calculate the azeotropic pressure, consider the condition
Consider the following set of equations in the given order as:
Now, use the values of
as:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
INTRO.TO CHEM.ENGR.THERMO.-EBOOK>I<
- For spherical sand particles with Dp = 0.03 and ρparticles = 150 lbm / ft3 estimate the minimum fluidizing velocity for air and for water. Assume ε = 0.3. In the case of the water we must rederive Eq. 11.42, taking into account the buoyant force on the particles. Below are the provide answers. Please show all work to get to the correct answers.arrow_forwardPlease show all workarrow_forward2. A moving bed adsorption column needs to be designed to separate hydrophobic proteins from a fermentation broth. The following adsorption equilibrium data was observed in preliminary isotherm studies. The resin used was activated carbon with a porosity of 0.2. The overall mass transfer coefficient was determined to be 10 h¹, and the ratio of volumetric flow rate of broth to resin is 10. Determine the diameter of the column if the column height is limited to 2.5 m (indoor operation) with a flow rate of 20 m³/h, influent concentration of 7 g/L, and effluent concentration of 0.1 g/L. qi (mg/kg) Ci (g/L) 0.1 4.7 7.5 0.25 10.6 0.5 15.0 1.0 23.7 2.5 33.5 5.0 41.1 7.5arrow_forward
- 3. You are given a mixture of four proteins, whose properties are listed in the table below. Propose a process to purify each protein so that you end up with four solutions of pure protein. What resin would you use to bind the protein(s)? What changes to the buffer would you make to desorb the protein(s)? Contains an N-terminal His6-tag. Two 50 kDa subunits contain a non-heme Fe2+ in the active site. Protein Size (kDa) pl Specific Properties A 100 6.0 B 40 7.7 C 240 8.3 Ꭰ 225 5.5 Contains FAD redox center and an NADH binding domain. Composed of six 40-kDa subunits, each of which contains a [2Fe-2S] cluster. Composed of three subunits: 100 kDa structural subunit, 75 kDa subunit with a molybdopterin center, and 50 kDa subunit with FAD and an NADH binding domain.arrow_forwardb) Explain the key features of the Langmuir adsorption model - Drawing a diagram with empty and occupied sites. Show how new molecules would adsorb. drawing the diagram, showing free and empty sites, and their number (to use for next section) - Define the capacity and binding affinity parameters in terms of things shown on the diagram Defining the capacity and binding affinity parameters in terms of bound, free sites, and free molecules - Plot what would be a typical breakthrough curve and give an explanation approximately when breakthrough would occur plotting a typical sigmoidal breakthrough curve and saying it would certainly occur by the time capacity is used, but also could be much earlier if the affinity is lowarrow_forwardWater at 20°C flows at a steady average velocity of 5.25 m/s through a smooth pipe of diameter 5.08 cm. The flow is fully developed through the entire section of pipe. The total pipe length is 10.56 m, and there are two 90' elbows. Determine the friction coefficient and the head loss due to friction per meter length of the pipe. Control volume Prepared by Engr. Kirsten Gaarrow_forward
 Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
 Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning
Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The
Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The





