
On December 19, 2007, the T2 Laboratories, Inc., reactor exploded in a runaway reaction. The reaction of methyl cyclopentadienyl dimer and sodium produces sodium methyl cyclopentadiene and hydrogen:
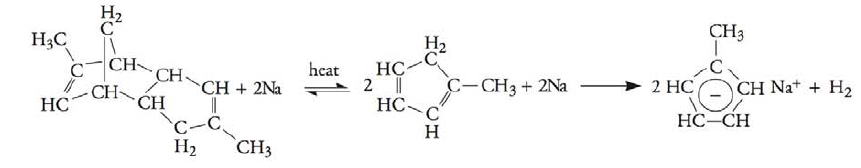
The reactor has to be cooled when its temperature reaches
If the rare constant for a typical reaction is
if all the heat were released at once?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 13 Solutions
EBK STUDENT SOLUTIONS MANUAL TO ACCOMPA
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
- Silicon forms a series of compounds analogous to the al-kanes and having the general formula SinH2n+2. The first of these compounds is silane, SiH4, which is used in the electronics industry to produce thin ultrapure silicon films. SiH4(g) is somewhat difficult to work with because it is py-ropboric at room temperature—meaning that it bursts into flame spontaneously when exposed to air. (a) Write an equation for the combustion of SiH4(g). (The reaction is analogous to hydrocarbon combustion, and SiO2 is a solid under standard conditions. Assume the water produced will be a gas.) (b) Use the data from Appendix E to calculate ? for this reaction. (c) Calculate G and show that the reaction is spontaneous at 25°C. (d) Compare G for this reaction to the combustion of methane. (See the previous problem.) Are the reactions in these two exercises enthalpy or entropy driven? Explain.arrow_forwardAmoxicillin is an antibiotic packaged as a powder. When it is used to treat babies and small animals, the pharmacist or veterinarian must suspend it in water, so that it can be administered orally with a medicine dropper. The label says to dispose of unused suspension after 14 days. It also points out that refrigeration is required. In the context of this chapter, what is implied in the latter two statements?arrow_forwardSubstances that poison a catalyst pose a major concern for many engineering designs, including those for catalytic converters. One design option is to add materials that react with potential poisons before they reach the catalyst. Among the commonly encountered catalyst poisons are silicon and phosphorus, which typically form phosphate or silicate ions in the oxidizing environment of an engine. Group 2 elements are added to the catalyst to react with these contaminants before they reach the working portion of the catalytic converter. If estimates show that a catalytic converter will be exposed to 625 g of silicon during its lifetime, what mass of beryllium would need to be included in the design?arrow_forward
- Can a reaction mechanism ever be proven correct? Can it be proven incorrect?arrow_forwardO to 185s? 185 to 416? 416 to 815 s? The decomposition of N,O, can be described by the equation 2 N,0,(soln) → 4 NO, (soln) + 0, (g) Consider the data in the table for the reaction at 45 °C in carbon tetrachloride solution. t (s) [N,0,] (M) 1.876 185 1.670 416 1.444 815 1.124 Given the data, calculate the average rate of reaction for each successive time interval.arrow_forwardScientists can determine the age of ancient objects by the method of radiocarbon dating. The bombardment of the upper atmosphere by cosmic rays converts nitrogen to a radioactive isotope of carbon, 14C, with a half-life of about 5,730 years. Vegetation absorbs carbon dioxide through the atmosphere, and animal life assimilates 14C through food chains. When a plant or animal dies, it stops replacing its carbon, and the amount of 14C present begins to decrease through radioactive decay. Therefore, the level of radioactivity must also decay exponentially. Dinosaur fossils are too old to be reliably dated using carbon-14. Suppose we had a 66 million year old dinosaur fossil. What percent of the living dinosaur's 14C would be remaining today? (Round your answer to five decimal places.) 0.0000007537 X % Suppose the minimum detectable amount is 0.2%. What is the maximum age (in years) of a fossil that we could date using 14C? (Round your answer to the nearest year.) yrarrow_forward
- Scientists can determine the age of ancient objects by the method of radiocarbon dating. The bombardment of the upper atmosphere by cosmic rays converts nitrogen to a radioactive isotope of carbon, 14C, with a half-life of about 5,730 years. Vegetation absorbs carbon dioxide through the atmosphere, and animal life assimilates 14C through food chains. When a plant or animal dies, it stops replacing its carbon, and the amount of 14C present begins to decrease through radioactive decay. Therefore, the level of radioactivity must also decay exponentially. a) Dinosaur fossils are too old to be reliably dated using carbon-14. Suppose we had a 67 million year old dinosaur fossil. What percent of the living dinosaur's 14C would be remaining today? (Round your answer to five decimal places.) b) Suppose the minimum detectable amount is 0.7%. What is the maximum age (in years) of a fossil that we could date using 14C? (Round your answer to the nearest year.)arrow_forwardSucrose (C12H22O11)(C12H22O11), which is commonly known as table sugar, reacts in dilute acid solutions to form two simpler sugars, glucose and fructose, both of which have the formula C6H12O6C6H12O6. At 23 ∘C∘C and in 0.5 M HClM HCl, the following data were obtained for the disappearance of sucrose: Time (min)(min) C12H22O11(M)C12H22O11(M) 0 0.316 39 0.274 80 0.238 140 0.190 210 0.146 What is the rate constant?arrow_forward89. At 700 K acetaldehyde decomposes in the gas phase to methane and carbon monoxide. The reaction is: CH3CHO(g) CH4(g) + CO(g) A sample of CH3CHO is heated to 700 K and the pressure is measured as 220 mbar before any reaction takes place. The kinetics of the reaction are then followed by measurements of total pressure and these data are obtained: t (s) PTotal (mbar) 0 220 1000 240 3000 270 7000 310 4 Find the rate law, the specific rate constant, and the total pres- sure after 2.00 × 104 s.arrow_forward
- The total pressure of the following system is used to monitor the progress of the chemical reaction. SO₂Cl2(g) → SO2(g) + Cl.(g) The reaction is initiated, and the following data are obtained: 3 6 0 9 12 Time (h) 15 17.26 18.90 19.99 20.71 PTotal (kPa) 11.07 14.79 Pso₂Cl₂ Pso₂ Pcl₂ Additional information: As the reaction proceeds, stoichiometry dictates that for every mole of SO₂Cl₂ that dissociates one mole of each of SO₂ and Cl₂ is produced. Defining the extent of dissociation/reaction as, and the initial pressure as Po, the total pressure is given by: Ptotal = Pso₂Cl₂ + Pso₂+ Pal₂ = (Po-5)+5+5 a) Calculate the pressure of each component at each time interval, i.e. complete the above table. b) Use a graphical method and determine what the order of the reaction is with respect to SO,Cl₂? (i) Show the plot as well as the linear fit of the data. (ii) Motivate your answer. c) Determine the rate constant for this reaction.arrow_forwardChlorine dioxide (ClO₂) is a disinfectant used in municipal water treatment plants. It dissolves in basic solution producing ClO3 and ClO₂": 2 CLO₂(g) + 2 OH (aq) → ClO3(aq) + ClO₂ (aq) + H₂O(l) › The following kinetic data were obtained at 298 K for the reaction. Experiment [CIO₂]0 (M) [OH-]o (M) Initial Rate (M/s) 1 0.060 0.030 0.0248 2 0.020 0.030 0.00827 3 0.020 0.090 0.0247 Determine the rate law by indicating the values of "x" and "y" in the general rate law below. Rate = K[ClO₂]X[OH-]Y X = 1 = 1 y = OB b. Calculate the rate constant for this reaction at 298 K. Sig. Figs. are important. M-1. S-1 Rate constant, k = 184.4arrow_forward*Stoichiometry Ethylene oxide, C2H4O, may be made by passing ethylene, C2H4, and air over a catalyst at 2500C. When the resulting mixture is cooled and passed through water, the ethylene oxide combines with water to form ethylene glycol (CH2OH)2. In one experiment a 5% by volume ethylene – 95% by volume air mixture is passed over the catalyst. Some of the ethylene does not react, some forms ethylene oxide, and some is oxidized completely to form CO2 and water vapor. The entire gas mixture enters directly into an absorption system where it is contacted by water. The gases leaving the absorber contain all the N2, unreacted C2H4, unused O2, and the CO2 formed. They are saturated with water vapor at a partial pressure of 15.4 mm Hg. The total pressure is 730 mm Hg. An Orsat Analysis of the gases leaving the absorber shows 1.075% C2H4, 80.7 % N2 ad 4.30% CO2. One mole of liquid water is fed to the absorber per 100 moles of the gas fed to the catalyst chamber. What is the composition (%mole)…arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemical Principles in the LaboratoryChemistryISBN:9781305264434Author:Emil Slowinski, Wayne C. Wolsey, Robert RossiPublisher:Brooks Cole
Chemical Principles in the LaboratoryChemistryISBN:9781305264434Author:Emil Slowinski, Wayne C. Wolsey, Robert RossiPublisher:Brooks Cole Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning




