
Principles Of Foundation Engineering 9e
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781337705035
Author: Das, Braja M.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 13, Problem 13.10P
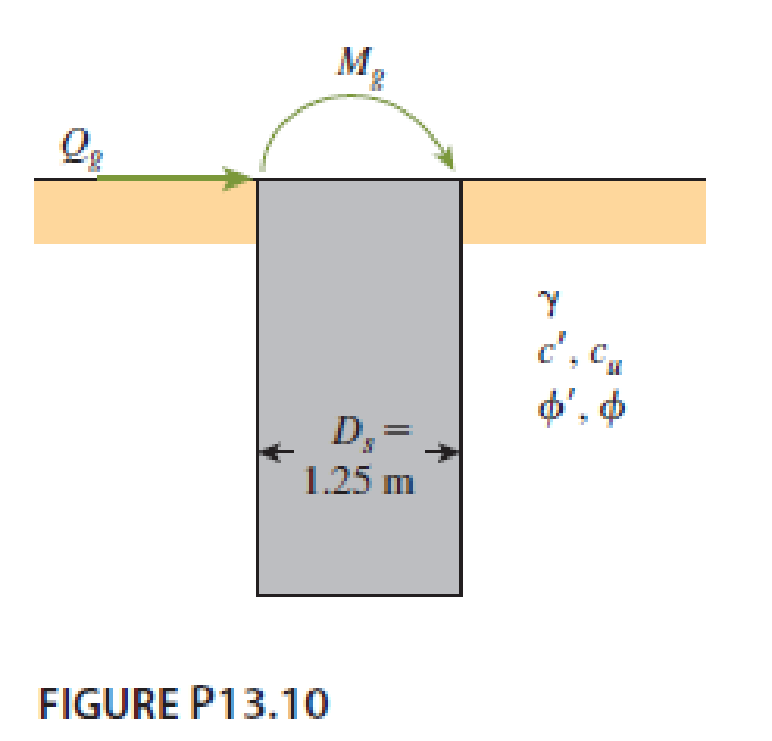
A free-headed drilled shaft is shown in Figure P13.10. Let Qg = 260 kN, Mg = 0, γ = 17.5 kN/m3, ϕ′ = 35°, c' = 0, and Ep = 22 × 106 kN/m2. Determine
- a. The ground line deflection, xo
- b. The maximum bending moment in the drilled shaft
- c. The maximum tensile stress in the shaft
- d. The minimum penetration of the shaft needed for this analysis
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
4. Draw a stress-strain curve (in tension and compression) for a reinforced concrete
beam below. Label the important parts of the plot. Find the linear elastic approximation
obtained using the transformed technique, and plot over the same strain ranges.
24"
4"
20"
16"
f = 8,000 psi
8- #11 bars
Grade 60 steel
4"
(f, = 60 ksi and
E₁ = 29000 ksi)
Why is Historical Data important compared to other sourses of information when estimating construction projects?
Need help, please show all work, steps, units and round to 3 significant figures. Thank you!!
Chapter 13 Solutions
Principles Of Foundation Engineering 9e
Ch. 13 - Prob. 13.1PCh. 13 - Prob. 13.2PCh. 13 - Prob. 13.3PCh. 13 - Determine the ultimate load-carrying capacity of...Ch. 13 - For the same data given in Problem 13.4, determine...Ch. 13 - Prob. 13.6PCh. 13 - A 3 ft diameter straight drilled shaft is shown in...Ch. 13 - Prob. 13.8PCh. 13 - Figure P13.9 shows a drilled shaft extending into...Ch. 13 - A free-headed drilled shaft is shown in Figure...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Need help. Find the answer to the boxes marked in red. Thanks!arrow_forwardFor the gravity dam shown in the figure, The following data are available: -Unit weight of concrete (Yconc) = 2.4 ton/m³ -Vertical upward earth quake factor (K,) = 0.1 -Neglect Wave pressure, silt pressure and ice force μ=0.65 a-Find heel and toe stresses (Pmin & Pmax) b-Is this structure safe against tension? c-Find the factor of safety against sliding and overturning (F.S, & F.Sover) 165 m 160 m t 10 m T I 4 m 50 100 marrow_forwardFor the gravity dam shown in the figure, The following data are available: -Unit weight of concrete (Yeone) 2.4 ton/m³ Vertical down ward earth quake factor (K,) = 0.1 Neglect Wave pressure, silt pressure and ice force The wind velocity (V)-45 Km/hr Straight length of water expanse (F) 75 Km =0.7 14-70m 3h T a- Find the factor of safety against sliding and overturning (F.Slid F.Sover) b- Find the toe and heel stresses (hma, and hmin.) c-Check tension. 8marrow_forward
- QUESTION 2-(40 Points) In the case where other information is given in the figure, the wall is under the effect of a uniform lateral wind load of 0.7 kN/m2. Since the foundation is sized according to the safe bearing capacity of the soil and the safe bearing capacity remains the same, find the width of this foundation asymmetrically (with uniform base pressure). Draw the vertical section of the wall of the asymmetric foundation and write its dimensions and values on it. Draw the T and M diagrams along the width. The foundation thickness is the same in both cases. q=0.7 kN/m2 5 m R Duvar Nd=Wd 0.7 m T K 0 0.6 0.5 1.7 m Yb-24 kN/m3 0.6 m T + foundationarrow_forwardCan you pls. Explain on how to get "BETA T" and "BETA C" on this study about VALUE OF TRAVEL TIME.arrow_forward440 CHAPTER 9 ANALYSIS OF STATICALLY INDETERMIN 9-23. Determine the reactions at the supports, then draw the moment diagrams for each member. Assume A and B are pins and the joint at C is fixed connected. EI is constant. Se 9-2 12 kN 2 m 2 m 6 kN/m A 6 m Prob. 9-23 Barrow_forward
- I need a solution to this problemarrow_forwardThree forces act on the ring. If the resultant force FR has a magnitude and direction as shown, determine the magnitude and the coordinate direction angles of force F3. == F2 = 110 N F3 F₁ = 80 N 3 X 45° FR = 120 N 30° yarrow_forwardFIND the CENTROID and the MOMENT OF INERTIA through the centroidal x axisarrow_forward
- (b) For the cantilever beam shown in Fig. 3, a roller support has been added at mid-span. Given that El is constant, use the force method to determine the following: (i) The reaction force at support C. (ii) The reaction forces at fixed support A. (15 marks) C 25 kN B 2 m 2 m Fig. 3: A propped cantilever beam [Q2=25 marks]arrow_forwardYou are working on a 1-km highway extension project that requires the construction of a 4-m tall soil embankment with a top width of 15-m and 2H:1V slopes. A borrow-pit (i.e., a place where soils are excavated, to then be placed elsewhere for construction projects) has been identified with e = 0.74, emax = 0.9, emin = 0.5. To avoid excessive road deformations, the soil will be compacted to a relative density of DR = 90% when placed in the embankment. Your boss estimates that extracting 100,000 m^3 of material from the borrow-pit should be enough for this project. Is your boss correct, or is more material than that needed? To decide, answer these questions: a) What volume of soil, as placed, is required to build the embankment? [Tip: draw the embankment] b) What is the void ratio of the material when placed in the embankment? c) What is the relative density of the material in the borrow-pit? d) When soil is extracted from the borrow-pit and then compacted it the embankment, how do…arrow_forwardThere are 20 cars traveling at constant speeds on a 1 mile long ring track and the cars can pass each other freely. On the track 25% of the cars are traveling at 20 mph, 50% of the cars are traveling 10 mph, and the remaining 25% of the cars are traveling at an unknown speed. It was known that the space mean speed of all the cars on the track is 20 mph. (a) What is the speed that the remaining 25% of cars are traveling at? (b) If an observer standing on the side of the track counted the number and measured the speed of all cars that passed her for one hour, what is the time-mean speed of all the cars the observer counted? (c) What is the flow rate measured by the observer? (d) What is the car density on the track? Does density times space mean speed equal flow rate?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305081550
Author:Braja M. Das
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305635180
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305970939
Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled Sobhan
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Difference between Direct and Bending stress || Combined stresses; Author: Civil Engineering;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZXGSSddI5ew;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY