
Calculus, Single Variable: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)
3rd Edition
ISBN: 9780134766850
Author: William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric Schulz
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 1.3, Problem 12E
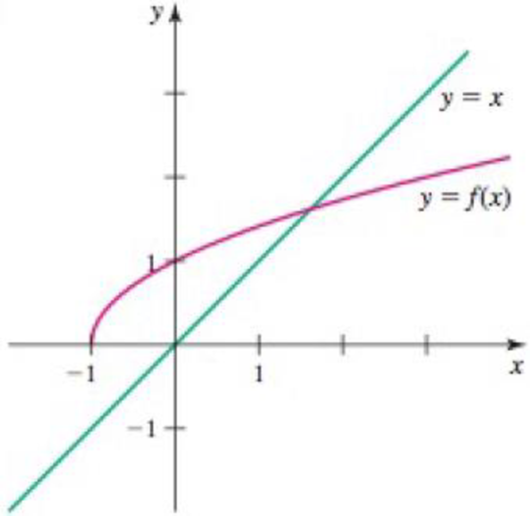
Graphs of inverses Sketch the graph of the inverse function.
40. 
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
An airplane flies due west at an airspeed of 428 mph. The wind blows in the direction of 41° south of west
at 50 mph. What is the ground speed of the airplane? What is the bearing of the airplane?
428 mph
41°
50 mph
a. The ground speed of the airplane is
b. The bearing of the airplane is
mph.
south of west.
Rylee's car is stuck in the mud. Roman and Shanice come along in a truck to help pull her out. They attach
one end of a tow strap to the front of the car and the other end to the truck's trailer hitch, and the truck
starts to pull. Meanwhile, Roman and Shanice get behind the car and push. The truck generates a
horizontal force of 377 lb on the car. Roman and Shanice are pushing at a slight upward angle and generate
a force of 119 lb on the car. These forces can be represented by vectors, as shown in the figure below. The
angle between these vectors is 20.2°. Find the resultant force (the vector sum), then give its magnitude
and its direction angle from the positive x-axis.
119 lb
20.2°
377 lb
a. The resultant force is
(Tip: omit degree notations from your answers; e.g. enter cos(45) instead of cos(45°))
b. It's magnitude is
lb.
c. It's angle from the positive x-axis is
Find a plane containing the point (3, -3, 1) and the line of intersection of the planes 2x + 3y - 3z = 14
and -3x - y + z = −21.
The equation of the plane is:
Chapter 1 Solutions
Calculus, Single Variable: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)
Ch. 1.1 - If f(x)=x22x, find f(1),f(x2),f(t), and f(p1).Ch. 1.1 - State the domain and range of f(x)=(x2+1)1.Ch. 1.1 - If f(x)=x2+1 and g(x)=x2, find fg and gf.Ch. 1.1 - Refer to Figure 1.12. Find the hiker's average...Ch. 1.1 - Explain why the graph of a nonzero function is...Ch. 1.1 - Use the terms domain, range, independent variable,...Ch. 1.1 - Is the independent variable of a function...Ch. 1.1 - Vertical line test Decide whether graphs A, B, or...Ch. 1.1 - The entire graph of f is given. State the domain...Ch. 1.1 - Which statement about a function is true? (i) For...
Ch. 1.1 - Prob. 6ECh. 1.1 - Determine the domain and range of f(x)=3x210.Ch. 1.1 - Domain in context Determine an appropriate domain...Ch. 1.1 - Domain in context Determine an appropriate domain...Ch. 1.1 - If f(x) = 1/(x3 + 1), what is f(2)? What is f(y2)?Ch. 1.1 - Let f(x)=2x+1 and g(x)=1/(x1). Simplify the...Ch. 1.1 - Find functions f and g such that f(g(x))=(x2+1)5....Ch. 1.1 - Explain how to find the domain of fg if you know...Ch. 1.1 - If f(x)=x and g(x)=x32, simplify the expressions...Ch. 1.1 - Composite functions from graphs Use the graphs of...Ch. 1.1 - Composite functions from tables Use the table to...Ch. 1.1 - Rising radiosonde The National Weather Service...Ch. 1.1 - World record free fall On October 14, 2012, Felix...Ch. 1.1 - Suppose f is an even function with f(2) = 2 and g...Ch. 1.1 - Complete the left half of the graph of g if g is...Ch. 1.1 - Prob. 21ECh. 1.1 - Prob. 22ECh. 1.1 - Domain and range State the domain and range of the...Ch. 1.1 - Domain and range State the domain and range of the...Ch. 1.1 - Domain and range State the domain and range of the...Ch. 1.1 - Domain and range State the domain and range of the...Ch. 1.1 - Domain State the domain of the function....Ch. 1.1 - Domain State the domain of the function....Ch. 1.1 - Domain State the domain of the function....Ch. 1.1 - Domain State the domain of the function....Ch. 1.1 - Launching a rocket A small rocket is launched...Ch. 1.1 - Draining a tank (Torricellis law) A cylindrical...Ch. 1.1 - Composite functions and notation Let f(x) = x2 4,...Ch. 1.1 - Composite functions and notation Let f(x) = x2 4,...Ch. 1.1 - Composite functions and notation Let f(x) = x2 4,...Ch. 1.1 - Composite functions and notation Let f(x) = x2 4,...Ch. 1.1 - Composite functions and notation Let f(x) = x2 4,...Ch. 1.1 - Composite functions and notation Let f(x) = x2 4,...Ch. 1.1 - Composite functions and notation Let f(x) = x2 4,...Ch. 1.1 - Composite functions and notation Let f(x) = x2 4,...Ch. 1.1 - Composite functions and notation Let f(x) = x2 4,...Ch. 1.1 - Composite functions and notation Let f(x) = x2 4,...Ch. 1.1 - Working with composite functions Find possible...Ch. 1.1 - Working with composite functions Find possible...Ch. 1.1 - Working with composite functions Find possible...Ch. 1.1 - Working with composite functions Find possible...Ch. 1.1 - More composite functions Let f(x) = |x|, g(x) = x2...Ch. 1.1 - More composite functions Let f(x) = |x|, g(x) = x2...Ch. 1.1 - Prob. 49ECh. 1.1 - More composite functions Let f(x) = |x|, g(x) = x2...Ch. 1.1 - More composite functions Let f(x) = |x|, g(x) = x2...Ch. 1.1 - More composite functions Let f(x) = |x|, g(x) = x2...Ch. 1.1 - Prob. 53ECh. 1.1 - More composite functions Let f(x) = |x|, g(x) = x2...Ch. 1.1 - Missing piece Let g(x) = x2 + 3. Find a function f...Ch. 1.1 - Missing piece Let g(x) = x2 + 3. Find a function f...Ch. 1.1 - Missing piece Let g(x) = x2 + 3. Find a function f...Ch. 1.1 - Missing piece Let g(x) = x2 + 3. Find a function f...Ch. 1.1 - Missing piece Let g(x) = x2 + 3. Find a function f...Ch. 1.1 - Missing piece Let g(x) = x2 + 3. Find a function f...Ch. 1.1 - Explain why or why not Determine whether the...Ch. 1.1 - Working with difference quotients Simplify the...Ch. 1.1 - Working with difference quotients Simplify the...Ch. 1.1 - Working with difference quotients Simplify the...Ch. 1.1 - Working with difference quotients Simplify the...Ch. 1.1 - Working with difference quotients Simplify the...Ch. 1.1 - Working with difference quotients Simplify the...Ch. 1.1 - Working with difference quotients Simplify the...Ch. 1.1 - Working with difference quotients Simplify the...Ch. 1.1 - Working with difference quotients Simplify the...Ch. 1.1 - Working with difference quotients Simplify the...Ch. 1.1 - Working with difference quotients Simplify the...Ch. 1.1 - Working with difference quotients Simplify the...Ch. 1.1 - Working with difference quotients Simplify the...Ch. 1.1 - GPS data A GPS device tracks the elevation E (in...Ch. 1.1 - Elevation vs. Distance The following graph,...Ch. 1.1 - Interpreting the slope of secant lines In each...Ch. 1.1 - Interpreting the slope of secant lines In each...Ch. 1.1 - Symmetry Determine whether the graphs of the...Ch. 1.1 - Symmetry Determine whether the graphs of the...Ch. 1.1 - Symmetry Determine whether the graphs of the...Ch. 1.1 - Symmetry Determine whether the graphs of the...Ch. 1.1 - Prob. 83ECh. 1.1 - Prob. 84ECh. 1.1 - Symmetry Determine whether the graphs of the...Ch. 1.1 - Symmetry Determine whether the graphs of the...Ch. 1.1 - Composition of even and odd functions from graphs...Ch. 1.1 - Composition of even and odd functions from tables...Ch. 1.1 - Absolute value graph Use the definition of...Ch. 1.1 - Graphing semicircles Show that the graph of...Ch. 1.1 - Graphing semicircles Show that the graph of...Ch. 1.1 - Even and odd at the origin a. If f(0) is defined...Ch. 1.1 - Polynomial calculations Find a polynomial f that...Ch. 1.1 - Polynomial calculations Find a polynomial f that...Ch. 1.1 - Polynomial calculations Find a polynomial f that...Ch. 1.1 - Polynomial calculations Find a polynomial f that...Ch. 1.1 - Difference quotients Simplify the difference...Ch. 1.1 - Difference quotients Simplify the difference...Ch. 1.1 - Difference quotients Simplify the difference...Ch. 1.1 - Difference quotients Simplify the difference...Ch. 1.1 - Prob. 101ECh. 1.1 - Prob. 102ECh. 1.1 - Prob. 103ECh. 1.1 - Prob. 104ECh. 1.2 - Are all polynomials rational functions? Are all...Ch. 1.2 - Prob. 2QCCh. 1.2 - Prob. 3QCCh. 1.2 - Prob. 4QCCh. 1.2 - Prob. 1ECh. 1.2 - Prob. 2ECh. 1.2 - Prob. 3ECh. 1.2 - Prob. 4ECh. 1.2 - Prob. 5ECh. 1.2 - Describe what is meant by a piecewise linear...Ch. 1.2 - Graphs of piecewise functions Write a definition...Ch. 1.2 - The graph of y=x is shifted 2 units to the right...Ch. 1.2 - How do you obtain the graph of y = f(x + 2) from...Ch. 1.2 - How do you obtain the graph of y = 3f(x) from the...Ch. 1.2 - How do you obtain the graph of y = f(3x) from the...Ch. 1.2 - How do you obtain the graph of y = 4(x + 3)2 + 6...Ch. 1.2 - Transformations of y = |x| The functions f and g...Ch. 1.2 - Transformations Use the graph of f in the figure...Ch. 1.2 - Graph of a linear function Find and graph the...Ch. 1.2 - Graph of a linear function Find and graph the...Ch. 1.2 - Linear function Find the linear function whose...Ch. 1.2 - Linear function Find the linear function whose...Ch. 1.2 - Yeast growth Consider a colony of yeast cells that...Ch. 1.2 - Yeast growth Consider a colony of yeast cells that...Ch. 1.2 - Demand function Sales records indicate that if...Ch. 1.2 - Fundraiser The Biology Club plans to have a...Ch. 1.2 - Bald eagle population Since DDT was banned and the...Ch. 1.2 - Taxicab fees A taxicab ride costs 3.50 plus 2.50...Ch. 1.2 - Defining piecewise functions Write a definition of...Ch. 1.2 - Graphs of piecewise functions Write a definition...Ch. 1.2 - Parking fees Suppose that it costs 5 per minute to...Ch. 1.2 - Taxicab fees A taxicab ride costs 3.50 plus 2.50...Ch. 1.2 - Piecewise linear functions Graph the following...Ch. 1.2 - Piecewise linear functions Graph the following...Ch. 1.2 - Piecewise linear functions Graph the following...Ch. 1.2 - Piecewise linear functions Graph the following...Ch. 1.2 - Piecewise linear functions Graph the following...Ch. 1.2 - Piecewise linear functions Graph the following...Ch. 1.2 - Graphs of functions a. Use a graphing utility to...Ch. 1.2 - Graphs of functions a. Use a graphing utility to...Ch. 1.2 - Graphs of functions a. Use a graphing utility to...Ch. 1.2 - Graphs of functions a. Use a graphing utility to...Ch. 1.2 - Graphs of functions a. Use a graphing utility to...Ch. 1.2 - Graphs of functions a. Use a graphing utility to...Ch. 1.2 - Features of a graph Consider the graph of the...Ch. 1.2 - Features of a graph Consider the graph of the...Ch. 1.2 - Relative acuity of the human eye The fovea...Ch. 1.2 - Slope functions Determine the slope function S(x)...Ch. 1.2 - Slope functions Determine the slope function for...Ch. 1.2 - Slope functions Determine the slope function for...Ch. 1.2 - Slope functions Determine the slope function S(x)...Ch. 1.2 - Slope functions Determine the slope function S(x)...Ch. 1.2 - Area functions Let A(x) be the area of the region...Ch. 1.2 - Area functions Let A(x) be the area of the region...Ch. 1.2 - Area functions Let A(x) be the area of the region...Ch. 1.2 - Area functions Let A(x) be the area of the region...Ch. 1.2 - Explain why or why not Determine whether the...Ch. 1.2 - Shifting a graph Use a shift to explain how the...Ch. 1.2 - Transformations of f(x) = x2 Use shifts and...Ch. 1.2 - Transformations of f(x)=x Use shifts and scalings...Ch. 1.2 - Shifting and scaling Use shifts and scalings to...Ch. 1.2 - Shifting and scaling Use shifts and scalings to...Ch. 1.2 - Shifting and scaling Use shifts and scalings to...Ch. 1.2 - Shifting and scaling Use shifts and scalings to...Ch. 1.2 - Shifting and scaling Use shifts and scalings to...Ch. 1.2 - Shifting and scaling Use shifts and scalings to...Ch. 1.2 - Shifting and scaling Use shifts and scalings to...Ch. 1.2 - Shifting and scaling Use shifts and scalings to...Ch. 1.2 - Intersection problems Find the following points of...Ch. 1.2 - Intersection problems Use analytical methods to...Ch. 1.2 - Intersection problems Use analytical methods to...Ch. 1.2 - Two semicircles The entire graph of f consists of...Ch. 1.2 - Piecewise function Plot a graph of the function...Ch. 1.2 - Floor function The floor function, or greatest...Ch. 1.2 - Ceiling function The ceiling function, or smallest...Ch. 1.2 - Sawtooth wave Graph the sawtooth wave defined by...Ch. 1.2 - Square wave Graph the square wave defined by...Ch. 1.2 - Roots and powers Make a sketch of the given pairs...Ch. 1.2 - Roots and powers Make a sketch of the given pairs...Ch. 1.2 - Roots and powers Make a sketch of the given pairs...Ch. 1.2 - Tennis probabilities Suppose the probability of a...Ch. 1.2 - Temperature scales a. Find the linear function C =...Ch. 1.2 - Automobile lease vs. purchase A car dealer offers...Ch. 1.2 - Walking and rowing Kelly has finished a picnic on...Ch. 1.2 - Optimal boxes Imagine a lidless box with height h...Ch. 1.2 - Composition of polynomials Let f be an nth-degree...Ch. 1.2 - Parabola vertex property Prove that if a parabola...Ch. 1.2 - Parabola properties Consider the general quadratic...Ch. 1.2 - Factorial function The factorial function is...Ch. 1.3 - Is it possible to raise a positive number b to a...Ch. 1.3 - Prob. 2QCCh. 1.3 - Prob. 3QCCh. 1.3 - Prob. 4QCCh. 1.3 - Prob. 5QCCh. 1.3 - Prob. 6QCCh. 1.3 - For b 0, what are the domain and range of f(x) =...Ch. 1.3 - Prob. 2ECh. 1.3 - Prob. 3ECh. 1.3 - Sketch a graph of a function that is one-to-one on...Ch. 1.3 - Prob. 5ECh. 1.3 - Prob. 6ECh. 1.3 - Prob. 7ECh. 1.3 - Prob. 8ECh. 1.3 - Find the inverse of the function f(x) = 2x. Verify...Ch. 1.3 - Find the inverse of the function f(x)=x, for x 0....Ch. 1.3 - Graphs of inverses Sketch the graph of the inverse...Ch. 1.3 - Graphs of inverses Sketch the graph of the inverse...Ch. 1.3 - Prob. 13ECh. 1.3 - Prob. 14ECh. 1.3 - Explain the meaning of logbx.Ch. 1.3 - How is the property bx+ y = bxby related to the...Ch. 1.3 - Prob. 17ECh. 1.3 - Express 25 using base e.Ch. 1.3 - Prob. 19ECh. 1.3 - For a certain constant a 1, ln a 3.8067. Find...Ch. 1.3 - Where do inverses exist? Use analytical and/or...Ch. 1.3 - Where do inverses exist? Use analytical and/or...Ch. 1.3 - Where do inverses exist? Use analytical and/or...Ch. 1.3 - Where do inverses exist? Use analytical and/or...Ch. 1.3 - Where do inverses exist? Use analytical and/or...Ch. 1.3 - Where do inverses exist? Use analytical and/or...Ch. 1.3 - Graphing inverse functions Find the inverse...Ch. 1.3 - Graphing inverse functions Find the inverse...Ch. 1.3 - Graphing inverse functions Find the inverse...Ch. 1.3 - Graphing inverse functions Find the inverse...Ch. 1.3 - Graphing inverse functions Find the inverse...Ch. 1.3 - Graphing inverse functions Find the inverse...Ch. 1.3 - Finding inverse functions Find the inverse f1(x)...Ch. 1.3 - Finding inverse functions Find the inverse f1(x)...Ch. 1.3 - Finding inverse functions Find the inverse f1(x)...Ch. 1.3 - Finding inverse functions Find the inverse f1(x)...Ch. 1.3 - Finding inverse functions Find the inverse f1(x)...Ch. 1.3 - Finding inverse functions Find the inverse f1(x)...Ch. 1.3 - Finding inverse functions Find the inverse f1(x)...Ch. 1.3 - Finding inverse functions Find the inverse f1(x)...Ch. 1.3 - Finding inverse functions Find the inverse f1(x)...Ch. 1.3 - Finding inverse functions Find the inverse f1(x)...Ch. 1.3 - Splitting up curves The unit circle x2 + y2 = 1...Ch. 1.3 - Splitting up curves The equation y4 = 4x2 is...Ch. 1.3 - Properties of logarithms Assume logb x = 0.36,...Ch. 1.3 - Properties of logarithms Assume logb x = 0.36,...Ch. 1.3 - Properties of logarithms Assume logb x = 0.36,...Ch. 1.3 - Properties of logarithms Assume logb x = 0.36,...Ch. 1.3 - Properties of logarithms Assume logb x = 0.36,...Ch. 1.3 - Properties of logarithms Assume logb x = 0.36,...Ch. 1.3 - Solving logarithmic equations Solve the following...Ch. 1.3 - Solving logarithmic equations Solve the following...Ch. 1.3 - Solving logarithmic equations Solve the following...Ch. 1.3 - Solving logarithmic equations Solve the following...Ch. 1.3 - Solving logarithmic equations Solve the following...Ch. 1.3 - Solving logarithmic equations Solve the following...Ch. 1.3 - Solving equations Solve the following equations....Ch. 1.3 - Solving equations Solve the following equations....Ch. 1.3 - Solving equations Solve the following equations....Ch. 1.3 - Solving equations Solve the following equations....Ch. 1.3 - Using inverse relations One hundred grams of a...Ch. 1.3 - Mass of juvenile desert tortoises In a study...Ch. 1.3 - Investment Problems An investment of P dollars is...Ch. 1.3 - Investment Problems An investment of P dollars is...Ch. 1.3 - Height and time The height in feet of a baseball...Ch. 1.3 - Velocity of a skydiver The velocity of a skydiver...Ch. 1.3 - Calculator base change Write the following...Ch. 1.3 - Calculator base change Write the following...Ch. 1.3 - Calculator base change Write the following...Ch. 1.3 - Calculator base change Write the following...Ch. 1.3 - Changing bases Convert the following expressions...Ch. 1.3 - Changing bases Convert the following expressions...Ch. 1.3 - Changing bases Convert the following expressions...Ch. 1.3 - Changing bases Convert the following expressions...Ch. 1.3 - Changing bases Convert the following expressions...Ch. 1.3 - Changing bases Convert the following expressions...Ch. 1.3 - Explain why or why not Determine whether the...Ch. 1.3 - Graphs of exponential functions The following...Ch. 1.3 - Graphs of logarithmic functions The following...Ch. 1.3 - Graphs of modified exponential functions Without...Ch. 1.3 - Graphs of modified logarithmic functions Without...Ch. 1.3 - Population model A culture of bacteria has a...Ch. 1.3 - Charging a capacitor A capacitor is a device that...Ch. 1.3 - Large intersection point Use any means to...Ch. 1.3 - Finding all inverses Find all the inverses...Ch. 1.3 - Finding all inverses Find all the inverses...Ch. 1.3 - Finding all inverses Find all the inverses...Ch. 1.3 - Finding all inverses Find all the inverses...Ch. 1.3 - Finding all inverses Find all the inverses...Ch. 1.3 - Finding all inverses Find all the inverses...Ch. 1.3 - Reciprocal bases Assume that b 0 and b 1. Show...Ch. 1.3 - Proof of rule L1 Use the following steps to prove...Ch. 1.3 - Prob. 93ECh. 1.3 - Proof of rule L3 Use the following steps to prove...Ch. 1.3 - Prob. 95ECh. 1.3 - Prob. 96ECh. 1.3 - Nice property Prove that (logb c)(logc b) = 1, for...Ch. 1.4 - What is the radian measure of a 270 angle? What is...Ch. 1.4 - Evaluate cos (11/6) and sin (5/4).Ch. 1.4 - Prob. 3QCCh. 1.4 - Prob. 4QCCh. 1.4 - Evaluate sec11 and tan11.Ch. 1.4 - Prob. 1ECh. 1.4 - Prob. 2ECh. 1.4 - Prob. 3ECh. 1.4 - Prob. 4ECh. 1.4 - Prob. 5ECh. 1.4 - Explain what is meant by the period of a...Ch. 1.4 - What are the three Pythagorean identities for the...Ch. 1.4 - Given that sin=1/5 and =2/5, use trigonometric...Ch. 1.4 - Solve the equation sin = 1, for 0 2.Ch. 1.4 - Solve the equation sin 2=1, for 02.Ch. 1.4 - Where is the tangent function undefined?Ch. 1.4 - What is the domain of the secant function?Ch. 1.4 - Explain why the domain of the sine function must...Ch. 1.4 - Why do the values of cos1 x lie in the interval...Ch. 1.4 - Evaluate cos1(cos(5/4)).Ch. 1.4 - Evaluate sin1(sin(11/6)).Ch. 1.4 - The function tan x is undefined at x = /2. How...Ch. 1.4 - State the domain and range of sec1 x.Ch. 1.4 - Evaluating trigonometric functions Without using a...Ch. 1.4 - Evaluating trigonometric functions Without using a...Ch. 1.4 - Evaluating trigonometric functions Without using a...Ch. 1.4 - Evaluating trigonometric functions Without using a...Ch. 1.4 - Evaluating trigonometric functions Without using a...Ch. 1.4 - Evaluating trigonometric functions Without using a...Ch. 1.4 - Evaluating trigonometric functions Without using a...Ch. 1.4 - Evaluating trigonometric functions Without using a...Ch. 1.4 - Evaluating trigonometric functions Without using a...Ch. 1.4 - Evaluating trigonometric functions Without using a...Ch. 1.4 - Evaluating trigonometric functions Without using a...Ch. 1.4 - Evaluating trigonometric functions Without using a...Ch. 1.4 - Evaluating trigonometric functions Without using a...Ch. 1.4 - Evaluating trigonometric functions Without using a...Ch. 1.4 - Evaluating trigonometric functions Without using a...Ch. 1.4 - Evaluating trigonometric functions Without using a...Ch. 1.4 - Solving trigonometric equations Solve the...Ch. 1.4 - Solving trigonometric equations Solve the...Ch. 1.4 - Solving trigonometric equations Solve the...Ch. 1.4 - Solving trigonometric equations Solve the...Ch. 1.4 - Solving trigonometric equations Solve the...Ch. 1.4 - Solving trigonometric equations Solve the...Ch. 1.4 - Solving trigonometric equations Solve the...Ch. 1.4 - Solving trigonometric equations Solve the...Ch. 1.4 - Solving trigonometric equations Solve the...Ch. 1.4 - Solving trigonometric equations Solve the...Ch. 1.4 - Solving trigonometric equations Solve the...Ch. 1.4 - Solving trigonometric equations Solve the...Ch. 1.4 - Projectile range A projectile is launched from the...Ch. 1.4 - Projectile range A projectile is launched from the...Ch. 1.4 - Inverse sines and cosines Without using a...Ch. 1.4 - Inverse sines and cosines Without using a...Ch. 1.4 - Inverse sines and cosines Without using a...Ch. 1.4 - Inverse sines and cosines Without using a...Ch. 1.4 - Inverse sines and cosines Without using a...Ch. 1.4 - Inverse sines and cosines Without using a...Ch. 1.4 - Inverse sines and cosines Without using a...Ch. 1.4 - Inverse sines and cosines Without using a...Ch. 1.4 - Inverse sines and cosines Without using a...Ch. 1.4 - Inverse sines and cosines Without using a...Ch. 1.4 - Using right triangles Use a right-triangle sketch...Ch. 1.4 - Using right triangles Use a right-triangle sketch...Ch. 1.4 - Right-triangle relationships Draw a right triangle...Ch. 1.4 - Right-triangle relationships Draw a right triangle...Ch. 1.4 - Right-triangle relationships Draw a right triangle...Ch. 1.4 - Right-triangle relationships Draw a right triangle...Ch. 1.4 - Right-triangle relationships Draw a right triangle...Ch. 1.4 - Right-triangle relationships Draw a right triangle...Ch. 1.4 - Trigonometric identities 29. Prove that sec=1cos.Ch. 1.4 - Trigonometric identities 30. Prove that...Ch. 1.4 - Trigonometric identities 31. Prove that tan2 + 1...Ch. 1.4 - Trigonometric identities 32. Prove that...Ch. 1.4 - Trigonometric identities 33. Prove that sec (/2 )...Ch. 1.4 - Trigonometric identities 34. Prove that sec (x + )...Ch. 1.4 - Identities Prove the following identities. 73....Ch. 1.4 - Identities Prove the following identities. 74....Ch. 1.4 - Evaluating inverse trigonometric functions Without...Ch. 1.4 - Evaluating inverse trigonometric functions Without...Ch. 1.4 - Evaluating inverse trigonometric functions Without...Ch. 1.4 - Prob. 78ECh. 1.4 - Prob. 79ECh. 1.4 - Evaluating inverse trigonometric functions Without...Ch. 1.4 - Evaluating inverse trigonometric functions Without...Ch. 1.4 - Prob. 82ECh. 1.4 - Right-triangle relationships Use a right triangle...Ch. 1.4 - Right-triangle relationships Use a right triangle...Ch. 1.4 - Right-triangle relationships Use a right triangle...Ch. 1.4 - Right-triangle relationships Use a right triangle...Ch. 1.4 - Right-triangle relationships Use a right triangle...Ch. 1.4 - Right-triangle relationships Use a right triangle...Ch. 1.4 - Right-triangle pictures Express in terms of x...Ch. 1.4 - Right-triangle pictures Express in terms of x...Ch. 1.4 - Explain why or why not Determine whether the...Ch. 1.4 - One function gives all six Given the following...Ch. 1.4 - One function gives all six Given the following...Ch. 1.4 - One function gives all six Given the following...Ch. 1.4 - One function gives all six Given the following...Ch. 1.4 - Amplitude and period Identify the amplitude and...Ch. 1.4 - Amplitude and period Identify the amplitude and...Ch. 1.4 - Amplitude and period Identify the amplitude and...Ch. 1.4 - Prob. 99ECh. 1.4 - Prob. 100ECh. 1.4 - Little-known fact The shortest day of the year...Ch. 1.4 - Prob. 102ECh. 1.4 - Prob. 103ECh. 1.4 - Graphing sine and cosine functions Beginning with...Ch. 1.4 - Graphing sine and cosine functions Beginning with...Ch. 1.4 - Graphing sine and cosine functions Beginning with...Ch. 1.4 - Graphing sine and cosine functions Beginning with...Ch. 1.4 - Designer functions Design a sine function with the...Ch. 1.4 - Designer functions Design a sine function with the...Ch. 1.4 - Field goal attempt Near the end of the 1950 Rose...Ch. 1.4 - A surprising result The Earth is approximately...Ch. 1.4 - Daylight function for 40 N Verify that the...Ch. 1.4 - Block on a spring A light block hangs at rest from...Ch. 1.4 - Viewing angles An auditorium with a flat floor has...Ch. 1.4 - Ladders Two ladders of length a lean against...Ch. 1.4 - Pole in a corner A pole of length L is carried...Ch. 1 - Explain why or why not Determine whether the...Ch. 1 - Functions Decide whether graph A, graph B, or both...Ch. 1 - Prob. 3RECh. 1 - Prob. 4RECh. 1 - Prob. 5RECh. 1 - Prob. 6RECh. 1 - Prob. 7RECh. 1 - Prob. 8RECh. 1 - Prob. 9RECh. 1 - Prob. 10RECh. 1 - Prob. 11RECh. 1 - Prob. 12RECh. 1 - Prob. 13RECh. 1 - Evaluating functions from graphs Assume f is an...Ch. 1 - Prob. 15RECh. 1 - Prob. 16RECh. 1 - Evaluating functions from graphs Assume f is an...Ch. 1 - Prob. 18RECh. 1 - Prob. 19RECh. 1 - Prob. 20RECh. 1 - Prob. 21RECh. 1 - Prob. 22RECh. 1 - Prob. 23RECh. 1 - Prob. 24RECh. 1 - Prob. 25RECh. 1 - Prob. 26RECh. 1 - Prob. 27RECh. 1 - Prob. 28RECh. 1 - Prob. 29RECh. 1 - Prob. 30RECh. 1 - Prob. 31RECh. 1 - Prob. 32RECh. 1 - Prob. 33RECh. 1 - Prob. 34RECh. 1 - Prob. 35RECh. 1 - Prob. 36RECh. 1 - Prob. 37RECh. 1 - Intersection points Graph the equations y = x2 and...Ch. 1 - Prob. 39RECh. 1 - Prob. 40RECh. 1 - Prob. 41RECh. 1 - Prob. 42RECh. 1 - Prob. 43RECh. 1 - Prob. 44RECh. 1 - Prob. 45RECh. 1 - Prob. 46RECh. 1 - Prob. 47RECh. 1 - Prob. 48RECh. 1 - Solving equations Solve each equation. 49....Ch. 1 - Solving equations Solve each equation. 50....Ch. 1 - Using inverse relations The population P of a...Ch. 1 - Graphs of logarithmic and exponential functions...Ch. 1 - Existence of inverses Determine the largest...Ch. 1 - Prob. 54RECh. 1 - Prob. 55RECh. 1 - Prob. 56RECh. 1 - Prob. 57RECh. 1 - Prob. 58RECh. 1 - Prob. 59RECh. 1 - Prob. 60RECh. 1 - Prob. 61RECh. 1 - Prob. 62RECh. 1 - Prob. 63RECh. 1 - Prob. 64RECh. 1 - Prob. 65RECh. 1 - Prob. 66RECh. 1 - Prob. 67RECh. 1 - Prob. 68RECh. 1 - Prob. 69RECh. 1 - Prob. 70RECh. 1 - Prob. 71RECh. 1 - Prob. 72RECh. 1 - Prob. 73RECh. 1 - Prob. 74RECh. 1 - Prob. 75RECh. 1 - Prob. 76RECh. 1 - Prob. 77RECh. 1 - Prob. 78RECh. 1 - Prob. 79RECh. 1 - Prob. 80RECh. 1 - Prob. 81RECh. 1 - Prob. 82RECh. 1 - Prob. 83RECh. 1 - Prob. 84RECh. 1 - Prob. 85RECh. 1 - Prob. 86RECh. 1 - Prob. 87RECh. 1 - Prob. 88RECh. 1 - Prob. 89RECh. 1 - Sum of integers Let S(n)=1+2++n, where n is a...Ch. 1 - Little-known fact The shortest day of the year...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, calculus and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Determine whether the lines L₁ : F(t) = (−2, 3, −1)t + (0,2,-3) and L2 : ƒ(s) = (2, −3, 1)s + (−10, 17, -8) intersect. If they do, find the point of intersection. ● They intersect at the point They are skew lines They are parallel or equalarrow_forwardAnswer questions 2arrow_forwardHow does a fourier transform works?arrow_forward
- Determine the radius of convergence of a power series:12.6.5, 12.6.6, 12.6.7, 12.6.8Hint: Use Theorem12.5.1 and root test, ratio test, integral testarrow_forwardCan you answer this question and give step by step and why and how to get it. Can you write it (numerical method)arrow_forwardCan you answer this question and give step by step and why and how to get it. Can you write it (numerical method)arrow_forward
- There are three options for investing $1150. The first earns 10% compounded annually, the second earns 10% compounded quarterly, and the third earns 10% compounded continuously. Find equations that model each investment growth and use a graphing utility to graph each model in the same viewing window over a 20-year period. Use the graph to determine which investment yields the highest return after 20 years. What are the differences in earnings among the three investment? STEP 1: The formula for compound interest is A = nt = P(1 + − − ) n², where n is the number of compoundings per year, t is the number of years, r is the interest rate, P is the principal, and A is the amount (balance) after t years. For continuous compounding, the formula reduces to A = Pert Find r and n for each model, and use these values to write A in terms of t for each case. Annual Model r=0.10 A = Y(t) = 1150 (1.10)* n = 1 Quarterly Model r = 0.10 n = 4 A = Q(t) = 1150(1.025) 4t Continuous Model r=0.10 A = C(t) =…arrow_forwardUse a graphing utility to find the point of intersection, if any, of the graphs of the functions. Round your result to three decimal places. (Enter NONE in any unused answer blanks.) y = 100e0.01x (x, y) = y = 11,250 ×arrow_forward5. For the function y-x³-3x²-1, use derivatives to: (a) determine the intervals of increase and decrease. (b) determine the local (relative) maxima and minima. (e) determine the intervals of concavity. (d) determine the points of inflection. (e) sketch the graph with the above information indicated on the graph.arrow_forward
- Can you solve this 2 question numerical methodarrow_forward1. Estimate the area under the graph of f(x)-25-x from x=0 to x=5 using 5 approximating rectangles Using: (A) right endpoints. (B) left endpoints.arrow_forward9. Use fundamental theorem of calculus to find the derivative d a) *dt sin(x) b)(x)√1-2 dtarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning- Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
 Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...
Algebra
ISBN:9780079039897
Author:Carter
Publisher:McGraw Hill

Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...
Algebra
ISBN:9781680331141
Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURT
Publisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt

College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:9781305652231
Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Cengage

Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:9781337278461
Author:Ron Larson
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Power Series; Author: Professor Dave Explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OxVBT83x8oc;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Power Series & Intervals of Convergence; Author: Dr. Trefor Bazett;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XHoRBh4hQNU;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY