
A 10-lb block B rests as shown on a 20-lb bracket A. The coefficients of friction are μs = 0.30 and μk = 0.25 between block B and bracket A, and there is no friction in the pulley or between the bracket and the horizontal surface. (a) Determine the maximum weight of block C if block B is not to slide on bracket A. (b) If the weight of block C is 10 percent larger than the answer found in a, determine the accelerations of A, B, and C.
Fig. P12.31
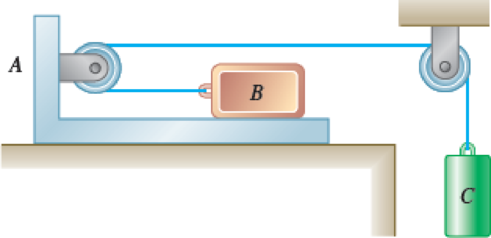
(a)
Find the maximum weight of block C if block B is not to slide on bracket A.
Answer to Problem 12.31P
The maximum weight of block C if block B is not to slide on bracket A is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The weight of block B
The weight of bracket A
The coefficient of static friction between block B and bracket A
The coefficient of kinetic friction between block B and bracket A
Calculation:
Let as consider the horizontal coordinate of A is
left of A.
Let as consider the horizontal coordinate of B is
left of A.
Let as consider
Sketch the system with coordinates points as shown in Figure (1).
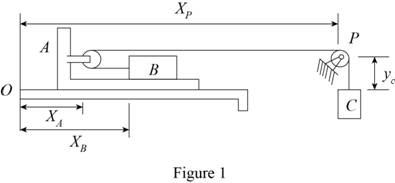
Write the general equation of mass (m):
Here, W is the weight, g is the acceleration due to gravity.
Consider the constraint of cord.
Write the total length of cable length (L).
Here,
Differentiate Equation (1) with respect to t to write velocity of the blocks.
Here,
Differentiate Equation (2) with respect to t to write acceleration of the blocks.
Here,
No slip between bracket A and block B. Therefore, the acceleration of bracket A is equal to acceleration of block B.
Substitute
From Equation (4) and (5), consider
Sketch the free body diagram and kinetic diagram of bracket A as shown in Figure (2).
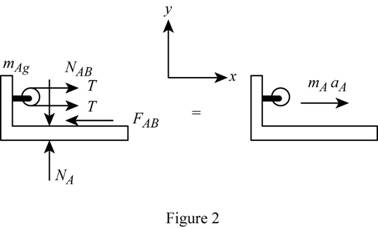
Refer Figure (2).
Apply Newton’s law of equation along x-axis.
Here, T is the tension in the cable,
Substitute
Here,
Sketch the free body diagram and kinetic diagram of block B as shown in Figure (3).
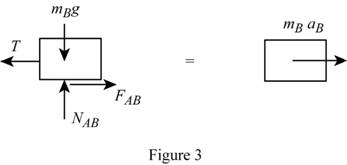
Refer Figure (3).
Apply Newton’s law of equation along x-axis.
Substitute
Here,
Apply Newton’s law of equation along y-axis.
Here,
Write the equation of frictional force
Substitute
Sketch the free body diagram and kinetic diagram of block C as shown in Figure (4).
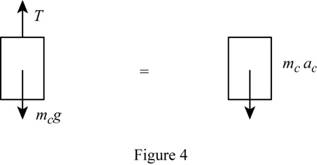
Refer Figure (4).
Apply Newton’s law of equation along y-axis.
Substitute
Here,
Adding Equation (5), (6), and (9).
Substitute Equation (6) in Equation (12).
Subtract Equation (6) and (9).
Substitute Equation (6) and (10) in Equation (14).
Subtracting Equation (13) and (9).
Substitute 0.30 for
Thus, the maximum weight of block C if block B is not to slide on bracket A is
(b)
Find the accelerations of bracket A, block B and block C.
Answer to Problem 12.31P
The accelerations of bracket A is
The accelerations of block B is
The accelerations of block C is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The weight of block C is 10 % larger than the answer found in part (a).
Calculation:
Find the weight of block C.
The slip is occurring. Therefore consider the kinetic acceleration.
Write the equation of frictional force
Substitute
Subtract Equation (6) and (9).
Substitute Equation (17) in Equation (18).
Substitute 0.25 for
Rewrite the Equation (5).
Substitute 10 lb for
Find the accelerations of bracket A, block B and block C.
Solve Equation (3), (20), and (21).
Thus, the accelerations of bracket A is
Thus, the accelerations of block B is
Thus, the accelerations of block C is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
VECTOR MECH...,STAT.+DYNA.(LL)-W/ACCESS
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and Applications
Starting Out with Programming Logic and Design (5th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Introduction To Programming Using Visual Basic (11th Edition)
Vector Mechanics For Engineers
- can you explain how in a coordinate frame transformation: v = {v_n}^T {n-hat} and then it was found that {n-hat} = [C]^T {b-hat} so v_n = {v_n}^T [C]^T {b-hat}, how does that equation go from that to this --> v_n = [C]^T v_barrow_forward6) If (k = 0,7 cm) find Imax for figure below. 225mm 100mm ثلاثاء. 100mm 150mm 75mm Ans: Tmax=45:27 N/cm F-400 Narrow_forwardThe man has a weight W and stands halfway along the beam. The beam is not smooth, but the planes at A and B are smooth (and plane A is horizontal). Determine the magnitude of the tension in the cord in terms of W and θ.arrow_forward
- A 15 cm-OD pipe is buried with its centerline 1.25 m below the surface of the ground [k of soil is 0.35 W/(m K)]. An oil having a density of 800 kg/m³ and a specific heat of 2.1 kJ/(kg K) flows in the pipe at 5.6 L/s. Assuming a ground surface temperature of 5°C and a pipe wall temperature of 95°C, estimate the length of pipe in which the oil temperature decreases by 5.5°C. + Tε = 5ºC Z= 1.25 m D= 15 cm 7p=95°Carrow_forwardFind the solution of the following Differential Equations 1) 4y+y=0, y(0)=2, y'(0) = 0. 2) y+y=0, y(0) = A, y'(0) = B. 3) "+2y'-8y=0, y(0)=1, y'(0)=8. 4) y"-2y-3y=0, y(0)=1, y'(0)=7. 5) y"-ky' =0, y(0)=2, y'(0) =k. 6) y+ky'-2k2y=0, y(0)=2, y'(0) = 2k. 7) y'+4y=0, y(0)=2.8 y+y-17sin(21) y(0)=-1. 9) y-y'-6y=0, y(0)=6. y'(0)=13. 10) y-y=0, 11) y"-4y+4y=0, y(0)=4, y'(0) = 0. y(0) = 2.1, y'(0)=3.9 12) y+2y+2y=0, y(0)=1, y'(0)=-3. 13) "+7y+12y=21e", y(0)=3.5, y'(0)=-10. 14) "+9y=10e", y(0)=0. y'(0) = 0. 15) y+3y+2.25y=91³ +64. y(0)=1, y'(0) = 31.5 16) "-6y+5y= 29 cos(21), y(0)=3.2, y'(0) = 6.2 17) y+2y+2y=0, y(0)=0, y'(0)=1. 18) y+2y+17y=0, y(0)=0, y'(0)=12. 19) y-4y+5y=0, y(0)-1, y'(0) 2. 20) 9y-6y+y=0. y(0)=3, y'(0)=1. 21) -2y+10y=0, y(0)=3, y'(0)=3. 22) 4y-4y+37y=0, (0) 3. y(0) 1.5 23) 4y-8y+5y=0, (0)-0, y(0) 1. 24) y+y+1.25y=0, y(0) 1. y'(0) -0.5 25) y+y=2 cos(1). y(0) 2. y'(0) = 0. 26) -4y+3y=0, (0)-3, y'(0) = 7. 27) y+2y+y=e", y(0)-0. y'(0) = 0. 29) 28) y+2y-3y-10sinh(2),…arrow_forwardNote: Please provide a clear, step-by-step simplified handwritten working out (no explanations!), ensuring it is done without any AI involvement. I require an expert-level answer, and I will assess and rate based on the quality and accuracy of your work and refer to the provided image for more clarity. Make sure to double-check everything for correctness before submitting appreciate your time and effort!. Question:arrow_forward
- 4. Block A and B are two different pieces of wood. Determine the minimum dimension for "a", if the shear stress of the wood is 50Mpa. The thickness of the wood is 30cm. 600N Aarrow_forward1. Determine the reaction force at A. 60 kN 5 B 1 m 1 m- -1 m 4 3 m 30 kN marrow_forwardFind the Laplace Transform of the following functions 1) f() cos(ar) Ans. F(s)=7 2ws 2) f() sin(at) Ans. F(s)= s² + a² 3) f(r)-rcosh(at) Ans. F(s)= 2as 4)(t)=sin(at) Ans. F(s)= 2 5) f(1) = 2te' Ans. F(s)= (S-1) 5+2 6) (1) e cos() Ans. F(s) = (+2)+1 7) (1) (Acostẞr)+ Bsin(Br)) Ans. F(s)- A(s+a)+BB (s+a)+B 8) f()-(-)() Ans. F(s)= 9)(1)(1) Ans. F(s): 10) f(r),()sin() Ans. F(s): 11) 2 k 12) 0 13) 0 70 ㄷ.. a 2a 3a 4a 2 3 4 14) f(1)=1, 0<1<2 15) (1) Ksin(t) 0arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
