
A 10-Ib block B rests as shown on a 20-1b bracket A. The coefficients of friction are
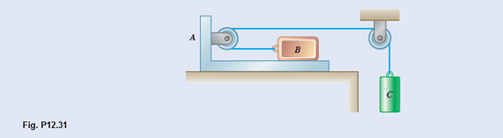
(a)
Maximum weight of block C if block B is not to slide on bracket A.
Answer to Problem 12.31P
Maximum weight of block C is
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Concept used:
Kinematics :
Let
Let
Note that
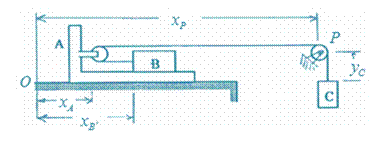
The cable length is fixed.
Differentiating and noting that
Here.
Kinetics :
Let
The free body diagrams are shown here:
Bracket A:
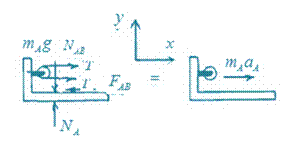
Block B:
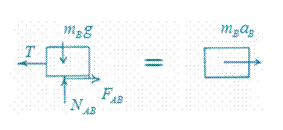
Block C:
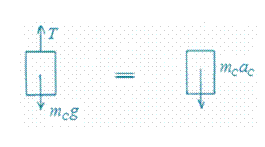
Bracket A:
Block B:
Block C:
Adding Eqs. (2). (3) and (4) and transposing.
Subtracting Eq. (4) from Eq. (3) and transposing.
No slip between A and B.
From Eq. (1).
From Eq. (5).
For impeding slip.
Substituting into Eq. (6).
Solving for
(b)
Accelerations of A, B, and C, if the weight of block C is 10 percent larger than the result of part a.
Answer to Problem 12.31P
Accelerations of A. B and C:
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Since slip is occurring.
Eq. (6) becomes.
Or:
With given data. Eq. (5) becomes
Solving Eqs. (1). (7). and (8) gives
So,
And,
And
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Vector Mechanics For Engineers
- question 5 and 6 from dynamics I need to show all work step by step problemsarrow_forwardStudy Area Document Sharing User Settings Access Pearson mylabmastering.pearson.com P Pearson MyLab and Mastering The crash cushion for a highway barrier consists of a nest of barrels filled with an impact-absorbing material. The barrier stopping force is measured versus the vehicle penetration into the barrier. (Figure 1) Part A P Course Home b My Questions | bartleby Review Determine the distance a car having a weight of 4000 lb will penetrate the barrier if it is originally traveling at 55 ft/s when it strikes the first barrel. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Figure 1 of 1 36 μΑ S = Value Units Submit Request Answer Provide Feedback ? Next >arrow_forwardWater is the working fluid in an ideal Rankine cycle. Saturated vapor enters the turbine at 12 MPa, and the condenser pressure is 8 kPa. The mass flow rate of steam entering the turbine is 50 kg/s. Determine: (a) the net power developed, in kW. (b) the rate of heat transfer to the steam passing through the boiler, in kW. (c) the percent thermal efficiency. (d) the mass flow rate of condenser cooling water, in kg/s, if the cooling water undergoes a temperature increase of 18°C with negligible pressure change in passing through the condenser.arrow_forward
- 4. The figure below shows a bent pipe with the external loading FA 228 lb, and M₁ = M₂ = 1 kip-ft. The force Fernal loading FA = 300 lb, FB: parallel to the y-axis, and and yc = 60°. = 125 lb, Fc = acts parallel to the x-z plane, the force FB acts Cartesian resultan Coordinate direction angles of Fc are ac = 120°, ẞc = 45°, a. Compute the resultant force vector of the given external loading and express it in EST form. b. Compute the resultant moment vector of the given external loading about the origin, O, and express it in Cartesian vector form. Use the vector method while computing the moments of forces. c. Compute the resultant moment vector of the given external loading about the line OA and express it in Cartesian vector form. :00 PM EST k ghoufran@buffaternal du 2 ft M₁ A 40° FA M2 C 18 in 1 ft Fc 25 houfran@bald.edu - Feb 19, 3 ft FBarrow_forwardThe differential equation of a cruise control system is provided by the following equation: Find the closed loop transfer function with respect to the reference velocity (vr) . a. Find the poles of the closed loop transfer function for different values of K. How does the poles move as you change K? b. Find the step response for different values of K and plot in MATLAB. What can you observe? c. For the given transfer function, find tp, ts, tr, Mp . Plot the resulting step response. G(s) = 40/(s^2 + 4s + 40)arrow_forwardAuto Controls Perform the partial fraction expansion of the following transfer function and find the impulse response: G(s) = (s/2 + 5/3) / (s^2 + 4s + 6) G(s) =( 6s^2 + 50) / (s+3)(s^2 +4)arrow_forward
- Study Area Document Sharing User Settings mylabmastering.pearson.com Access Pearson P Pearson MyLab and Mastering The 150-lb skater passes point A with a speed of 6 ft/s. (Figure 1) Figure 1 of 1 Part A P Course Home b My Questions | bartleby Determine his speed when he reaches point B. Neglect friction. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. με ? VB = Value Units Submit Request Answer Part B Determine the normal force exerted on him by the track at this point. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. ☐ о Α NB = Value Units Submit Request Answer Provide Feedback ? ■Review Next >arrow_forwardmylabmastering.pearson.com Access Pearson P Pearson MyLab and Mastering P Course Home b My Questions | bartleby Study Area Document Sharing User Settings The 100-kg crate is subjected to the forces shown. The crate is originally at rest. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and the surface is μk = 0.2. (Figure 1) Part A Determine the distance it slides in order to attain a speed of 8.1 m/s. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Figure 500 N 1 of 1 Α S = Value Units Submit Request Answer Provide Feedback ? ■Review Next >arrow_forwardThe differential equation of a DC motor can be described by the following equation Find the transfer function between the applied voltage ( Va)and the motor speed (thetadot m). What is the steady state speed of the motor after a voltage (Va = 10V) has been applied. Find the transfer function between the applied voltage (Va) and the shaft angle (thetadot m) .arrow_forward
- Study Area Document Sharing User Settings Access Pearson mylabmastering.pearson.com P Pearson MyLab and Mastering The crash cushion for a highway barrier consists of a nest of barrels filled with an impact-absorbing material. The barrier stopping force is measured versus the vehicle penetration into the barrier. (Figure 1) Part A P Course Home b My Questions | bartleby Review Determine the distance a car having a weight of 4000 lb will penetrate the barrier if it is originally traveling at 55 ft/s when it strikes the first barrel. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Figure 1 of 1 36 μΑ S = Value Units Submit Request Answer Provide Feedback ? Next >arrow_forwardStudy Area Document Sharing User Settings mylabmastering.pearson.com Access Pearson P Pearson MyLab and Mastering Part A P Course Home b My Questions | bartleby ■Review The sports car has a mass of 2.5 Mg and accelerates at 6 m/s², starting from rest. (Figure 1) If the drag resistance on the car due to the wind is FD = (10v) N, where v is the velocity in m/s, determine the power supplied to the engine when t = 5 s. The engine has a running efficiency of € = 0.66. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Figure 1 of 1 о Α ? P = Value Units Submit Request Answer Return to Assignment Provide Feedbackarrow_forwardAccess Pearson Study Area mylabmastering.pearson.com P Pearson MyLab and Mastering Document Sharing User Settings The car in (Figure 1) having a mass of 2 Mg is originally traveling at 2 m/s. Assume 0 = 22°. Figure 1 of 1 Part A P Course Home b My Questions | bartleby ■Review Determine the distance it must be towed by a force F = 4 kN in order to attain a speed of 6 m/s. Neglect friction and the mass of the wheels. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Α ? S = Value Units Submit Request Answer Provide Feedback Next >arrow_forward
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
