
1.
Prepare the transaction in the sales journal, cash receipts journal and general journal and verify the total column and rule the column.
1.
Explanation of Solution
Sales Journal
Sales journal is one form of special journal book, which records all the sales transactions that are sold to customers on credit. In a single column sales journal, debit aspect of
Prepare the given transaction in a sales journal and verify the total column and rule the column:
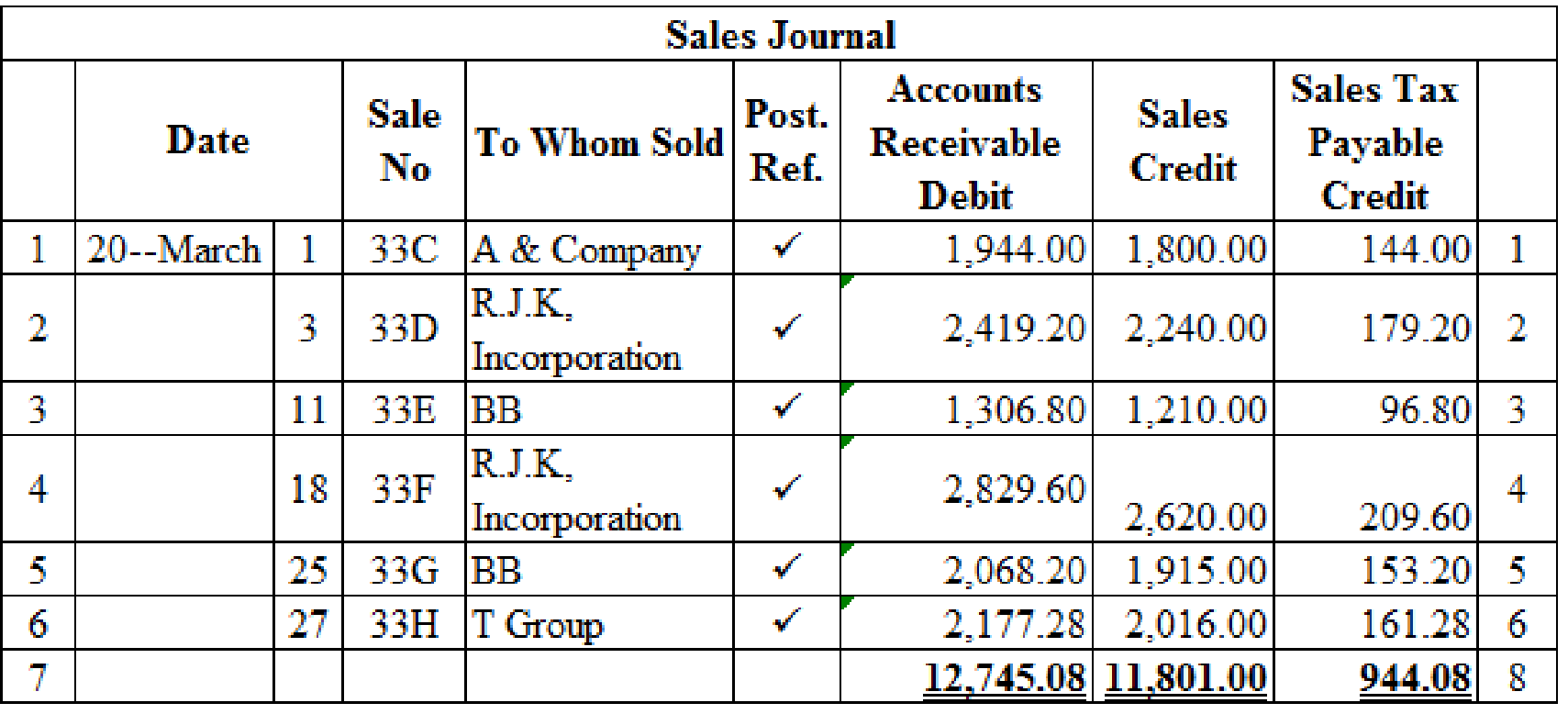
Table (1)
Working note 1:
Calculate the amount of accounts receivable (debit) on dated 1st March:
Working note 2:
Calculate the amount of accounts receivable (debit) on dated 3rd March:
Working note 3:
Calculate the amount of accounts receivable (debit) on dated 11th March:
Working note 4:
Calculate the amount of accounts receivable (debit) on dated 18th March:
Working note 5:
Calculate the amount of accounts receivable (debit) on dated 25th March:
Working note 6:
Calculate the amount of accounts receivable (debit) on dated 27th March:
Verification of total debit and credit column:
Cash Receipts Journal: It is a special book where only cash receipts transactions that are received from customers, merchandise sales and service made in cash and collection of accounts receivable are recorded.
The following are the some examples of transactions that would be recorded in the Other Accounts credit column of the cash receipts journal:
- • Cash received as interest on notes payable
- • Interest revenue received from debtors
- • Cash receipts from bank loans
- • Cash receipts for capital investments
Prepare the given transactions in the cash receipts journal and verify the total column and rule the column:
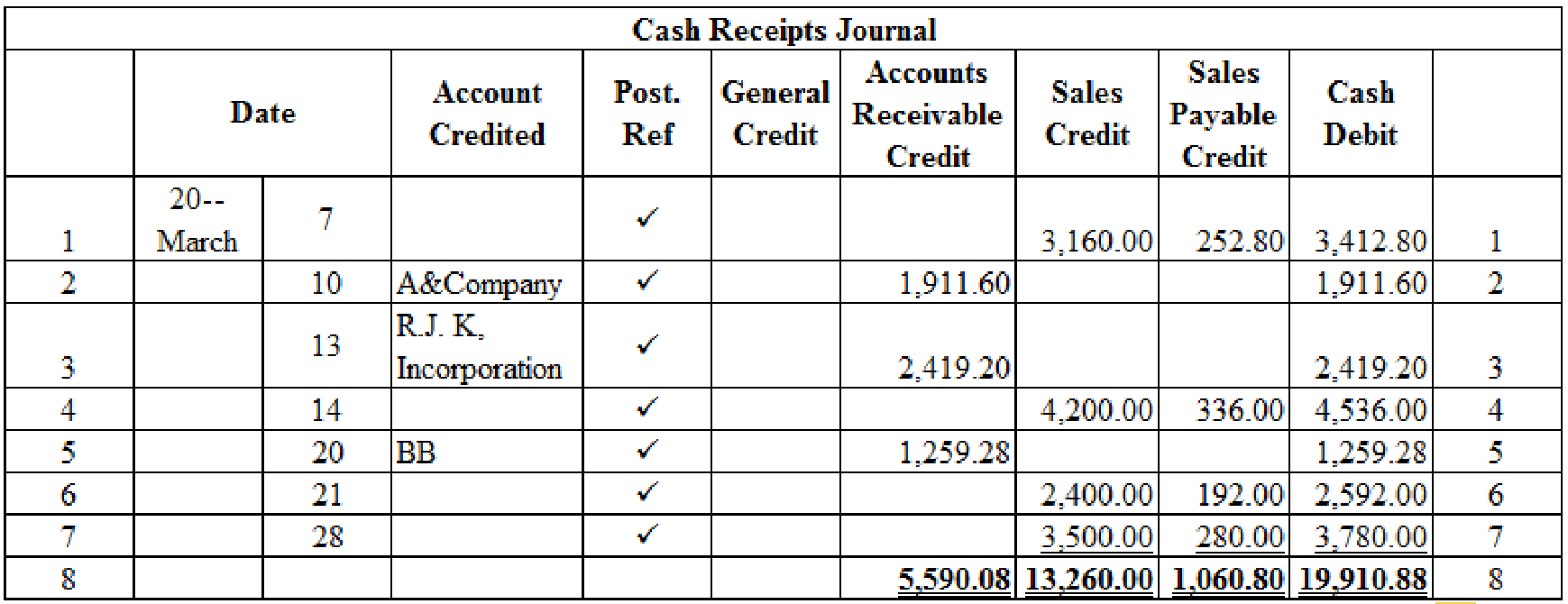
Table (2)
Working note 1:
Calculate the amount of cash on dated 7th March:
Working note 2:
Calculate the amount of cash on dated 14th March:
Working note 3:
Calculate the amount of cash on dated 21st March:
Working note 4:
Calculate the amount of cash on dated 28th March:
Verification of total debit and credit column:
Use the general journal to record the sales returns and allowances:
General Journal: It is a book where all the monetary transactions are recorded in the form of journal entries on the date of their occurrence in a chronological order.
Transaction on March 5:
| General Journal | ||||||
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| 20-- | ||||||
| March | 5 | Sales Returns and Allowances | 401.1 | 30.00 | ||
| Sales Tax Payable | 231 | 2.40 | ||||
| Accounts Receivable, A &Company | 122/✓ | 32.40 | ||||
| (Record merchandise returned) | ||||||
Table (3)
Description:
- ■ Sales Returns and Allowances is a contra-revenue account, and contra-revenue accounts decrease the equity value, and a decrease in equity is debited.
- ■ Sales Tax Payable is a liability account. Since the payable decreased due to returns, the liability decreased, and a decrease in liability is debited.
- ■ Accounts Receivable, A &Company is an asset account. Since inventory is returned, amount to be received has decreased, asset account is decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
Working Note:
Compute sales tax payable amount.
Transaction on March 16:
| General Journal | ||||||
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| 20-- | ||||||
| March | 16 | Sales Returns and Allowances | 401.1 | 44.00 | ||
| Sales Tax Payable | 231 | 3.52 | ||||
| Accounts Receivable, BB | 122/✓ | 47.52 | ||||
| (Record merchandise returned) | ||||||
Table (4)
Description:
- ■ Sales Returns and Allowances is a contra-revenue account, and contra-revenue accounts decrease the equity value, and a decrease in equity is debited.
- ■ Sales Tax Payable is a liability account. Since the payable decreased due to returns, the liability decreased, and a decrease in liability is debited.
- ■ Accounts Receivable, BB is an asset account. Since inventory is returned, amount to be received has decreased, asset account is decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
Working Note 1:
Compute sales tax payable amount.
Working note 2:
Compute accounts receivable amount.
2.
Post the prepared journals to the general ledger, and the accounts receivable ledger accounts.
2.
Explanation of Solution
Posting transactions: The process of transferring the journalized transactions into the accounts of the ledger is known as posting the transactions.
Post the prepared journals to the general ledger:
| ACCOUNT Cash ACCOUNT NO. 101 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 20-- | |||||||
| March | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 9,741.00 | |||
| 31 | CR9 | 19,910.88 | 29,651.88 | ||||
Table (5)
| ACCOUNT Accounts Receivable ACCOUNT NO. 122 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 20-- | |||||||
| March | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 1,058.25 | |||
| 5 | J5 | 32.40 | 1,025.85 | ||||
| 16 | J5 | 47.52 | 978.33 | ||||
| 31 | S6 | 12,745.08 | 13,723.41 | ||||
| 31 | CR9 | 5,590.08 | 8,133.33 | ||||
Table (6)
| ACCOUNT Sales Tax Payable ACCOUNT NO. 231 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 20-- | |||||||
| March | 5 | J5 | 2.40 | 2.40 | |||
| 16 | J5 | 3.52 | 5.92 | ||||
| 31 | S6 | 944.08 | 938.16 | ||||
| 31 | CR9 | 1,060.80 | 1,998.96 | ||||
Table (7)
| ACCOUNT Sales ACCOUNT NO. 401 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 20-- | |||||||
| March | 31 | S6 | 11,801.00 | 11,801.00 | |||
| 31 | CR9 | 13,260.00 | 25,061.00 | ||||
Table (8)
| ACCOUNT Sales Returns and Allowances ACCOUNT NO. 401.1 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 20-- | |||||||
| March | 5 | J5 | 30.00 | 30.00 | |||
| 16 | J5 | 44.00 | 74.00 | ||||
Table (9)
Post the journals to the accounts receivable ledger:
| NAME Corporation A & Company | ||||||
| ADDRESS 1424 J Creek Road, N, In 47448-2245 | ||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance ($) | |
| 20-- | ||||||
| March | 1 | S6 | 1,944.00 | 1,944.00 | ||
| 5 | J5 | 32.40 | 1,911.60 | |||
| 10 | CR9 | 1,911.60 | 0 | |||
Table (10)
| NAME BB | ||||||
| ADDRESS 6422 E. B Road, B, In 47401-7756 | ||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance ($) | |
| 20-- | ||||||
| March | 11 | S6 | 1,306.80 | 1,306.80 | ||
| 16 | J5 | 47.52 | 1,259.28 | |||
| 20 | CR9 | 1,259.28 | 0 | |||
| 25 | S6 | 2,068.20 | 2,068.20 | |||
Table (11)
| NAME RJ Incorporation | ||||||
| ADDRESS 3315 l Avenue, B, in 47401-7223 | ||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance ($) | |
| 20-- | ||||||
| March | 3 | S6 | 2,419.20 | 2,419.20 | ||
| 13 | CR9 | 2,419.20 | 0 | |||
| 18 | S6 | 2,829.60 | 2,829.60 | |||
Table (12)
| NAME T Group | ||||||
| ADDRESS 2300 E. National Road, Cd, IN 46229-4824 | ||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance ($) | |
| 20-- | ||||||
| March | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 1,058.25 | ||
| 27 | S6 | 2,177.28 | 3,235.53 | |||
Table (13)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27 (New in Accounting from Heintz and Parry)
 College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College PubPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College PubPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College- Century 21 Accounting Multicolumn JournalAccountingISBN:9781337679503Author:GilbertsonPublisher:Cengage
 Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning




