
Concept explainers
The following accounts appear in the ledger of Sheldon Company on January 31, the end of this fiscal year.


The data needed for adjustments on January 31 are as follows:
a–b. Merchandise inventory, January 31, $55,750.
c. Insurance expired for the year, $1,285.
d.
e. Accrued wages on January 31, $1,556.
f. Supplies used during the year $1,503.
Required
- 1. Prepare a work sheet for the fiscal year ended January 31. Ignore this step if using QuickBooks or general ledger.
- 2. Prepare an income statement.
- 3. Prepare a statement of owner’s equity. No additional investments were made during the year. Ignore this step if using CLGL.
- 4. Prepare a
balance sheet . - 5. Journalize the
adjusting entries . - 6. Journalize the closing entries.
Check Figure
Net loss, $1,737
1.
Indicate the given adjustments and complete the worksheet for Company S for the year ended January 31, 20--.
Explanation of Solution
Worksheet: Worksheet is an accounting tool that help accountants to record adjustments and up-date balances required to prepare financial statements. Worksheet is a central place where trial balance, adjustments, adjusted trial balance, income statement, and balance sheet are presented.
Indicate the given adjustments and complete the worksheet for Company S for the year ended January 31, 20--.
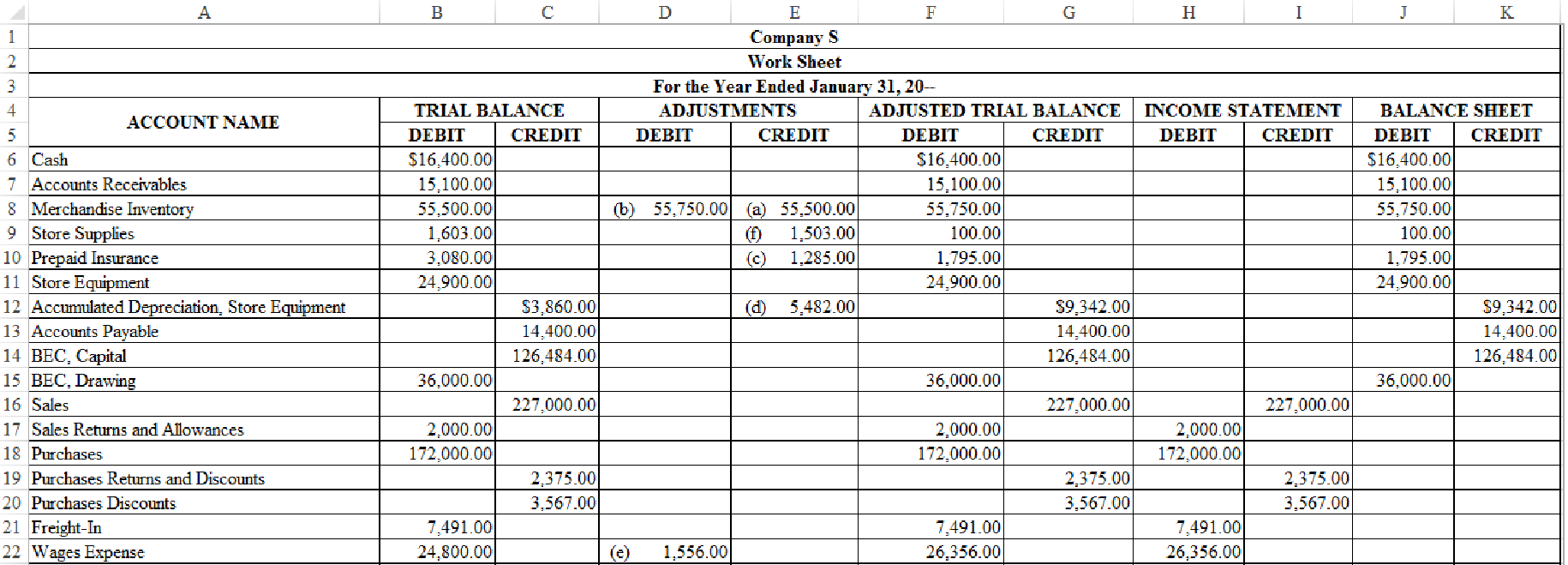
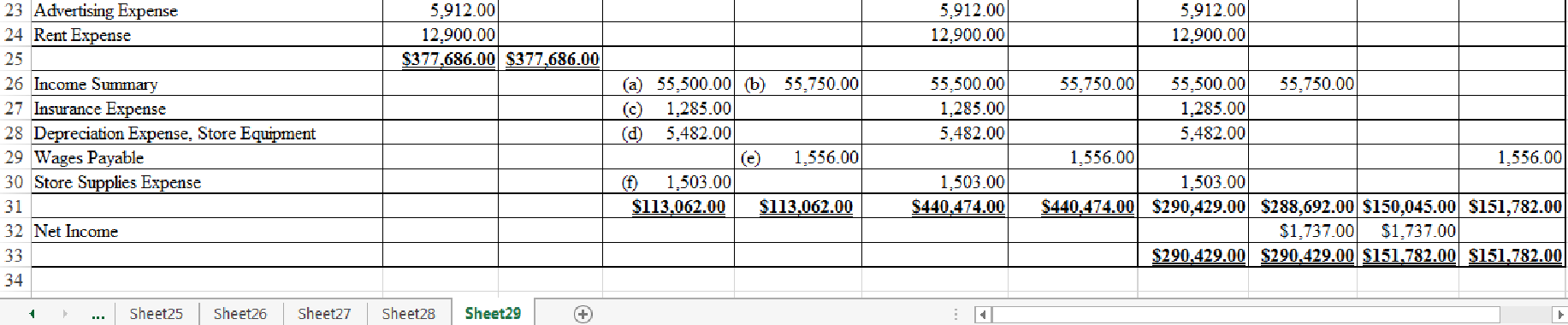
Figure-(1)
2.
Prepare an income statement for Company S for the year ended January 31, 20--.
Explanation of Solution
Income statement: The financial statement which reports revenues and expenses from business operations and the result of those operations as net income or net loss for a particular time period is referred to as income statement.
Prepare an income statement for Company S for the year ended January 31, 20--.
| Company S | ||||
| Income Statement | ||||
| For the Year Ended January 31, 20-- | ||||
| Revenue from sales: | ||||
| Sales | $227,000 | |||
| Less: Sales returns and allowances | 2,000 | |||
| Net sales | $225,000 | |||
| Cost of goods sold: | ||||
| Merchandise inventory, February 1, 20-- | $55,500 | |||
| Purchases | $172,000 | |||
| Less: Purchase returns and allowances | $2,375 | |||
| Purchases discounts | 3,567 | 5,942 | ||
| Net purchases | 166,058 | |||
| Add: Freight-in | 7,491 | |||
| Delivered cost of purchases | 173,549 | |||
| Cost of goods available for sale | 229,049 | |||
| Less: Merchandise inventory, June 30, 20-- | 55,750 | |||
| Cost of goods sold | 173,299 | |||
| Gross profit | 51,701 | |||
| Operating expenses: | ||||
| Wages expense | 26,536 | |||
| Advertising expense | 5,912 | |||
| Rent expense | 12,900 | |||
| Store supplies expense | 1,503 | |||
| Insurance expense | 1,285 | |||
| Depreciation expense, Store equipment | 5,482 | |||
| Total operating expenses | 53,438 | |||
| Net income (loss) | $(1,737) | |||
Table (1)
Thus, the income statement of Company C for the year ended June 30, 20—reposts the net loss of $1,737.
3.
Prepare a statement of owners’ equity for Company S for the year ended January 31, 20--.
Explanation of Solution
Statement of owners’ equity: This statement reports the beginning owner’s equity and all the changes which led to ending owners’ equity. Additional capital, net income from income statement is added to, and drawings is deducted from beginning owner’s equity to arrive at the end result, ending owner’s equity.
Prepare a statement of owners’ equity for Company S for the year ended January 31, 20--.
| Company S | ||
| Statement of Owners’ Equity | ||
| For the Year Ended January 31, 20-- | ||
| MES, Capital, July 1, 20-- | $126,484 | |
| Net loss for the year | $1,737 | |
| Less: Withdrawals for the year | 36,000 | |
| Decrease in capital | 37,737 | |
| BEC, Capital, June 30, 20-- | $88,747 | |
Table (2)
Thus, the statement of owners’ equity of Company S for the year ended January 31, 20—reports the capital amount of $88,747.
4.
Prepare a balance sheet for Company S, based on the account balances from work sheet, and capital of the owner from the statement of owners’ equity prepared in Part (3).
Explanation of Solution
Balance sheet: This financial statement reports a company’s resources (assets) and claims of creditors (liabilities) and owners (owners’ equity) over those resources. The resources of the company are assets which include money contributed by owners and creditors. Hence, the main elements of the balance sheet are assets, liabilities, and owners’ equity.
Prepare the balance sheet for Company S as at January 31, 20--.
| Company S | ||
| Balance Sheet | ||
| January 31, 20-- | ||
| Assets | ||
| Current Assets: | ||
| Cash | $16,400 | |
| Accounts Receivable | 15,100 | |
| Merchandise Inventory | 55,750 | |
| Store Supplies | 100 | |
| Prepaid Insurance | 1,795 | |
| Total Current Assets | $89,145 | |
| Property and Equipment: | ||
| Store Equipment | 24,900 | |
| Less: Accumulated Depreciation | 9,342 | |
| Total Property and Equipment | 15,558 | |
| Total Assets | $104,703 | |
| Liabilities | ||
| Current Liabilities: | ||
| Accounts Payable | 14,400 | |
| Wages Payable | 1,556 | |
| Total Liabilities | $15,956 | |
| Owners’ Equity | ||
| BEC, Capital | 88,747 | |
| Total Liabilities and Owners’ Equity | $104,703 | |
Table (3)
Thus, the balance sheet of Company S as at January 31, 20—reports the total assets, and total liabilities and owners’ equity of $104,703.
5.
Prepare adjusting journal entries for Company S.
Explanation of Solution
Adjusting entries: Adjusting entries are those entries which are recorded at the end of the year, to update the income statement accounts (revenue and expenses) and balance sheet accounts (assets, liabilities, and owners’ or stockholders’ equity) to maintain the records according to accrual basis principle and matching concept.
Journal entry: Journal entry is a set of economic events which can be measured in monetary terms. These are recorded chronologically and systematically.
Debit and credit rules:
- Debit an increase in asset account, increase in expense account, decrease in liability account, and decrease in stockholders’ equity accounts.
- Credit decrease in asset account, increase in revenue account, increase in liability account, and increase in stockholders’ equity accounts.
Prepare adjusting journal entries for Company S.
Adjusting entry for removing beginning inventory:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| 20-- | ||||||
| January | 31 | Income Summary | 55,500 | |||
| Merchandise Inventory | 55,500 | |||||
| (Record the entry to remove beginning inventory) | ||||||
Table (4)
Description:
- Income Summary is a clearing account which closes revenue, expense, drawings, and net of revenues and expenses to capital accounts. The account is debited to eliminate the beginning inventory balance.
- Merchandise Inventory is an asset account. Since beginning inventory is eliminated and transferred to Income Summary account, asset account decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
Adjusting entry for entering the ending inventory:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| 20-- | ||||||
| January | 31 | Merchandise Inventory | 55,750 | |||
| Income Summary | 55,750 | |||||
| (Record the entry to enter ending inventory) | ||||||
Table (5)
Description:
- Merchandise Inventory is an asset account. Since ending inventory or physical count of inventory at the end of the period is entered to record in the financial statements, asset account increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- Income Summary is a clearing account which closes revenue, expense, drawings, and net of revenues and expenses to capital accounts. The account is credited to enter the ending inventory balance.
Adjusting entry for the wages payable:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| 20-- | ||||||
| January | 31 | Wages Expense | 1,556 | |||
| Wages Payable | 1,556 | |||||
| (Record accrued wages expenses) | ||||||
Table (6)
Description:
- Wages Expense is an expense account. Since expenses decrease equity, equity value is decreased, and a decrease in equity is debited.
- Wages Payable is a liability account. Since amount of payables has increased, liability decreased, and an increase in liability is credited.
Adjusting entry for the insurance expense:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| 20-- | ||||||
| January | 31 | Insurance Expense | 1,285 | |||
| Prepaid Insurance | 1,285 | |||||
| (Record part of prepaid insurance expired) | ||||||
Table (7)
Description:
- Insurance Expense is an expense account. Since expenses decrease equity, equity value is decreased, and a decrease in equity is debited.
- Prepaid Insurance is an asset account. Since amount of insurance is expired, asset account decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
Adjusting entry for the depreciation expense, store equipment:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| 20-- | ||||||
| January | 31 | Depreciation Expense, Store Equipment | 5,482 | |||
| Accumulated Depreciation, Store Equipment | 5,482 | |||||
| (Record depreciation expense) | ||||||
Table (8)
Description:
- Depreciation Expense, Store Equipment is an expense account. Since expenses decrease equity, equity value is decreased, and a decrease in equity is debited.
- Accumulated Depreciation, Store Equipment is a contra-asset account, and contra-asset accounts would have a normal credit balance, hence, the account is credited.
Adjusting entry for the supplies expense:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| 20-- | ||||||
| January | 31 | Store Supplies Expense | 1,503 | |||
| Store supplies | 1503 | |||||
| (Record part of supplies consumed) | ||||||
Table (9)
Description:
- Store Supplies Expense is an expense account. Since expenses decrease equity, equity value is decreased, and a decrease in equity is debited.
- Store Supplies is an asset account. Since amount of supplies is consumed, asset account decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
6.
Prepare closing entries for Company S.
Explanation of Solution
Closing entries: The journal entries prepared to close the temporary accounts to capital account are referred to as closing entries. The revenue, expense, and drawing accounts are referred to as temporary accounts because the information and figures in these accounts is held temporarily and consequently transferred to permanent account at the end of accounting year.
Steps in closing procedure:
- 1. Close the revenue accounts and the income statement accounts with credit balances to Income Summary account.
- 2. Close the expense accounts and the income statement accounts with debit balances to Income Summary account.
- 3. Close the Income Summary account and transfer the net income or net loss balance to the Capital account.
- 4. Close the Drawing account to Capital account.
Prepare closing entries for Company S.
Step 1:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| June | 30 | Sales | 227,000 | |||
| Purchases Returns and Allowances | 2,375 | |||||
| Purchases Discounts | 3,567 | |||||
| Income Summary | 232,942 | |||||
| (Record closing of revenue and income statement accounts with credit balances to Income Summary account) | ||||||
Table (10)
Description:
- Sales is a revenue account. Revenue accounts have normal credit balance. Since revenue is closed to Income Summary account, the account is debited.
- Purchases Returns and Allowances and Purchase Discounts are contra-cost accounts and have normal credit balances. Since contra-cost accounts are closed to Income Summary account, the accounts are debited.
- Income Summary is a clearing account which closes revenue, expense, drawings, and net of revenues and expenses to capital accounts. The account is credited to hold the transferred balance from revenue account and other income statement accounts with credit balances.
Step 2:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| January | 31 | Income Summary | 234,929 | |||
| Sales Returns and Allowances | 2,000 | |||||
| Purchases | 172,000 | |||||
| Freight-In | 7,491 | |||||
| Wages Expense | 26,356 | |||||
| Advertising Expense | 5,912 | |||||
| Rent Expense | 12,900 | |||||
| Store Supplies Expense | 1,503 | |||||
| Insurance Expense | 1,285 | |||||
| Depreciation Expense, Store Equipment | 5,482 | |||||
| (Record closing of expenses and income statement accounts with debit balances to Income Summary account) | ||||||
Table (11)
Description:
- Income Summary is a clearing account which closes revenue, expense, drawings, and net of revenues and expenses to capital accounts. The account is debited to hold the transferred balance from expense accounts other income statement accounts with debit balances.
- Sales Returns and Allowances is contra-revenue account and has a normal debit balances. Since contra-revenue accounts are closed to Income Summary account, the account is credited.
- Purchases, Freight-In, Wages Expense, Advertising Expense, Rent Expense, Store Supplies Expense, Insurance Expense, and Depreciation Expense-Store Equipment, are expense accounts. Expense account has a normal debit balance. Since expenses are closed to Income Summary account, the accounts are credited.
Step 3:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| January | 31 | MES, Capital | 1,737 | |||
| Income Summary | 1,737 | |||||
| (Record closing of net loss to capital account) | ||||||
Table (12)
Description:
- MES, Capital is a capital account. Since net loss is transferred to the account, the account value decreased, and a decrease in capital is debited.
- Income Summary is a clearing account which closes revenue, expense, drawings, and net of revenues and expenses to capital accounts. Since net loss is closed, the account is reversed, hence, the Income Summary account is credited.
Step 4:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| January | 31 | MES, Capital | 36,000 | |||
| MES, Drawing | 36,000 | |||||
| (Record closing of drawing to capital account) | ||||||
Table (13)
Description:
- MES, Capital is a capital account. Since drawings is transferred to the account, the value decreased, and a decrease in capital is debited.
- MES, Drawing is a capital account. Since drawings is transferred, the account is credited to reverse the previously debited effect.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
College Accounting: A Career Approach (with Quickbooks Accountant 2015 Cd-rom)
Additional Business Textbook Solutions
Fundamentals of Management (10th Edition)
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis (16th Edition)
Horngren's Accounting (12th Edition)
Operations Management: Processes and Supply Chains (12th Edition) (What's New in Operations Management)
Intermediate Accounting (2nd Edition)
Financial Accounting, Student Value Edition (5th Edition)
- Total overhead applied is?arrow_forwardSolve this Accounting Problemarrow_forwardVenture Ltd. used 8,500 machine hours (Driver) on Job # 23. Total machine hours are 25,000. Assume Job # 23 is the only job sold during the accounting period. What is the overhead applied in COGS if the total overhead applied is $175,000?arrow_forward
- General accountarrow_forwardOhms Company manufactures plugs at a cost of $41 per unit, which includes $5 of fixed overhead. Ohms needs 30,000 of these plugs annually (as part of a larger product it produces). Wire Company has offered to sell these units to Ohms at $43 per unit. If Ohms decides to purchase the plugs, $60,000 of the annual fixed overhead cost will be eliminated, and the company may be able to rent the facility previously used for manufacturing the plugs. If Ohms Company purchases the plugs but does not rent the unused facility, the company would: Save $5.00 per unit. Lose $8.00 per unit. Save $4.00 per unit. Lose $5.00 per unit. Save $3.00 per unit.arrow_forward4 POINTSarrow_forward
- Provide answer general accountingarrow_forwardtre 3 3.14134,54arrow_forward128361 MENTS was extracted by as at 30 June 2018. als to agree. 30 June 2018 Dr with each other. Trial Balance as at 31 December 2017 32.7X D. Fearon extracted the following trial balance from his books. He could not get the totals to agree Dr Cr Cr $ $ $ $ 87,050 Capital 25,621 62,400 Drawings 13,690 110° 305 410 Sales 94,630 Multiple Each multipl answers: (A) question and (B), (C) or (D piece of pape of questions written atter When you your answer 3,168 Purchases 258 60,375 61 A debit 595 Returns inwards and outwards 1,210 1,109 10,000-35 Wages and salaries 2,000 14,371 12,490 Sundry expenses чут -598 8,120 5,045 Inventory 1.1.2017 8,792 168 account (A) we (B) we (C) we h that 6,790+85 Accounts receivable and accounts 16811,370 4,290 (D) we payable 4,520 Loan from J. Chandler 2000 62 Inventor 5,000 17,017 Equipment 16,000 period is 1,134 Bank 1500 (A) carri 5,790 109,522 109,522 Suspense (B) carri 1,546 (C) tran 132,196 132,196 nd: by $350. ercast by $100. 50, have been entered in n…arrow_forward
 Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College Pub
College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College Pub Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,





