
At the movies: The following table provides information about the top grossing movies of all time.
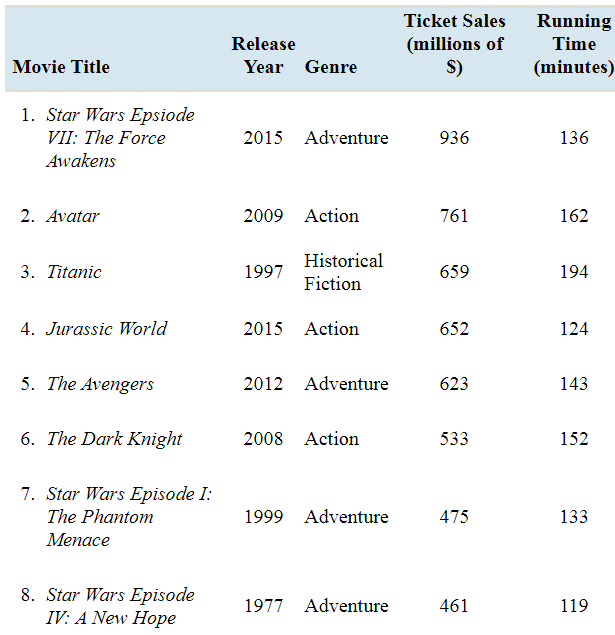

- Which of the columns represent qualitative variables?
- Which of the columns represent quantitative variables?
- Which of the columns represent nominal variables?
- Which of the columns represent ordinal variables?
a.
To identify:the columns that represent qualitative variables.
Answer to Problem 48E
The columns Movie Title and Genre represent qualitative variables.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
| Movie Title | Release Year | Genre | Ticket Sales (millions of $) | Running Time (minutes) |
| 1. Star Wars Episode VII: The Force Awakens | 2015 | Adventure | 936 | 136 |
| 2. Avatars | 2009 | Action | 761 | 162 |
| 3. Titanic | 1997 | Historical Fiction | 659 | 194 |
| 4. Jurassic World | 2015 | Action | 652 | 124 |
| 5. The Avengers | 2012 | Adventure | 623 | 143 |
| 6. The Dark Knight | 2008 | Action | 533 | 152 |
| 7. Star Wars Episode I: The Phantom Menace | 1999 | Adventure | 475 | 133 |
| 8. Star Wars Episode IV: A New Hope | 1977 | Adventure | 461 | 119 |
| 9. Avengers: Age of Ultron | 2015 | Action | 459 | 141 |
| 10. The Dark Knight | 2012 | Action | 448 | 164 |
Concept Involved:
There are various methods of collecting information by sampling. Once the information has been collected, the collection is called a data set. Variables can be divided into two types: qualitative and quantitative. Qualitative variables are also called categorical variable, classify individuals into categories. Quantitative variables are numerical and tell how much of something there is.
Qualitative variables come in two types: ordinal variables and nominal variables.
Ordinal variables are qualitative variables whose categories have a natural ordering.
Nominal variables are qualitative variables whose categories have no natural ordering.
Quantitative variables can be either discrete or continuous.
Discrete variables are those whose possible values can be listed. Often, discrete variables result from counting something, so the possible values of the variable are 0, 1, 2 and so forth.
Continuous variables can, in principle, take on any value within some interval.
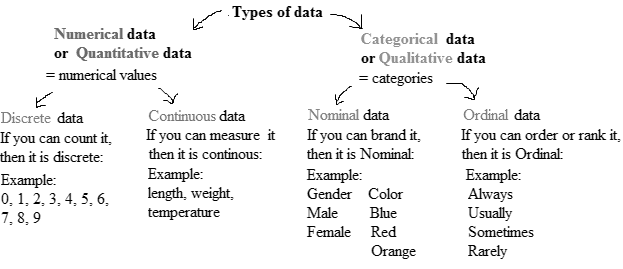
The variable which classifies individuals into categories is called qualitative variable, and the variable which provide information about quantity or number of something is quantitative variable. The Movie Title and Genre classifies the top grossing movies of all time.
Therefore, the columns Movie Title and Genre represent qualitative variables.
b.
To identify:the columns that represent quantitative variables.
Answer to Problem 48E
The columns Ticket Sales (millions of $) and Running Time (minutes) represent quantitative variables.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
| Movie Title | Release Year | Genre | Ticket Sales (millions of $) | Running Time (minutes) |
| 1. Star Wars Episode VII: The Force Awakens | 2015 | Adventure | 936 | 136 |
| 2. Avatars | 2009 | Action | 761 | 162 |
| 3. Titanic | 1997 | Historical Fiction | 659 | 194 |
| 4. Jurassic World | 2015 | Action | 652 | 124 |
| 5. The Avengers | 2012 | Adventure | 623 | 143 |
| 6. The Dark Knight | 2008 | Action | 533 | 152 |
| 7. Star Wars Episode I: The Phantom Menace | 1999 | Adventure | 475 | 133 |
| 8. Star Wars Episode IV: A New Hope | 1977 | Adventure | 461 | 119 |
| 9. Avengers: Age of Ultron | 2015 | Action | 459 | 141 |
| 10. The Dark Knight | 2012 | Action | 448 | 164 |
Concept Involved:
There are various methods of collecting information by sampling. Once the information has been collected, the collection is called a data set. Variables can be divided into two types: qualitative and quantitative. Qualitative variables are also called categorical variable, classify individuals into categories. Quantitative variables are numerical and tell how much of something there is.
Qualitative variables come in two types: ordinal variables and nominal variables.
Ordinal variables are qualitative variables whose categories have a natural ordering.
Nominal variables are qualitative variables whose categories have no natural ordering.
Quantitative variables can be either discrete or continuous.
Discrete variables are those whose possible values can be listed. Often, discrete variables result from counting something, so the possible values of the variable are 0, 1, 2 and so forth.
Continuous variables can, in principle, take on any value within some interval.
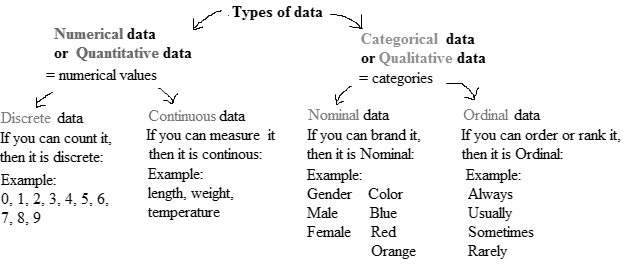
The variable which classifies individuals into categories is called qualitative variable, and the variable which provide information about quantity or number of something is quantitative variable. The Tickets Sales (millions of $) and Running Time (minutes) represent how many of something of there is present.
Therefore, these columns represents quantitative variable.
c.
To identify:the columns that represent nominal variables.
Answer to Problem 48E
The columns Genre represent nominal variables.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
| Movie Title | Release Year | Genre | Ticket Sales (millions of $) | Running Time (minutes) |
| 1. Star Wars Episode VII: The Force Awakens | 2015 | Adventure | 936 | 136 |
| 2. Avatars | 2009 | Action | 761 | 162 |
| 3. Titanic | 1997 | Historical Fiction | 659 | 194 |
| 4. Jurassic World | 2015 | Action | 652 | 124 |
| 5. The Avengers | 2012 | Adventure | 623 | 143 |
| 6. The Dark Knight | 2008 | Action | 533 | 152 |
| 7. Star Wars Episode I: The Phantom Menace | 1999 | Adventure | 475 | 133 |
| 8. Star Wars Episode IV: A New Hope | 1977 | Adventure | 461 | 119 |
| 9. Avengers: Age of Ultron | 2015 | Action | 459 | 141 |
| 10. The Dark Knight | 2012 | Action | 448 | 164 |
Concept Involved:
There are various methods of collecting information by sampling. Once the information has been collected, the collection is called a data set. Variables can be divided into two types: qualitative and quantitative. Qualitative variables are also called categorical variable, classify individuals into categories. Quantitative variables are numerical and tell how much of something there is.
Qualitative variables come in two types: ordinal variables and nominal variables.
Ordinal variables are qualitative variables whose categories have a natural ordering.
Nominal variables are qualitative variables whose categories have no natural ordering.
Quantitative variables can be either discrete or continuous.
Discrete variables are those whose possible values can be listed. Often, discrete variables result from counting something, so the possible values of the variable are 0, 1, 2 and so forth.
Continuous variables can, in principle, take on any value within some interval.
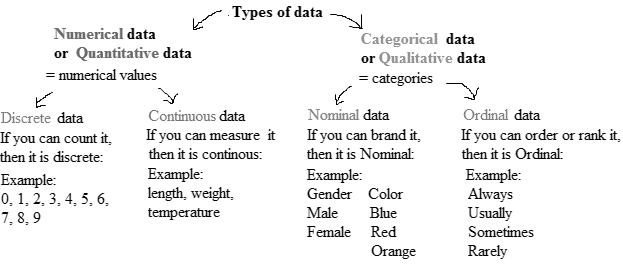
The values are classified into categories in a nominal variable, but no natural ordering is there in categories, whereas, the values are also classified into categories in an ordinary variable but a natural ordering is there in categories.
Therefore, the Genre column has categories but doesn’t have natural ordering.
d.
To identify:the columns that represent ordinal variables.
Answer to Problem 48E
The column Movie Title represent ordinal variables.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
| Movie Title | Release Year | Genre | Ticket Sales (millions of $) | Running Time (minutes) |
| 1. Star Wars Episode VII: The Force Awakens | 2015 | Adventure | 936 | 136 |
| 2. Avatars | 2009 | Action | 761 | 162 |
| 3. Titanic | 1997 | Historical Fiction | 659 | 194 |
| 4. Jurassic World | 2015 | Action | 652 | 124 |
| 5. The Avengers | 2012 | Adventure | 623 | 143 |
| 6. The Dark Knight | 2008 | Action | 533 | 152 |
| 7. Star Wars Episode I: The Phantom Menace | 1999 | Adventure | 475 | 133 |
| 8. Star Wars Episode IV: A New Hope | 1977 | Adventure | 461 | 119 |
| 9. Avengers: Age of Ultron | 2015 | Action | 459 | 141 |
| 10. The Dark Knight | 2012 | Action | 448 | 164 |
Concept Involved:
There are various methods of collecting information by sampling. Once the information has been collected, the collection is called a data set. Variables can be divided into two types: qualitative and quantitative. Qualitative variables are also called categorical variable, classify individuals into categories. Quantitative variables are numerical and tell how much of something there is.
Qualitative variables come in two types: ordinal variables and nominal variables.
Ordinal variables are qualitative variables whose categories have a natural ordering.
Nominal variables are qualitative variables whose categories have no natural ordering.
Quantitative variables can be either discrete or continuous.
Discrete variables are those whose possible values can be listed. Often, discrete variables result from counting something, so the possible values of the variable are 0, 1, 2 and so forth.
Continuous variables can, in principle, take on any value within some interval.
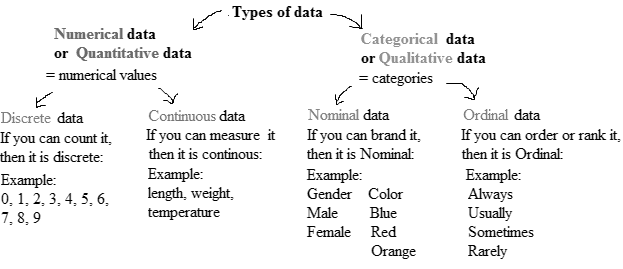
The values are classified into categories in a nominal variable, but no natural ordering is there in categories, whereas, the values are also classified into categories in an ordinary variable but a natural ordering is there in categories. The variable movie title classifies the top grossing movies of all time.
Therefore, column Movie Title represents ordinal variables.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
ELEMENTARY STATISTICS-ALEKS ACCESS CODE
- At the same restaurant as in Question 19 with the same normal distribution, what's the chance of it taking no more than 15 minutes to get service?arrow_forwardClint, obviously not in college, sleeps an average of 8 hours per night with a standard deviation of 15 minutes. What's the chance of him sleeping between 7.5 and 8.5 hours on any given night? 0-(7-0) 200 91109s and doiw $20 (8-0) mol 8520 slang $199 galbrog seam side pide & D (newid se od poyesvig as PELEO PER AFTE editiw noudab temand van Czarrow_forwardTimes to complete a statistics exam have a normal distribution with a mean of 40 minutes and standard deviation of 6 minutes. Deshawn's time comes in at the 90th percentile. What percentage of the students are still working on their exams when Deshawn leaves?arrow_forward
- Suppose that the weights of cereal boxes have a normal distribution with a mean of 20 ounces and standard deviation of half an ounce. A box that has a standard score of o weighs how much? syed by ilog ni 21arrow_forwardBob scores 80 on both his math exam (which has a mean of 70 and standard deviation of 10) and his English exam (which has a mean of 85 and standard deviation of 5). Find and interpret Bob's Z-scores on both exams to let him know which exam (if either) he did bet- ter on. Don't, however, let his parents know; let them think he's just as good at both subjects. algas 70) sering digarrow_forwardSue's math class exam has a mean of 70 with a standard deviation of 5. Her standard score is-2. What's her original exam score?arrow_forward
- Clint sleeps an average of 8 hours per night with a standard deviation of 15 minutes. What's the chance he will sleep less than 7.5 hours tonight? nut bow visarrow_forwardSuppose that your score on an exam is directly at the mean. What's your standard score?arrow_forwardOne state's annual rainfall has a normal dis- tribution with a mean of 100 inches and standard deviation of 25 inches. Suppose that corn grows best when the annual rainfall is between 100 and 150 inches. What's the chance of achieving this amount of rainfall? wved now of sociarrow_forward
- 13 Suppose that your exam score has a standard score of 0.90. Does this mean that 90 percent of the other exam scores are lower than yours?arrow_forwardBob's commuting times to work have a nor- mal distribution with a mean of 45 minutes and standard deviation of 10 minutes. How often does Bob get to work in 30 to 45 minutes?arrow_forwardBob's commuting times to work have a nor- mal distribution with a mean of 45 minutes and standard deviation of 10 minutes. a. What percentage of the time does Bob get to work in 30 minutes or less? b. Bob's workday starts at 9 a.m. If he leaves at 8 a.m., how often is he late?arrow_forward
 Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305071742Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305071742Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning College AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305115545Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
College AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305115545Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning





