
Concept explainers
Top ten video games: According to Wikipedia, the following are the top ten selling video games of all time.
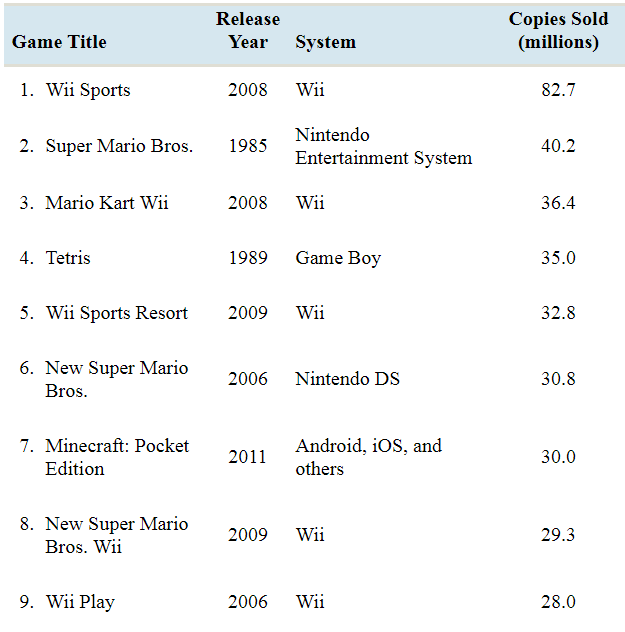
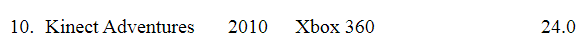
- Which of the columns represent qualitative variables?
- Which of the columns represent quantitative variables?
- Which of the columns represent nominal variables?
- Which of the columns represent ordinal variables?
a.
To identify:the columns that represent qualitative variables.
Answer to Problem 47E
The columns Game Title and System represent qualitative variables.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
| Game Title | Release Year | System | Copies Sold (millions) |
| 1. 1. Wii Sports | 2008 | Wii | 82.7 |
| 2. 2. Super Mario Bros. | 1985 | Nintendo Entertainment System | 40.2 |
| 3. 3. Mario Kart Wii | 2008 | Wii | 36.4 |
| 4. 4. Tetris | 1989 | Game Boy | 35.0 |
| 5. 5. Wii Sports Resort | 2009 | Wii | 32.8 |
| 6. 6. New Super Mario Bros | 2006 | Nintendo DS | 30.8 |
| 7. 7. Minecraft: Pocket Edition | 2011 | Android, iOS, and others | 30.0 |
| 8. 8. New Super Mario Bros. Wii | 2009 | Wii | 29.3 |
| 9. 9. Wii Play | 2006 | Wii | 28.0 |
| 10. 10. Kinect Adventures | 2010 | Xbox 360 | 24.0 |
Concept Involved:
There are various methods of collecting information by sampling. Once the information has been collected, the collection is called a data set. Variables can be divided into two types: qualitative and quantitative. Qualitative variables are also called categorical variable, classify individuals into categories. Quantitative variables are numerical and tell how much of something there is.
Qualitative variables come in two types: ordinal variables and nominal variables.
Ordinal variables are qualitative variables whose categories have a natural ordering.
Nominal variables are qualitative variables whose categories have no natural ordering.
Quantitative variables can be either discrete or continuous.
Discrete variables are those whose possible values can be listed. Often, discrete variables result from counting something, so the possible values of the variable are 0, 1, 2 and so forth.
Continuous variables can, in principle, take on any value within some interval.
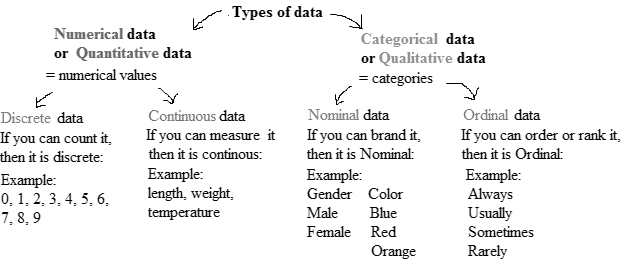
The variable which classifies individuals into categories is called qualitative variable, and the variable which provide information about quantity or number of something is quantitative variable. The Game Title and System classifies the top ten selling video games of all time.
Therefore, the columns Game Title and System represent qualitative variables.
b.
To identify:the columns that represent quantitative variables.
Answer to Problem 47E
The columns Copies sold (millions) represent quantitative variables.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
| Game Title | Release Year | System | Copies Sold (millions) |
| 1. Wii Sports | 2008 | Wii | 82.7 |
| 2. Super Mario Bros. | 1985 | Nintendo Entertainment System | 40.2 |
| 3. Mario Kart Wii | 2008 | Wii | 36.4 |
| 4. Tetris | 1989 | Game Boy | 35.0 |
| 5. Wii Sports Resort | 2009 | Wii | 32.8 |
| 6. New Super Mario Bros | 2006 | Nintendo DS | 30.8 |
| 7. Minecraft: Pocket Edition | 2011 | Android, iOS, and others | 30.0 |
| 8. New Super Mario Bros. Wii | 2009 | Wii | 29.3 |
| 9. Wii Play | 2006 | Wii | 28.0 |
| 10. Kinect Adventures | 2010 | Xbox 360 | 24.0 |
Concept Involved:
There are various methods of collecting information by sampling. Once the information has been collected, the collection is called a data set. Variables can be divided into two types: qualitative and quantitative. Qualitative variables are also called categorical variable, classify individuals into categories. Quantitative variables are numerical and tell how much of something there is.
Qualitative variables come in two types: ordinal variables and nominal variables.
Ordinal variables are qualitative variables whose categories have a natural ordering.
Nominal variables are qualitative variables whose categories have no natural ordering.
Quantitative variables can be either discrete or continuous.
Discrete variables are those whose possible values can be listed. Often, discrete variables result from counting something, so the possible values of the variable are 0, 1, 2 and so forth.
Continuous variables can, in principle, take on any value within some interval.
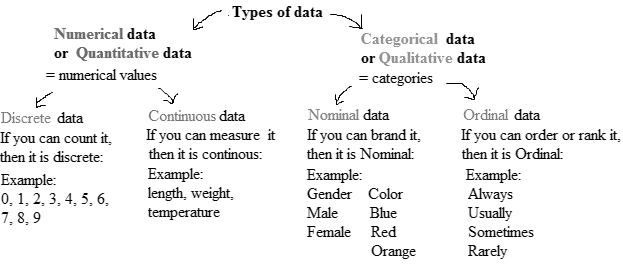
The variable which classifies individuals into categories is called qualitative variable, and the variable which provide information about quantity or number of something is quantitative variable. The column copies sold (in millions) represent how many of something is there.
Therefore, it represents quantitative variable.
c.
To identify:the columns that represent nominal variables.
Answer to Problem 47E
The columns System represent nominal variables.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
| Game Title | Release Year | System | Copies Sold (millions) |
| 1. Wii Sports | 2008 | Wii | 82.7 |
| 2. Super Mario Bros. | 1985 | Nintendo Entertainment System | 40.2 |
| 3. Mario Kart Wii | 2008 | Wii | 36.4 |
| 4. Tetris | 1989 | Game Boy | 35.0 |
| 5. Wii Sports Resort | 2009 | Wii | 32.8 |
| 6. New Super Mario Bros | 2006 | Nintendo DS | 30.8 |
| 7. Minecraft: Pocket Edition | 2011 | Android, iOS, and others | 30.0 |
| 8. New Super Mario Bros. Wii | 2009 | Wii | 29.3 |
| 9. Wii Play | 2006 | Wii | 28.0 |
| 10. Kinect Adventures | 2010 | Xbox 360 | 24.0 |
Concept Involved:
There are various methods of collecting information by sampling. Once the information has been collected, the collection is called a data set. Variables can be divided into two types: qualitative and quantitative. Qualitative variables are also called categorical variable, classify individuals into categories. Quantitative variables are numerical and tell how much of something there is.
Qualitative variables come in two types: ordinal variables and nominal variables.
Ordinal variables are qualitative variables whose categories have a natural ordering.
Nominal variables are qualitative variables whose categories have no natural ordering.
Quantitative variables can be either discrete or continuous.
Discrete variables are those whose possible values can be listed. Often, discrete variables result from counting something, so the possible values of the variable are 0, 1, 2 and so forth.
Continuous variables can, in principle, take on any value within some interval.
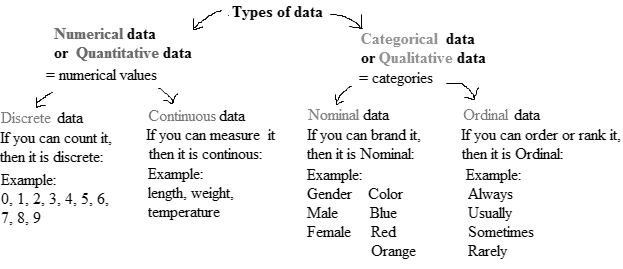
The values are classified into categories in a nominal variable, but no natural ordering is there in categories, whereas, the values are also classified into categories in an ordinary variable but a natural ordering is there in categories.
Therefore, the columns system represents nominal variables.
d.
To identify:the columns that represent ordinal variables.
Answer to Problem 47E
The columns Game Title represent ordinal variables.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
| Game Title | Release Year | System | Copies Sold (millions) |
| 1. Wii Sports | 2008 | Wii | 82.7 |
| 2. Super Mario Bros. | 1985 | Nintendo Entertainment System | 40.2 |
| 3. Mario Kart Wii | 2008 | Wii | 36.4 |
| 4. Tetris | 1989 | Game Boy | 35.0 |
| 5. Wii Sports Resort | 2009 | Wii | 32.8 |
| 6. New Super Mario Bros | 2006 | Nintendo DS | 30.8 |
| 7. Minecraft: Pocket Edition | 2011 | Android, iOS, and others | 30.0 |
| 8. New Super Mario Bros. Wii | 2009 | Wii | 29.3 |
| 9. Wii Play | 2006 | Wii | 28.0 |
| 10. Kinect Adventures | 2010 | Xbox 360 | 24.0 |
Concept Involved:
There are various methods of collecting information by sampling. Once the information has been collected, the collection is called a data set. Variables can be divided into two types: qualitative and quantitative. Qualitative variables are also called categorical variable, classify individuals into categories. Quantitative variables are numerical and tell how much of something there is.
Qualitative variables come in two types: ordinal variables and nominal variables.
Ordinal variables are qualitative variables whose categories have a natural ordering.
Nominal variables are qualitative variables whose categories have no natural ordering.
Quantitative variables can be either discrete or continuous.
Discrete variables are those whose possible values can be listed. Often, discrete variables result from counting something, so the possible values of the variable are 0, 1, 2 and so forth.
Continuous variables can, in principle, take on any value within some interval.
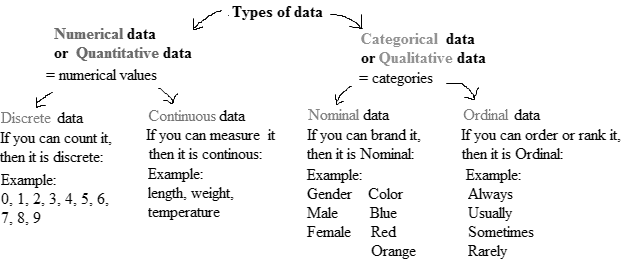
The values are classified into categories in a nominal variable, but no natural ordering is there in categories, whereas, the values are also classified into categories in an ordinary variable but a natural ordering is there in categories.The variable game title classifies the top ten selling video games.
Therefore, column Game Title represents ordinal variables.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
Loose Leaf Version For Elementary Statistics
- Can you help me understand this analysis? A 95.7% confidence interval is shown for the intention-to-treat analysis (accounting for alpha spending in interim analyses), and 95% confidence intervals are shown for the other two analyses. The widths of the confidence intervals have not been adjusted for multiplicity. The dashed line indicates the noninferiority margin of 4 percentage points.arrow_forwardTitle: Analyzing Customer Satisfaction for UnileverAs a member of Unilever's Customer Experience Management team, you are responsible forevaluating customer satisfaction levels and monitoring competitive moves. This case studyinvolves analyzing satisfaction data to test two key hypotheses about Unilever's performancerelative to its main competitor, Procter & Gamble (P&G).Unilever’s leadership team has emphasized the importance of customer satisfaction inmaintaining competitive advantage and market leadership. As part of this initiative, yourteam regularly monitors satisfaction scores and benchmarks them against competitors likeP&G.You are tasked with analyzing the provided dataset to answer the following questions:1. Does Unilever’s average customer satisfaction score meet the minimum threshold of2. 75%?Is there no significant difference between Unilever’s overall average satisfaction scoreand P&G’s average satisfaction score?arrow_forwardNeed help answering wuestionarrow_forward
- The following table shows a data set containing information for 25 of the shadow stocks tracked by the American Association of Individual Investors (aaii.com, February 2002). Shadow stocks are common stocks of smaller companies that are not closely followed by Wall Street analysts. Click on the datafile logo to reference the data. DATA file Company DeWolfe Companies Exchange Ticker Symbol Market Cap ($ millions) Price/ Gross Profit Earnings Ratio Margin (%) AMEX DWL 36.4 8.4 36.7 North Coast Energy OTC NCEB 52.5 6.2 59.3 Hansen Natural Corp. OTC HANS 41.1 14.6 44.8 MarineMax, Inc. NYSE HZO 111.5 7.2 23.8 Nanometrics Incorporated OTC NANO 228.6 38.0 53.3 TeamStaff, Inc. OTC TSTF 92.1 33.5 4.1 Environmental Tectonics AMEX ETC 51.1 35.8 35.9 Measurement Specialties AMEX MSS 101.8 26.8 37.6 SEMCO Energy, Inc. NYSE SEN 193.4 18.7 23.6 Party City Corporation OTC PCTY 97.2 15.9 36.4 Embrex, Inc. OTC EMBX 136.5 18.9 59.5 Tech/Ops Sevcon, Inc. AMEX ΤΟ 23.2 20.7 35.7 ARCADIS NV OTC ARCAF 173.4…arrow_forwardThe following table shows a data set containing information for 25 of the shadow stocks tracked by the American Association of Individual Investors (aaii.com, February 2002). Shadow stocks are common stocks of smaller companies that are not closely followed by Wall Street analysts. Click on the datafile logo to reference the data. DATA file Company DeWolfe Companies Exchange AMEX Ticker Symbol Market Cap Price/ Gross Profit Earnings Margin ($ millions) Ratio (%) DWL 36.4 8.4 36.7 North Coast Energy OTC NCEB 52.5 6.2 59.3 Hansen Natural Corp. OTC HANS 41.1 14.6 44.8 MarineMax, Inc. NYSE HZO 111.5 7.2 23.8 Nanometrics Incorporated OTC NANO 228.6 38.0 53.3 TeamStaff, Inc. OTC TSTF 92.1 33.5 4.1 Environmental Tectonics AMEX ETC 51.1 35.8 35.9 Measurement Specialties AMEX MSS 101.8 26.8 37.6 SEMCO Energy, Inc. NYSE SEN 193.4 18.7 23.6 Party City Corporation OTC PCTY 97.2 15.9 36.4 Embrex, Inc. OTC EMBX 136.5 18.9 59.5 Tech/Ops Sevcon, Inc. AMEX ΤΟ 23.2 20.7 35.7 ARCADIS NV OTC ARCAF 173.4…arrow_forwardThe following data show the year to date percent change (YTD % Change) for 30 stock-market indexes from around the word (The Wall Street Journal, August 26, 2013). a. What index has the largest positive YTD % Change? Round your answer to once decimal place. index with a YTD % Change of % b. Using a class width of 5 beginning with -20 and going to 40, develop a frequency distribution for the data. YTD % Change Frequency -20 - -15 -15 - -10 -10 - -5 -5 - 0 0 - 5 5 - 10 10 - 15 15 - 20 20 - 25 30 - 35 c. 1. 2. 3. 4.arrow_forward
- The following data show the year to date percent change (YTD % Change) for 30 stock-market indexes from around the word (The Wall Street Journal, August 26, 2013). Click on the datafile logo to reference the data. DATA file Country Australia Index S&P/ASX200 YTD % Change 10.2 Belgium Bel-20 12.6 Brazil São Paulo Bovespa -14.4 Canada S&P/TSX Comp 2.6 Chile Santiago IPSA -16.3 China Shanghai Composite -9.3 Eurozone EURO Stoxx 10.0 France CAC 40 11.8 Germany DAX 10.6 Hong Kong Hang Seng -3.5 India S&P BSE Sensex -4.7 Israel Tel Aviv 1.3 Italy FTSE MIB 6.6 Japan Nikkei 31.4 Mexico IPC All-Share -6.4 Netherlands AEX 9.3 Singapore Straits Times -2.5 South Korea Kospi -6.4 Spain IBEX 35 6.4 Sweden Switzerland SX All Share 13.8 Swiss Market 17.4 Taiwan Weighted 2.3 U.K. FTSE 100 10.1 U.S. S&P 500 16.6 U.S. DJIA 14.5 U.S. Dow Jones Utility 6.6 U.S. Nasdaq 100 17.4 U.S. Nasdaq Composite 21.1 World DJ Global ex U.S. 4.2 World DJ Global Index 9.9 a. What index has the largest positive YTD %…arrow_forwardDescribe a three step process you choose to determine how many elementary schools there are in the city of 5 million people.arrow_forwardQuiz: Exam 1 (Ch 1-4) z Scores Table-3.pdf x + edu/courses/308627/quizzes/2442507/take/questions/48957332 Canvas Hall It browser 5 Connect Set as default incorrect. • This exam is NOT resumable. Meaning, once you start the exam, you must complete it in its entirety. Any blank questions will be marked as By taking this exam, you agree to adhere to the academic integrity standards, which consist of NOT cheating in any way. To get the highest possible score, you are encouraged to review your notes before taking the exam. You may use your notes during the exam, but note that you should be familiar with the concepts and formulas before taking exam. z Scores Table.pdf Question 3 3 pts Here is a data from a survey asking young children how many hours they spend playing video games. The researchers reported the percent of boys and girls who played no games, less than 1 hour per day, 1-3 hours per day, or greater than 3 hours per day. The most common number of hours per day that boys played is…arrow_forward
- Write a Regression summary explaining significance of mode, explaining regression coefficients, significance of the independent variables, R and R square. Premiums earned Net income Dividends Underwriting Gain/ Loss 30.2 1.6 0.6 0.1 47.2 0.6 0.7 -3.6 92.8 8.4 1.8 -1.5 95.4 7.6 2 -4 100.4 6.3 2.2 -8.1 104.9 6.3 2.4 -10.8 113.2 2.2 2.3 -18.2 130.3 3.0 2.4 -21.4 161.9 13.5 2.3 -12.8 182.5 14.9 2.9 -5.9 193.3 11.7 2.9 -7.6arrow_forward1- Let A = {A1, A2, ...), in which A, A, = 0, when i j. a) Is A a π-system? If not, which element(s) should be added to A to become a π-system? b) Prove that σ(A) consists of the finite or countable unions of elements of A; i.c., A E σ(A) if and only if there exists finite or countable sequence {n} such that A = U₁An (Hint: Let F be such class; prove that F is a σ-filed containing A.) c) Let p ≥ 0 be a sequence of non-negative real numbers with Σip₁ = 1. Using p₁'s, how do you construct a probability measure on σ(A)? (Hint: use extension theorem.) 2- Construct an example for which P(lim sup A,) = 1 and P(lim inf An) = 0.arrow_forwardIn a town with 5000 adults, a sample of 50 is selected using SRSWOR and asked their opinion of a proposed municipal project; 30 are found to favor it and 20 oppose it. If, in fact, the adults of the town were equally divided on the proposal, what would be the probability of observing what has been observed? Approximate using the Binomial distribution. Compare this with the exact probability which is 0.0418.arrow_forward
 Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell
Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell





