
Analyze Performance Report for Decentralized Organization
Hall O’ Fame Products is a nationwide sporting goods manufacturer. The company operates with a widely based manufacturing and distribution system that has led to a highly decentralized management structure. Each division manager is responsible for producing and distributing corporate products in one of eight geographical areas of the country.
Division managers are evaluated using a performance measure that is calculated as the division’s contribution to corporate profits before taxes less a 20 percent investment charge on the division’s investment base. The investment base of each division is the sum of its year-end balances of
James Davenport, division manager for the California sector, prepared the year 2 and preliminary year 3 budgets for his division late in year 1. Final approval of the year 3 budget took place in late year 2 after adjustments for trends and other information developed during year 2. Preliminary work on the year 4 budget also took place at that time. In early October of year 3, Davenport asked the division controller to prepare a report that presents performance for the first nine months of year 3. The report follows:
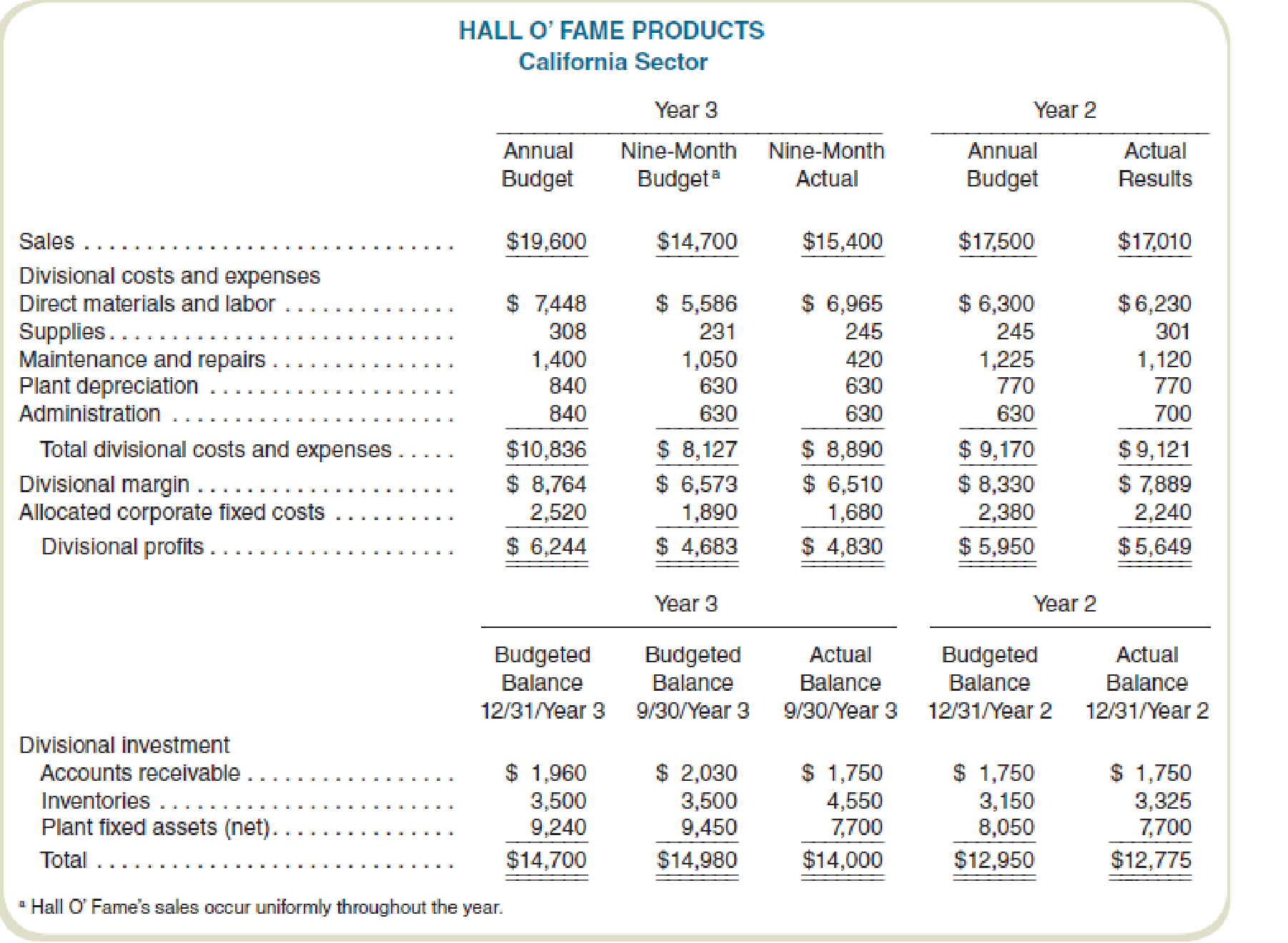
Required
- a. Evaluate the performance of James Davenport for the nine months ending September 30, year 3. Support your evaluation with pertinent facts from the problem.
- b. Identify the features of Hall O’ Fame’s division performance measurement reporting and evaluation system that need to be revised if it is to effectively reflect the responsibilities of the divisional managers.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 12 Solutions
Fundamentals Of Cost Accounting (6th Edition)
- CAL Ltd. sold $6,700,000 of 10% bonds, which were dated March 1, 2023, on June 1, 2023. The bonds paid interest on September 1 and March 1 of each year. The bonds' maturity date was March 1, 2033, and the bonds were issued to yield 12%. CAL's fiscal year-end was February 28, and the company followed IFRS. On June 1, 2024, CAL bought back $2,700,000 worth of bonds for $2,600,000 plus accrued interest. (a) Using 1. a financial calculator, or 2. Excel function PV, calculate the issue price of the bonds and prepare the entry for the issuance of the bonds. Hint: Use the account Interest Expense in your entry). there are 3 entries to be made herearrow_forwardDon't use ai to answer I will report you answerarrow_forward1. Stampede Company has two service departments — purchasing and maintenance, and two production departments — fabrication and assembly. The distribution of each service department's efforts to the other departments is shown below: FROM TO Purchasing Maintenance Fabrication Assembly Purchasing 0% 45% 45% 10% Maintenance 55% 0% 30% 15% The direct operating costs of the departments (including both variable and fixed costs) were as follows: Purchasing $ 138,000 Maintenance 60,000 Fabrication 114,000 Assembly 90,000 The total cost accumulated in the fabrication department using the direct method is: The answer is not 194100 2. Bifurcator Company produces three products — X, Y, and Z — from a joint process. Each product may be sold at the split-off point or processed further. Additional processing requires no special facilities, and production costs of further processing are entirely variable and traceable to the products involved. Last year all three products were…arrow_forward
- General accounting question please solvearrow_forwardDue Jan 26 11:59pm Module 2 Discussion Provide and discuss an example of a situation where a company would use a job cost sheet. As part of your analysis, be sure to explain the nature and importance of a job cost sheet. or Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of Job Order Costing. Be sure to include specific examples of the advantages/disadvantages that you discuss. 21 Replies, 18arrow_forwardNonearrow_forward
- Abcarrow_forwardchoose 4 nuber from 1 to 5 with repetitions allowed to create the largest standard deviation posiiblearrow_forward1. Stampede Company has two service departments — purchasing and maintenance, and two production departments — fabrication and assembly. The distribution of each service department's efforts to the other departments is shown below: FROM TO Purchasing Maintenance Fabrication Assembly Purchasing 0% 45% 45% 10% Maintenance 55% 0% 30% 15% The direct operating costs of the departments (including both variable and fixed costs) were as follows: Purchasing $ 138,000 Maintenance 60,000 Fabrication 114,000 Assembly 90,000 The total cost accumulated in the fabrication department using the direct method is: 2. Bifurcator Company produces three products — X, Y, and Z — from a joint process. Each product may be sold at the split-off point or processed further. Additional processing requires no special facilities, and production costs of further processing are entirely variable and traceable to the products involved. Last year all three products were processed beyond…arrow_forward
- Principles of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning  Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,



