
Ondi Airlines is interested in acquiring a new aircraft to service a new route. The route will be from Tulsa to Denver. The aircraft will fly one round-trip daily except for scheduled maintenance days. There are 15 maintenance days scheduled each year. The seating capacity of the aircraft is 150. Flights are expected to be fully booked. The average revenue per passenger per flight (one-way) is $235. Annual operating costs of the aircraft follow:
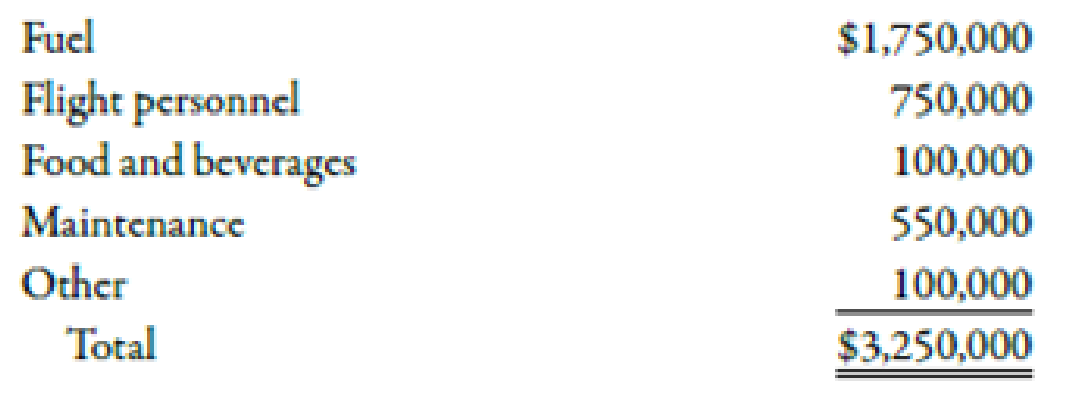
The aircraft will cost $120,000,000 and has an expected life of 20 years. The company requires a 12% return. Assume there are no income taxes.
Required:
- 1. Calculate the NPV for the aircraft. Should the company buy it?
- 2. In discussing the proposal, the marketing manager for the airline believes that the assumption of 100% booking is unrealistic. He believes that the booking rate will be somewhere between 70 and 90%, with the most likely rate being 80%. Recalculate the NPV by using an 80% seating capacity. Should the aircraft be purchased?
- 3. Calculate the average seating rate that would be needed so that NPV will equal zero. Round the seating rate to the nearest percent.
- 4. CONCEPTUAL CONNECTION Suppose that the price per passenger could be increased by 10% without any effect on demand. What is the average seating rate now needed to achieve an NPV equal to zero? What would you now recommend? Round the seating rate to the nearest percent.
1.
Find out the NPV of the aircraft. Also, recommend that the company should buy it or not.
Explanation of Solution
Net Present Value:
The remaining balance of the present value of a project’s inflows and outflows is known as net present value (NPV). It is a discounting model of capital investment decision. A project with a positive NPV increases the wealth of a firm whereas a project with a negative NPV decreases the wealth of a firm.
Use the following formula to calculate NPV of the investment:
Substitute $160,032,7521 for P and $120,000,000 for I in the above formula.
Therefore, net present value of the investment is $40,032,752.
The company should buy the aircraft because NPV is positive.
Working Note:
1. Calculation of expected cash flow:
Calculation of days of operation:
Calculation of revenue per year:
Calculation of annual cash flow:
Calculation of present value of future cash flow:
2.
Find out the NPV of the aircraft if the booking is 80% of seating capacity.
Explanation of Solution
Use the following formula to calculate NPV of the investment:
Substitute $123,171,0662 for P and $120,000,000 for I in the above formula.
Therefore, net present value of the investment is $3,171,066.
The company should buy the aircraft because NPV is positive.
Working Note:
2. Calculation of revised annual cash flow:
Calculation of present value of future cash flow:
3.
Calculate the seating rate at which NPV will equal zero.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate seating rate:
Use the following formula to calculate seats to be sold:
Substitute $55,1873 for revenue per day and $470 for revenue per seat in the above formula.
Therefore, seats to be sold in each trip are 118 seats.
Calculate seating rate:
Use the following formula to calculate the seating rate:
Substitute 118 seats for seats to be sold and 150 seats for total seats in the above formula.
Working Note:
3. Calculation of annual cash flow at which NPV equals 0:
Calculation of annual revenue:
Calculation of revenue per day:
4.
Calculate the seating rate at which NPV will equal zero and the price per passenger is increased by 10%. Also state the recommendations.
Explanation of Solution
Use the following formula to calculate seats to be sold:
Substitute $55,1873 for revenue per day and $5174 for revenue per seat in the above formula.
Therefore, seats to be sold in each trip are 107 seats.
Calculate seating rate:
Use the following formula to calculate the seating rate:
Substitute 107 seats for seats to be sold and 150 seats for total seats in the above formula.
The seating will be between 70% and 90% of the total seating. There is a possibility that the actual seating rate can be lower than the estimated rate. The interval is of 20% and it is most likely that NPV remain positive.
These analyses are drafted with the assumption that all the factors are constant. However, the price of the factors can change during the course of the useful of the aircraft.
Working Note:
4. Calculation of round trip average price:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Cengagenowv2, 1 Term Printed Access Card For Mowen/hansen/heitger?s Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone Of Business Decision-making, 7th
 Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENTPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENTPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning





