PHYS 212 FOR SCI+ENG W/MAST PHYS >ICP<
1st Edition
ISBN: 9781323834831
Author: Knight
Publisher: PEARSON C
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 12, Problem 42EAP
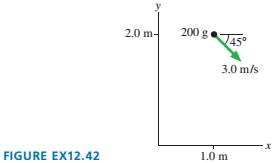
What are the magnitude and direction of the
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
l
No chatgpt pls will upvote Already got wrong chatgpt answer
No chatgpt pls
Chapter 12 Solutions
PHYS 212 FOR SCI+ENG W/MAST PHYS >ICP<
Ch. 12 - Prob. 1CQCh. 12 - If the angular velocity w is held constant, by...Ch. 12 - FIGURE Q12.3 shows three rotating disks, all of...Ch. 12 - 4. Must an object be rotating to have a moment of...Ch. 12 - 5. The moment of inertia of a uniform rod about an...Ch. 12 - 6. You have two solid steel spheres. Sphere 2 has...Ch. 12 - The professor hands you two spheres. They have the...Ch. 12 - Six forces are applied to the door in FIGURE...Ch. 12 - Prob. 9CQCh. 12 - Rank in order, from largest to smallest, the...
Ch. 12 - The solid cylinder and cylindrical shell in FIGURE...Ch. 12 - A diver in the pike position (legs straight, hands...Ch. 12 - Prob. 13CQCh. 12 - A high-speed drill reaches 2000 rpm in 0.50 s. a....Ch. 12 - A skater holds her arms outstretched as she spins...Ch. 12 - A ceiling fan with 80-cm-diameter blades is...Ch. 12 - An 18-cm-long bicycle crank arm, with a pedal at...Ch. 12 - Prob. 5EAPCh. 12 - The three masses shown in FIGURE EX12.6 are...Ch. 12 - The three masses shown in FIGURE EX12.7 are...Ch. 12 - A 100 g ball and a 200 g ball are connected by a...Ch. 12 - A thin, 100 g disk with a diameter of 8.0 cm...Ch. 12 - What is the rotational kinetic energy of the...Ch. 12 - The three200g masses in FIGURE EX12.11 are...Ch. 12 - A drum major twirls a 96-cm-long, 400 g baton...Ch. 12 - The four masses shown in FIGURE EX12.13 are...Ch. 12 - The four masses shown in FIGURE EXI2.13 are...Ch. 12 - The three masses shown in FIGURE EXI2.15 are...Ch. 12 - A 12-cm-diameter CD has a mass of 21 g. What is...Ch. 12 - A 25 kg solid door is 220 cm tall, 91 cm wide....Ch. 12 - Prob. 18EAPCh. 12 - In FIGURE EX12.19, what magnitude force provides...Ch. 12 - The 20-cm-diameter disk in FIGURE EX12.20 can...Ch. 12 - The axle in FIGURE EXI2.21 is half the distance...Ch. 12 - A 4.0-rn-long, 500 kg steel beam extends...Ch. 12 - An athlete at the gym holds a 3.0 kg steel ball in...Ch. 12 - An object’s moment of inertia is 2.0 kg m2. Its...Ch. 12 - An object whose moment of inertia is 4.0 kg m2...Ch. 12 - A 1.0 kg ball and a 2.0 kg ball are connected by a...Ch. 12 - Starting from rest, a 12-cm-diameter compact disk...Ch. 12 - A 4.0 kg, 36-cm-diameter metal disk, initially at...Ch. 12 - The two objects in FIGURE EXI2.29 are balanced on...Ch. 12 - Prob. 30EAPCh. 12 - The 3.0-rn-long, 100 kg rigid beam of FIGURE...Ch. 12 - A 5.0 kg cat and a 2.0 kg bowl of tuna fish are at...Ch. 12 - A car tire is 60cm in diameter. The car is...Ch. 12 - A 500 g, 8.0-cm-diameter can is filled with...Ch. 12 - Prob. 35EAPCh. 12 - A solid sphere of radius R is placed at a height...Ch. 12 - Prob. 37EAPCh. 12 - Evaluate the cross products AB and CD .Ch. 12 - Prob. 39EAPCh. 12 - Force F=10j N is exerted on a particle at 5i+5j m....Ch. 12 - A 1.3 kg ball on the end of a lightweight rod is...Ch. 12 - What are the magnitude and direction of the...Ch. 12 - What is the angular momentum vector of the 2.0 kg,...Ch. 12 - Prob. 44EAPCh. 12 - Prob. 45EAPCh. 12 - A 2.0 kg, 20-cm-diameter turntable rotates at 100...Ch. 12 - Prob. 47EAPCh. 12 - A toy gyroscope has a ring of mass M and radius R...Ch. 12 - Prob. 49EAPCh. 12 - Prob. 50EAPCh. 12 - Determine the moment of inertia about the axis of...Ch. 12 - What is the moment of inertia of a 2.0 kg,...Ch. 12 - Calculate by direct integration the moment of...Ch. 12 - Calculate the moment of inertia of the rectangular...Ch. 12 - a. A disk of mass M and radius R has a hole of...Ch. 12 - Consider a solid cone of radius R, height H, and...Ch. 12 - Prob. 57EAPCh. 12 - A 3.0-m-long ladder, as shown in Figure 12.35....Ch. 12 - In FIGURE P12.59, an 80 kg construction worker...Ch. 12 - Prob. 60EAPCh. 12 - Prob. 61EAPCh. 12 - A 120-cm-wide sign hangs from a 5.0 kg,...Ch. 12 - Prob. 63EAPCh. 12 - Flywheels are large, massive wheels used to store...Ch. 12 - of mass m1and m2are connected by a massless string...Ch. 12 - The 2.0 kg, 30-cm-diameter disk in FIGURE P12.66...Ch. 12 - A 30-cm-diameter, 1.2 kg solid turntable rotates...Ch. 12 - Your engineering team has been assigned the task...Ch. 12 - A hollow sphere is rolling along a horizontal...Ch. 12 - A 750 g disk and a 760 g ring, both 15 cm in...Ch. 12 - A cylinder of radius R, length L. and mass M is...Ch. 12 - The 5.0 kg, 60-cm-diameter disk in FIGURE P12.72...Ch. 12 - A thin, uniform rod of length L and mass M is...Ch. 12 - A long, thin rod of mass M and length L is...Ch. 12 - The marble rolls down the track shown in FIGURE...Ch. 12 - sThe sphere of mass M and radius R in FIGURE...Ch. 12 - A satellite follows the elliptical orbit shown in...Ch. 12 - A 10 g bullet traveling at 400 m/s strikes a 10...Ch. 12 - A 200 g, 40-cm-diameter turntable rotates on...Ch. 12 - Luc, who is 1.80 m tall and weighs 950 N, is...Ch. 12 - A merry-go-round is a common piece of playground...Ch. 12 - A 45 kg figure skater is spinning on the toes of...Ch. 12 - Prob. 83EAPCh. 12 - The earth’s rotation axis, which is tilted 23.5...Ch. 12 - sThe bunchberry flower has the fastest-moving...Ch. 12 - The two blocks in FIGURE CP12.86 are connected by...Ch. 12 - A rod of length L and mass M has a nonuniform mass...Ch. 12 - In FIGURE CP12.88, a 200 g toy car is placed on a...Ch. 12 - Prob. 89EAPCh. 12 - A 75 g, 30-cm-long rod hangs vertically on a...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- help me with the experimental set up for the excel i did. the grapharrow_forwardWhich of the following best describes how to calculate the average acceleration of any object? Average acceleration is always halfway between the initial acceleration of an object and its final acceleration. Average acceleration is always equal to the change in velocity of an object divided by the time interval. Average acceleration is always equal to the displacement of an object divided by the time interval. Average acceleration is always equal to the change in speed of an object divided by the time interval.arrow_forwardThe figure shows the velocity versus time graph for a car driving on a straight road. Which of the following best describes the acceleration of the car? v (m/s) t(s) The acceleration of the car is negative and decreasing. The acceleration of the car is constant. The acceleration of the car is positive and increasing. The acceleration of the car is positive and decreasing. The acceleration of the car is negative and increasing.arrow_forward
- Which figure could represent the velocity versus time graph of a motorcycle whose speed is increasing? v (m/s) v (m/s) t(s) t(s)arrow_forwardUnlike speed, velocity is a the statement? Poisition. Direction. Vector. Scalar. quantity. Which one of the following completesarrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvote Already got wrong chatgpt answerarrow_forward
- 3.63 • Leaping the River II. A physics professor did daredevil stunts in his spare time. His last stunt was an attempt to jump across a river on a motorcycle (Fig. P3.63). The takeoff ramp was inclined at 53.0°, the river was 40.0 m wide, and the far bank was 15.0 m lower than the top of the ramp. The river itself was 100 m below the ramp. Ignore air resistance. (a) What should his speed have been at the top of the ramp to have just made it to the edge of the far bank? (b) If his speed was only half the value found in part (a), where did he land? Figure P3.63 53.0° 100 m 40.0 m→ 15.0 marrow_forwardPlease solve and answer the question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forwardYou throw a small rock straight up from the edge of a highway bridge that crosses a river. The rock passes you on its way down, 5.00 s after it was thrown. What is the speed of the rock just before it reaches the water 25.0 m below the point where the rock left your hand? Ignore air resistance.arrow_forward
- Help me make a visualize experimental setup using a word document. For the theory below.arrow_forwardHow to solve this, given answerarrow_forwardThree point-like charges are placed at the corners of a square as shown in the figure, 28.0 cm on each side. Find the minimum amount of work required by an external force to move the charge q1 to infinity. Let q1=-2.10 μC, q2=+2.40 μС, q3=+3.60 μC.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:9780534408961
Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning
What is Torque? | Physics | Extraclass.com; Author: Extraclass Official;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zXxrAJld9mo;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY