
Concept explainers
Hercules Exercise Equipment Co. purchased a computerized measuring device two years ago for
A new piece of equipment will cost
The firm's tax rate is 25 percent and the cost of capital is 12 percent.
a. What is the book value of the old equipment?
b. What is the tax loss on the sale of the old equipment?
c. What is the tax benefit from the sale?
d. What is the
e. What is the net cost of the new equipment? (Include the inflow from the sale of the old equipment.)
f. Determine the depreciation schedule for the new equipment.
g. Determine the depreciation schedule for the remaining years of the old equipment.
h. Determine the incremental depreciation between the old and new equipment and the related tax shield benefits.
i. Compute the aftertax benefits of the cost savings.
j. Add the depreciation tax shield benefits and the aftertax cost savings, and determine the
k. Compare the present value of the incremental benefits (j) to the net cost of the new equipment (e). Should the replacement be undertaken?
a.
To calculate: The book value of the old equipment.
Introduction:
Book value:
It refers to the total worth of the company if it liquidates all its assets and pays off all the liabilities. It is also referred to as asset price in the balance sheet.
MACRS depreciation method:
MACRS stands for modified accelerated cost recovery system, which is a tool of depreciation used in the U.S. for tax purposes. This system places all the assets into categories with pre-specified depreciation periods.
Answer to Problem 33P
The calculation of the book value of the old equipment is shown below:
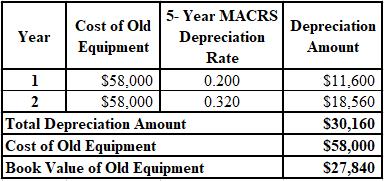
Hence, the book value of the old equipment is $27,480.
Explanation of Solution
The formulae used for calculation of the book value of the old equipment are shown below:
b.
To calculate: The tax loss incurred on the sale of the old equipment.
Introduction:
Tax loss:
It is the loss incurred when the total deduction claimed in a financial year exceeds the total assessable income of the year.
Answer to Problem 33P
The tax loss incurred on the sale of the old equipment is $3,040.
Explanation of Solution
The calculation of the tax loss on the sale of the old equipment is shown below:
c.
To calculate: The tax benefit from the sale of the old equipment.
Introduction:
Tax benefit:
It is the allowable deductions on the assessable income of the taxpayer, with an intent to reduce the tax liability and burden of the taxpayer.
Answer to Problem 33P
The tax benefit from the sale of the old equipment is $760.
Explanation of Solution
The calculation of the tax benefit from the sale of the old equipment is shown below:
d.
To calculate: The cash inflow received due to sale of old equipment.
Introduction:
Cash inflow:
It is the money received by the firm as the result of its operating, investing, and financing activities. It is the money which is received in the business and recorded in the cash flow statement.
Answer to Problem 33P
The cash inflow received due to sale of old equipment is $25,560.
Explanation of Solution
The calculation of the cash inflow from the sale of the old equipment is shown below:
e.
To calculate: The net cost of the new equipment.
Introduction:
Net cost:
The cost that is computed by deducting all the expenses related to an object, such as freight costs, discounts, etc. from the gross cost of the object.
Answer to Problem 33P
The net cost of the new equipment is $122,440.
Explanation of Solution
The calculation of the net cost of the new equipment is shown below:
f.
To prepare: The depreciation schedule of new equipment.
Introduction:
Depreciation schedule:
A table that shows the amount of depreciation of a particular asset over the years of its usage is termed as depreciation schedule.
MACRS depreciation method:
MACRS stands for modified accelerated cost recovery system, which is a tool of depreciation used in the U.S. for tax purposes. This system places all the assets into categories with pre-specified depreciation periods.
Answer to Problem 33P
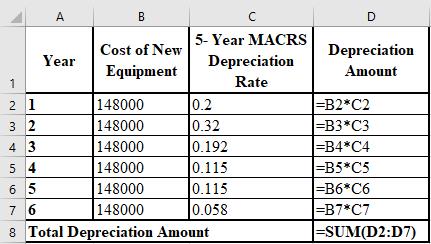
The depreciation schedule of new equipment is shown below:
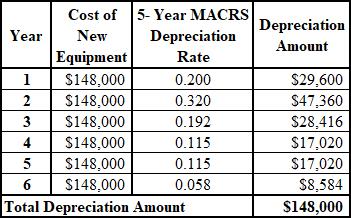
Explanation of Solution
The formulae used for the preparation of the depreciation schedule of new equipment are shown below:
g.
To prepare: The depreciation schedule of remaining years of the old equipment.
Introduction:
Depreciation schedule:
A table that shows the amount of depreciation of a particular asset over the years of its usage is termed as depreciation schedule.
MACRS depreciation method:
MACRS stands for modified accelerated cost recovery system, which is a tool of depreciation used in the U.S. for tax purposes. This system places all the assets into categories with pre-specified depreciation periods.
Answer to Problem 33P
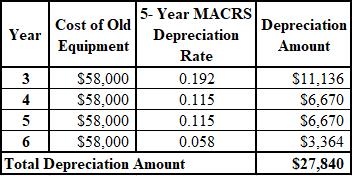
The depreciation schedule of remaining years of the old equipment is shown below:
Explanation of Solution
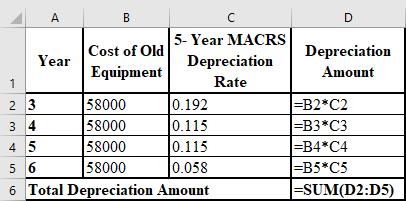
The formulae used for the preparation of the depreciation schedule of remaining years of the old equipment are shown below:
h.
To calculate: The incremental depreciation of old and new equipment and the depreciation tax shield benefit.
Introduction:
MACRS depreciation method:
MACRS stands for modified accelerated cost recovery system, which is a tool of depreciation used in the U.S. for tax purposes. This system places all the assets into categories with pre-specified depreciation periods.
Depreciation tax shield:
It is a particular kind of a tax shield provided to an individual or corporations in which depreciation as an expense is deducted from the taxable income.
Answer to Problem 33P
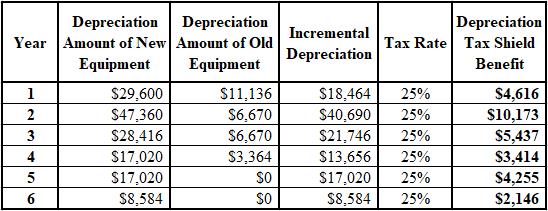
The calculation of the incremental depreciation of old and new equipment and the tax shield benefit is shown below:
Explanation of Solution
The formulae used for the calculation of the incremental depreciation of old and new equipment and the tax shield benefit are shown below:
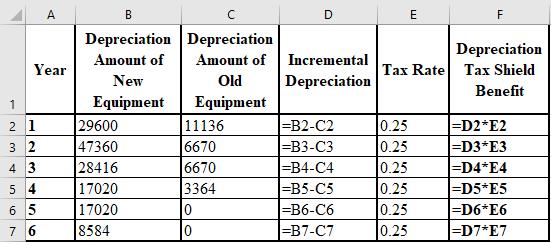
i.
To calculate: The after tax benefits of the cost savings.
Introduction:
After tax benefits:
After tax benefits are those deductions for which the individuals are eligible post the income tax is calculated.
Answer to Problem 33P
The calculation of the after tax benefits of the cost savings is shown below:
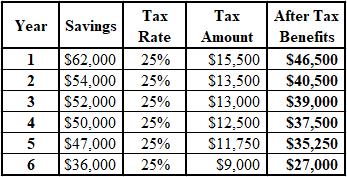
Explanation of Solution
The formulae used for the calculation of the after tax benefits of the cost savings are shown below:
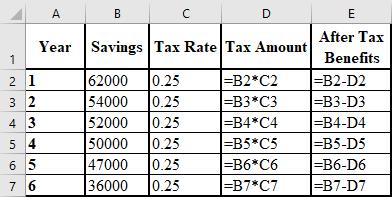
j.
To calculate: The present value of the total cash inflow (sum of depreciation tax shield and after tax benefits).
Introduction:
Present value (PV):
The current value of an investment or an asset is termed as its present value. It is calculated by discounting the future value of the investment or asset.
Cash inflow:
It is the money received by the firm as the result of its operating, investing, and financing activities. It is the money which is received in the business and recorded in the cash flow statement.
Answer to Problem 33P
The calculation of the PV of the total cash inflow is shown below:
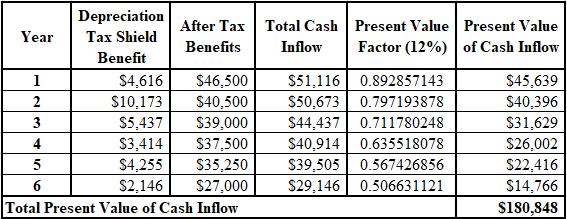
Explanation of Solution
The formulae used for the calculation of the PV of the total cash inflow are shown below:
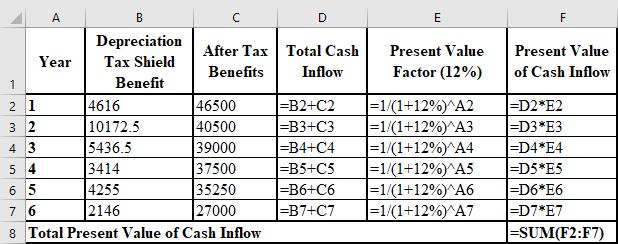
k.
To determine: Whether the replacement shall be undertaken or not.
Introduction:
Net present value (NPV):
It is the difference between the PV (present value) of cash inflows and the cash outflows. It is used in capital budgeting and planning of investment to assess the benefits and losses of any project or investment.
Answer to Problem 33P
The replacement should be undertaken because the NPV of the project is $58,408 and the positive NPV indicates that the replacement is beneficial for the corporation.
Explanation of Solution
The calculation of the NPV of the replacement is as follows:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Foundations Of Financial Management
- Problem Three (15 marks) You are an analyst in charge of valuing common stocks. You have been asked to value two stocks. The first stock NEWER Inc. just paid a dividend of $6.00. The dividend is expected to increase by 60%, 45%, 30% and 15% per year, respectively, in the next four years. Thereafter, the dividend will increase by 4% per year in perpetuity. Calculate NEWER’s expected dividend for t = 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5. The required rate of return for NEWER stock is 14% compounded annually. What is NEWER’s stock price? The second stock is OLDER Inc. OLDER Inc. will pay its first dividend of $10.00 three (3) years from today. The dividend will increase by 30% per year for the following four (4) years after its first dividend payment. Thereafter, the dividend will increase by 3% per year in perpetuity. Calculate OLDER’s expected dividend for t = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 and 8. The required rate of return for OLDER stock is 16% compounded annually. What is OLDER’s stock price? Now…arrow_forwardYou are considering a 10-year, $1,000 par value bond. Its coupon rate is 11%, and interest is paid semiannually. Bond valuation Years to maturity 10 Par value of bond $1,000.00 Coupon rate 11.00% Frequency interest paid per year 2 Effective annual rate 8.78% Calculation of periodic rate: Formulas Nominal annual rate #N/A Periodic rate #N/A Calculation of bond price: Formulas Number of periods #N/A Interest rate per period 0.00% Coupon payment per period #N/A Par value of bond $1,000.00 Price of bond #N/Aarrow_forwardHow much do investor psychology and market sentiment play into stock price movements? Do these emotional reactions having a bigger impact on short-term swings, or do they also shape long-term trends in a meaningful way?arrow_forward
- Explain The business of predatory tax return preparation, including: How they deceive the working poor,The marketing tactics the preparers use, and Other than paying high fees, what negative impact can the use of these unqualified and unregulated preparers have on the taxpayer?arrow_forwardExplain the changes in tax return preparation you would like to see in Alabama, based on what has been successful in other states.arrow_forwardExplain the understanding (or misunderstanding) of the working poor with tax return preparation within one page report.arrow_forward
- Explain the regulations or requirements for tax return preparers in Alabama.arrow_forwardquestion 1. Toodles Inc. had sales of $1,840,000. Cost of goods sold, administrative and selling expenses, and depreciation expenses were $1,180,000, $185,000 and $365,000 respectively. In addition, the company had an interest expense of $280,000 and a tax rate of 35 percent. (Ignore any tax loss carry-back or carry-forward provisions.)Arrange the financial information for Toodles Inc. in an income statement and compute its OCF?Question 2 Anti-Pandemic Pharma Co. Ltd. reports the following information in its income statement: Sales = $5,250,000;Costs = $2, 173,000;Other expenses = $187,400; Depreciation expense = $79,000; Interest expense= $53,555; Taxes = $76,000; Dividends = $69,000. $136,700 worth of new shares were also issued during the year and long-term debt worth $65,300 was redeemed.a) Compute the cash flow from assetsb) Compute the net change in working capitalQuestion 3Footfall Manufacturing Ltd. reports the following financial information at the end of the current year:…arrow_forwardAccrued Interest PayableCompute the interest for December accrued on each of the following notes payable owed by Riff-Raff'n Yell Inc., on December 31: Day of Calendar: 1 Lender: New Age Principal: $10,000 Interest Rate: 5% Term (Days) 120 Day of Calendar: 8 Lender: Wyvern Tavern Principal: $8,000 Interest Rate: 6% Term (Days) 90 Day of Calendar: 17 Lender: Cedar Tree Principal: $15,000 Interest Rate: 4% Term (Days) 90 Note: Use 360 days for calculations and round to the nearest dollar. Riff-Raff'n Yell, Inc. Lender (in alphabetical order) Accrued Interest Cedar Tree Answer 1 New Age Answer 2 Wyvern Tavern Answer 3arrow_forward
- Question Footfall afacturing pers The following fancial information at the end of the current years Inventory turnover ratio Fixed accetturnover ratio bot to assets ratia set profit ang ross profit margin the given information to fill at the templates for income statement and balance sheet geb In Statement of Footfall Manufacturing Ltd. for the year ending RELEASED BY THE CL MOME2003, FEBRUARY 9, 3005 Sales December 31, 20 Cast of other expec Earnings befo Camings afterarrow_forwardTreasury securities are issued and backed by the U.S. government and, therefore, are considered to be the lowest-risk securities on the market. As an investor looking for protection against inflation, you are considering the purchase of inflation-adjusted bonds known as U.S. Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities (TIPS). With these securities, the face value (which is paid at maturity) and the bond interest rate (which is paid semiannually) is regularly adjusted to account for inflation. However, for this problem only, assume the semi-annual interest payment (called the bond dividend) remains the same. You purchased a 10-year $10,000 TIPS bond with dividend of 4% per year payable semiannually (i.e., $200 every 6 months). Assume there is no inflation adjustment for the first 5 years, but in years 6 through 10, the bond face value increases by $850 each year. You use an expected investment return of 11% per year compounded semiannually. NOTE: This is a multi-part question. Once an…arrow_forwardNataro, Incorporated, has sales of $698,000, costs of $344,000, depreciation expense of $89,000, interest expense of $54,000, and a tax rate of 21 percent. What is the net income for this firm? Note: Do not round intermediate calculations and round your answer to the nearest whole number, e.g., 32. Net incomearrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT



