
Concept explainers
Keller Construction is considering two new investments. Project E calls for the purchase of earthmoving equipment. Project H represents an investment in a hydraulic lift. Keller wishes to use a
a. Determine the net present value of the projects based on a zero percent discount rate.
b. Determine the net present value of the projects based on a 9 percent discount rate.
c. The
d. If the two projects are not mutually exclusive, what would your acceptance or rejection decision be if the cost of capital (discount rate) is 8 percent? (Use the net present value profile for your decision; no actual numbers are necessary.)
e. If the two projects are mutually exclusive (the selection of one precludes the selection of the other), what would be your decision if the cost of capital is (1) 6 percent, (2) 13 percent, (3) 18 percent? Once again, use the net present value profile for your answer.
a.
To calculate: The NPV of the projects by using zero discount rate for Keller Construction Company.
Introduction:
Net present value (NPV):
It is the difference between the PV (present value) of cash inflows and the PV of cash outflows. It is used in capital budgeting and planning of investment to assess the benefits and losses of any project or investment.
Answer to Problem 23P
The NPV of the project E is $8,000 and project H is $5,000 based on zero discount rate for Keller Construction Company.
Explanation of Solution
The calculation of NPV of project E:
The calculation of NPV of project H:
Working Notes:
The calculation of inflows for project E:
The calculation of inflows for project H:
b.
To calculate: The NPV of the projects by using 9% discount rate for Keller Construction Company.
Introduction:
Net present value (NPV):
It is the difference between the PV (present value) of cash inflows and the PV of cash outflows. It is used in capital budgeting and planning of investment to assess the benefits and losses of any project or investment.
Present value (PV):
The current value of an investment or an asset is termed as its present value. It is calculated by discounting the future value of the investment or asset.
Answer to Problem 23P
The calculation of PV of inflows for Project E at 9%:
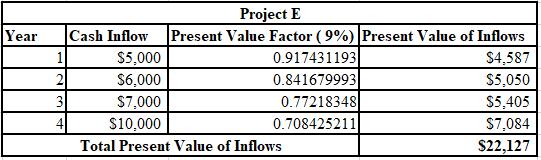
The calculation of PV of inflows for Project H at 9%:
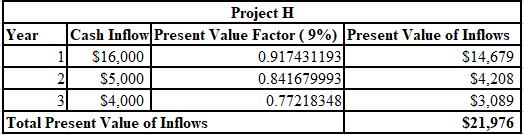
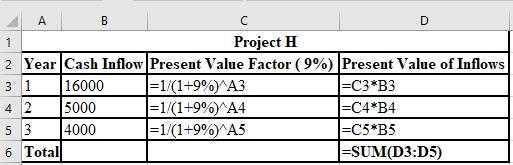
Thus, the NPV of project E is $2,127 and project H is $1,976.
Explanation of Solution
The calculation of NPV of project E:
The calculation of NPV of project H:
The formulae used for the calculation of PV of inflows for Project E:
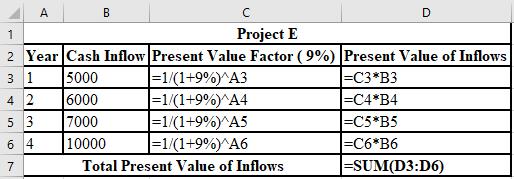
The formulae used for the calculation of PV of inflows for Project E:
c.
To plot: The graph for the NPV of the project according to the Fig. 12-3 for the Keller Construction Company.
Introduction:
Internal rate of return (IRR):
A method of capital budgeting that is used to measure the profitability of potential projects or investments. It is a discount that makes the NPV equals to zero for a specific project.
Answer to Problem 23P
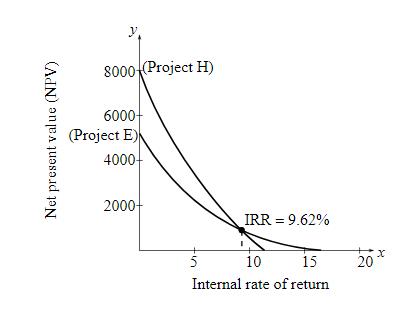
The graph for the NPV of the project according to the Fig. 12-3 for the Keller Construction Company:
Explanation of Solution
Calculation of IRR:
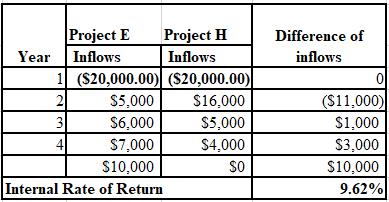
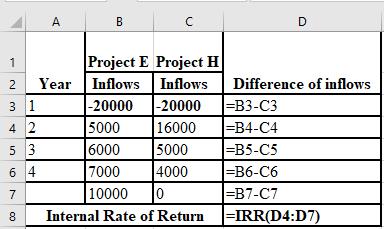
Working Note:
The formulae used in the calculation of IRR:
d.
To determine: The decision regarding the acceptance or the rejection of the projects, if the projects are mutually exclusive and discount rate of the cost of capital is 8% for the Keller Construction Company.
Introduction:
Net present value (NPV):
It is the difference between the PV (present value) of cash inflows and the PV of cash outflows. It is used in capital budgeting and planning of investment to assess the benefits and losses of any project or investment.
Present value (PV):
The current value of an investment or an asset is termed as its present value. It is calculated by discounting the future value of the investment or asset.
Answer to Problem 23P
The calculation of PV of project E and project H at 8%:
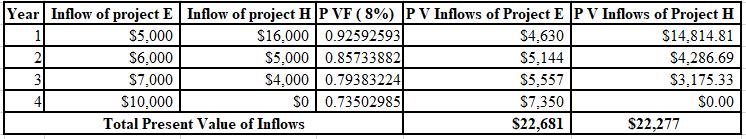
The NPV of project E is $2,681 and project H is $2,277. Thus, the NPV of project E is higher than the project H. Therefore, project E must be accepted as it is more profitable than the project H.
Explanation of Solution
The calculation of NPV of project E:
The calculation of NPV of project H:
The formulae used in the calculation of PV of project E and H at 8% are shown below:
e.
To determine: The decision regarding the acceptance or rejection of the projects, if the projects are mutually exclusive and discount rates of cost of capital are 6%, 13%, and 18% for the Keller Construction Company.
Introduction:
Net present value (NPV):
It is the difference between the PV (present value) of cash inflows and the PV of cash outflows. It is used in capital budgeting and planning of investment to assess the benefits and losses of any project or investment.
Present value (PV):
The current value of an investment or an asset is termed as its present value. It is calculated by discounting the future value of the investment or asset.
Answer to Problem 23P
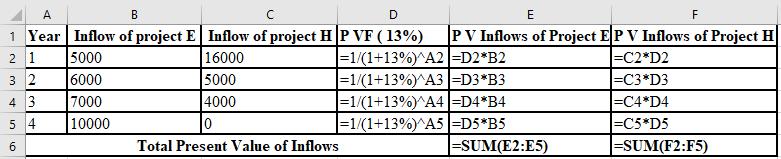
The calculation of PV of project E and project H at 6%:
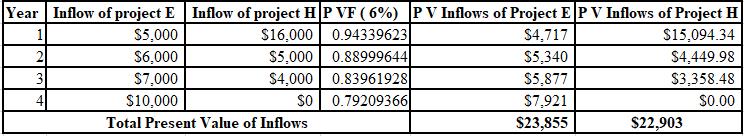
The NPV of project E is $3,855 and project H is $2,903. Thus, the NPV of project E is higher than the project H, So, project E must be accepted at 6% discount rate as it is superior to the project H.
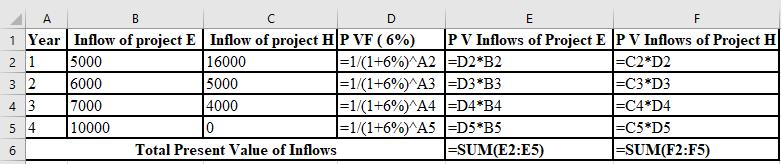
The calculation of PV of project E and project H at 13%:
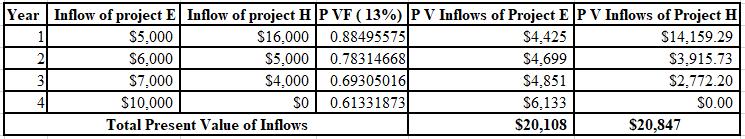
The NPV of project E is $108 and project H is $847. Thus, the NPV of project H is higher than the project E, So, project H must be accepted at 13% discount rate as it is superior to the project E.
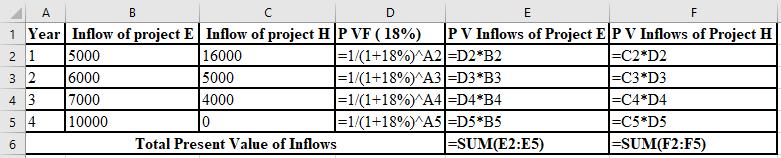
The calculation of PV of project E and project H at 18%:
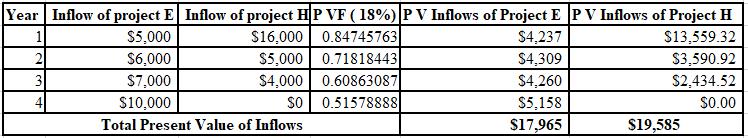
The NPV of project E is ($2,035) and project H is ($415). Thus, both projects must be rejected at 18% discount rate as NPV of both projects are negative.
Explanation of Solution
The calculation of NPV of project E at 6%:
The calculation of NPV of project H at 6%:
The calculation of NPV of project E at 13%:
The calculation of NPV of project H at 13%:
The calculation of NPV of project E at 18%:
The calculation of NPV of project H at 18%:
The formulae used in the calculation of PV of project E and H at 6% are shown below:
The formulae used in the calculation of PV of project E and H at 13% are shown below:
The formulae used in the calculation of PV of project E and H at 18% are shown below:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Foundations Of Financial Management
- Don't used Ai solution and don't used hand raitingarrow_forwardQ1: Blossom is 30 years old. She plans on retiring in 25 years, at the age of 55. She believes she will live until she is 105. In order to live comfortably, she needs a substantial retirement income. She wants to receive a weekly income of $5,000 during retirement. The payments will be made at the beginning of each week during her retirement. Also, Blossom has pledged to make an annual donation to her favorite charity during her retirement. The payments will be made at the end of each year. There will be a total of 50 annual payments to the charity. The first annual payment will be for $20,000. Blossom wants the annual payments to increase by 3% per year. The payments will end when she dies. In addition, she would like to establish a scholarship at Toronto Metropolitan University. The first payment would be $80,000 and would be made 3 years after she retires. Thereafter, the scholarship payments will be made every year. She wants the payments to continue after her death,…arrow_forwardCould you please help explain what is the research assumptions, research limitations, research delimitations and their intent? How the research assumptions, research limitations can shape the study design and scope? How the research delimitations could help focus the study and ensure its feasibility? What are the relationship between biblical principles and research concepts such as reliability and validity?arrow_forward
- What is the concept of the working poor ? Introduction form. Explain.arrow_forwardWhat is the most misunderstanding of the working poor? Explain.arrow_forwardProblem Three (15 marks) You are an analyst in charge of valuing common stocks. You have been asked to value two stocks. The first stock NEWER Inc. just paid a dividend of $6.00. The dividend is expected to increase by 60%, 45%, 30% and 15% per year, respectively, in the next four years. Thereafter, the dividend will increase by 4% per year in perpetuity. Calculate NEWER’s expected dividend for t = 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5. The required rate of return for NEWER stock is 14% compounded annually. What is NEWER’s stock price? The second stock is OLDER Inc. OLDER Inc. will pay its first dividend of $10.00 three (3) years from today. The dividend will increase by 30% per year for the following four (4) years after its first dividend payment. Thereafter, the dividend will increase by 3% per year in perpetuity. Calculate OLDER’s expected dividend for t = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 and 8. The required rate of return for OLDER stock is 16% compounded annually. What is OLDER’s stock price? Now assume that…arrow_forward
- Problem Three (15 marks) You are an analyst in charge of valuing common stocks. You have been asked to value two stocks. The first stock NEWER Inc. just paid a dividend of $6.00. The dividend is expected to increase by 60%, 45%, 30% and 15% per year, respectively, in the next four years. Thereafter, the dividend will increase by 4% per year in perpetuity. Calculate NEWER’s expected dividend for t = 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5. The required rate of return for NEWER stock is 14% compounded annually. What is NEWER’s stock price? The second stock is OLDER Inc. OLDER Inc. will pay its first dividend of $10.00 three (3) years from today. The dividend will increase by 30% per year for the following four (4) years after its first dividend payment. Thereafter, the dividend will increase by 3% per year in perpetuity. Calculate OLDER’s expected dividend for t = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 and 8. The required rate of return for OLDER stock is 16% compounded annually. What is OLDER’s stock price? Now assume that…arrow_forwardYour father is 50 years old and will retire in 10 years. He expects to live for 25 years after he retires, until he is 85. He wants a fixed retirement income that has the same purchasing power at the time he retires as $45,000 has today. (The real value of his retirement income will decline annually after he retires.) His retirement income will begin the day he retires, 10 years from today, at which time he will receive 24 additional annual payments. Annual inflation is expected to be 4%. He currently has $240,000 saved, and he expects to earn 8% annually on his savings. Required annuity payments Retirement income today $45,000 Years to retirement 10 Years of retirement 25 Inflation rate 4.00% Savings $240,000 Rate of return 8.00% Calculate value of…arrow_forwardProblem Three (15 marks) You are an analyst in charge of valuing common stocks. You have been asked to value two stocks. The first stock NEWER Inc. just paid a dividend of $6.00. The dividend is expected to increase by 60%, 45%, 30% and 15% per year, respectively, in the next four years. Thereafter, the dividend will increase by 4% per year in perpetuity. Calculate NEWER’s expected dividend for t = 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5. The required rate of return for NEWER stock is 14% compounded annually. What is NEWER’s stock price? The second stock is OLDER Inc. OLDER Inc. will pay its first dividend of $10.00 three (3) years from today. The dividend will increase by 30% per year for the following four (4) years after its first dividend payment. Thereafter, the dividend will increase by 3% per year in perpetuity. Calculate OLDER’s expected dividend for t = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 and 8. The required rate of return for OLDER stock is 16% compounded annually. What is OLDER’s stock price? Now assume that…arrow_forward
- Problem Three (15 marks) You are an analyst in charge of valuing common stocks. You have been asked to value two stocks. The first stock NEWER Inc. just paid a dividend of $6.00. The dividend is expected to increase by 60%, 45%, 30% and 15% per year, respectively, in the next four years. Thereafter, the dividend will increase by 4% per year in perpetuity. Calculate NEWER’s expected dividend for t = 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5. The required rate of return for NEWER stock is 14% compounded annually. What is NEWER’s stock price? The second stock is OLDER Inc. OLDER Inc. will pay its first dividend of $10.00 three (3) years from today. The dividend will increase by 30% per year for the following four (4) years after its first dividend payment. Thereafter, the dividend will increase by 3% per year in perpetuity. Calculate OLDER’s expected dividend for t = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 and 8. The required rate of return for OLDER stock is 16% compounded annually. What is OLDER’s stock price? Now assume that…arrow_forwardProblem Three (15 marks) You are an analyst in charge of valuing common stocks. You have been asked to value two stocks. The first stock NEWER Inc. just paid a dividend of $6.00. The dividend is expected to increase by 60%, 45%, 30% and 15% per year, respectively, in the next four years. Thereafter, the dividend will increase by 4% per year in perpetuity. Calculate NEWER’s expected dividend for t = 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5. The required rate of return for NEWER stock is 14% compounded annually. What is NEWER’s stock price? The second stock is OLDER Inc. OLDER Inc. will pay its first dividend of $10.00 three (3) years from today. The dividend will increase by 30% per year for the following four (4) years after its first dividend payment. Thereafter, the dividend will increase by 3% per year in perpetuity. Calculate OLDER’s expected dividend for t = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 and 8. The required rate of return for OLDER stock is 16% compounded annually. What is OLDER’s stock price? Now…arrow_forwardYou are considering a 10-year, $1,000 par value bond. Its coupon rate is 11%, and interest is paid semiannually. Bond valuation Years to maturity 10 Par value of bond $1,000.00 Coupon rate 11.00% Frequency interest paid per year 2 Effective annual rate 8.78% Calculation of periodic rate: Formulas Nominal annual rate #N/A Periodic rate #N/A Calculation of bond price: Formulas Number of periods #N/A Interest rate per period 0.00% Coupon payment per period #N/A Par value of bond $1,000.00 Price of bond #N/Aarrow_forward
- Principles of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT  Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning





