
An inductor is an electrical device that can store energy in the form of a magnetic field. In the simplest form, an inductor is a cylindrical coil of wire, and its inductance (L), measured in henrys [H), can be calculated by
Where
µ0 =.permeability of free space=4π × 10-7 [newtons per ampere squared, N/ A2]
n = number of turns of wire [dimensionless]
A = cross-sectional area of coil [square meters, m2]
l = length of coil [meters, m]
L = inductance [henrys, H] = [J /A2]
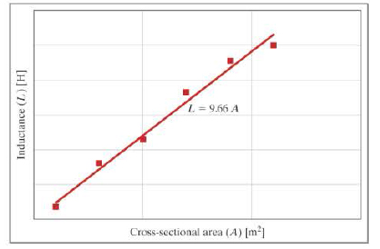 Several inductors were fabricated with the same number of turns of wire (n) and the same length (ℓ), but with different diameters, thus different cross-sectional areas (A). The inductances were measured and plotted as a function of cross-sectional area, and a mathematical model was developed to describe the relationship, as shown on the following graph.
Several inductors were fabricated with the same number of turns of wire (n) and the same length (ℓ), but with different diameters, thus different cross-sectional areas (A). The inductances were measured and plotted as a function of cross-sectional area, and a mathematical model was developed to describe the relationship, as shown on the following graph.
- a. What are the units of the slope (9.66)?
- b. For an inductor fabricated as described above, what is its diameter if its inductance is 0.4 henrys?
Give your answer in centimeters.
- c. If the length of the coil (ℓ) equals 0.2 meter, how many turns of wire (n) are in the inductor?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 12 Solutions
EBK THINKING LIKE AN ENGINEER
- Show all work pleasearrow_forwardDraw top, side, front view With pen(cil) and paper Multi view drawing and handwriting all of itarrow_forwardA wheel of diameter 150.0 mm and width 37.00 mm carrying a load 2.200 kN rolls on a flat rail. Take the wheel material as steel and the rail material as cast iron. Assume the figure given, which is based on a Poisson's ratio of 0.3, is applicable to estimate the depth at which the maximum shear stress occurs for these materials. At this critical depth, calculate the Hertzian stresses σr, σy, σz, and Tmax for the wheel. 1.0 0.8 0, т Ratio of stress to Pmax 0.4 0.6 90 69 0.2 0.5b b 1.5b Tmax 2b Distance from contact surface The Hertizian stresses are as follows: 02 = or = -23.8 psi for the wheel =| necessary.) σy for the wheel =| MPa σz for the wheel = MPa V4 for the wheel = | MPa 2.5b ཡི 3b MPa (Include a minus sign ifarrow_forward
- 4. Solve for the support reactions at A and B. W1 600 lb/ft W2 150 lb/ft A Barrow_forwardIn cold isostatic pressing, the mold is most typically made of which one of the following: thermosetting polymer tool steel sheet metal textile rubberarrow_forwardThe coefficient of friction between the part and the tool in cold working tends to be: lower higher no different relative to its value in hot workingarrow_forward
- The force F={25i−45j+15k}F={25i−45j+15k} lblb acts at the end A of the pipe assembly shown in (Figure 1). Determine the magnitude of the component F1 which acts along the member AB. Determine the magnitude of the component F2 which acts perpendicular to the AB.arrow_forwardHi can you please help me with the attached question?arrow_forwardHi can you please help me with the attached question?arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





