
(a)
Interpretation:
The major product obtained by the reaction of excess of given compound with
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Bond strength is depends on the formation of the radical, if the radical is involving in resonance which is weakest bond strength.
Chlorination:
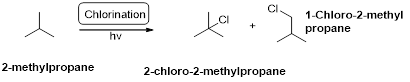
2-methylpropane undergoes radical chlorination and yields the 2-chloro-2-methylpropane and 1-chloro-2-methyl propane.
(b)
Interpretation:
The major product obtained by the reaction of excess of given compound with
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Bond strength is depends on the formation of the radical, if the radical is involving in resonance which is weakest bond strength.
Chlorination:
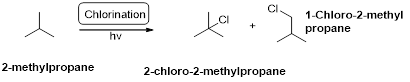
2-methylpropane undergoes radical chlorination and yields the 2-chloro-2-methylpropane and 1-chloro-2-methylpropane.
(c)
Interpretation:
The major product obtained by the reaction of excess of given compound with
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Bond strength is depends on the formation of the radical, if the radical is involving in resonance which is weakest bond strength.
Chlorination:
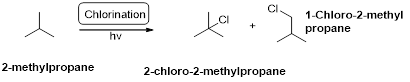
2-methylpropane undergoes radical chlorination and yields the 2-chloro-2-methylpropane and 1-chloro-2-methylpropane.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 12 Solutions
Student's Study Guide and Solutions Manual for Organic Chemistry
- Draw the product and the mechanism A. excess H*; 人 OH H*; B. C. D. excess OH ✓ OH H*; H₂O 1. LDA 2. H*arrow_forwardIn reactions whose kinetic equation is v = k[A]m, the rate coefficient k is always positive. Is this correct?arrow_forwardIf the concentration of A decreases exponentially with time, what is the rate equation? (A). -d[A] (B). dt d[A] = k[A] e-kt dtarrow_forward
- How many chiral centers are there in the following molecule? HO 0 1 ○ 2 ♡ 4 'N'arrow_forwardThe following chemical structure represents a molecule of what molecular formula?arrow_forwardWhich region(s) of the following phospholipid is/are hydrophobic? RO I hydro-water phobic-dislikes = Hydrophobic dislikes water ○ I only Il only I and III only II and IV only O II, III, and IV only III || IVarrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

