
(a)
Interpretation:
A multistep synthesis of the given compounds from the given starting material has to be given.
Concept introduction:
Bromination:

2-methyl propane undergoes radical bromination which yields the 2-bromo-2-methylpropane.because bromination will occur where the tertiary radical is present. (bromination reactions are more selective reaction).
Formation of
The
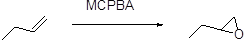
(b)
Interpretation:
A multistep synthesis of the given compounds from the given starting material has to be given.
Concept introduction:
Bromination:

2-methyl propane undergoes radical bromination which yields the 2-bromo-2-methylpropane.because bromination will occur where the tertiary radical is present. (bromination reactions are more selective reaction).
Oxidation of alcohol:
Alcohols reacts with hypochlorous (oxidizing agent) in the presence of acetic acid which yields the corresponding
Primary alcohols gives aldehyde, secondary alcohols gives ketone.
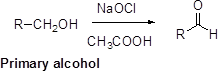
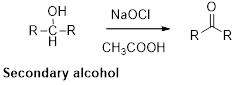
The alcohols reacts with acids like hydrochloric acid or hydrobromic acid, the bromine atom attacks back side of the carbon atoms which is bearing alcohol group and yields the corresponding product.
(c)
Interpretation:
A multistep synthesis of the given compounds from the given starting material has to be given.
Concept introduction:
Bromination:

2-methyl propane undergoes radical bromination which yields the 2-bromo-2-methylpropane.because bromination will occur where the tertiary radical is present. (bromination reactions are more selective reaction).
Oxidation of alcohol:
Alcohols reacts with hypochlorous (oxidizing agent) in the presence of acetic acid and yields the corresponding aldehyde and ketones.
Primary alcohols gives aldehyde, secondary alcohols gives ketone.
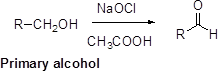
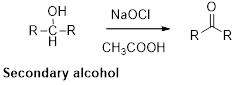
SN2 reaction:
The alcohols reacts with acids like hydrochloric acid or hydrobromic acid, the bromine atom attacks back side of the carbon atoms which is bearing alcohol group and yields the corresponding product.
(d)
Interpretation:
A multistep synthesis of the given compounds from the given starting material has to be given.
Concept introduction:
Bromination:

2-methyl propane undergoes radical bromination which yields the 2-bromo-2-methylpropane.because bromination will occur where the tertiary radical is present. (bromination reactions are more selective reaction).
Formation of epoxide:
The alkene can be converted to epoxide when alkene is treated with MCPBA (m-chloro perbenzoic acid)
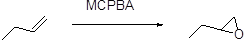
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 12 Solutions
Student's Study Guide and Solutions Manual for Organic Chemistry
- Given the following data, determine the rate constant, k, of the reaction H2(g) + 21C1(g) → 12(g) + 2HCl(g) = Experiment 1 2 3 1.65 × 10 5 torr ¹s -1 6.06 104 torr -1s-1 8.17 105 torr -1s-1 1.34 torr -1s-1 3.48103 torr -¹s−1 [H2] (torr) [ICI] (torr) Rate (torr/s) 250 325 1.34 250 81 0.331 50 325 0.266arrow_forwardPredict the temperature change produced by burning 3.55 g benzoic acid in a bomb calorimeter that has a heat capacity of 20.12 kJ/°C. The enthalpy of combustion of benzoic acid is −26.43 kJ/g.arrow_forwardDetermine the entropy change for the reaction SO 2 (g) + O2(g) → SO3(g) given the following information: Substance S° (J/mol K) . SO2(g) 248.2 O2(g) 205.0 SO3(g) 256.8arrow_forward
- Hydrochloric acid (HCl) reacts with sodium hydroxide (NaOH) to form sodium chloride (NaCl) and water. If ΔH ° = −56.13 kJ/mol and ΔS ° = 79.11 J/mol ⋅ K, what is the temperature of the reaction if ΔG ° = −80.89 kJ/mol?arrow_forwardFor a particular hypothetical reaction, A+B →2C, the value of AG° is -125 kJ/mol. What is the value of AG for this reaction at 35°C when [A] = 0.10 M, [B] = 0.05 M, and [C] = 2.0 × 10¹ M?arrow_forwardIn an experiment, 74.3 g of metallic copper was heated to 100.0°C and then quickly dropped into 200.0 mL of water in a calorimeter. The heat capacity of the calorimeter with the water was 875 J/°C. The initial temperature of the calorimeter was 27.5°C, and the final temperature after addition of the metal was 29.8°C. What is the value of the molar heat capacity of copper?arrow_forward
- The Haber-Bosch process permits the direct conversion of molecular nitrogen to ammonia, which can be used in large-scale fertilizer production. Given the balanced Haber-Bosch reaction and using the bond energies in the table below, estimate the enthalpy change associated with the reaction. N2(g) + 3H2(g) → 2NH3(g) Bond N=N N = N Energy (kJ/mol) 941 418 N-N H-H N-H 163 435 388arrow_forwardBenzoic acid is used to determine the heat capacity of bomb calorimeters because it can be obtained in pure form and its energy of combustion is known very accurately (−26.43 kJ/g). Determine the heat capacity of a calorimeter that had a temperature increase of 9.199°C when 3.500 g of benzoic acid was used.arrow_forwardGiven the standard enthalpies of formation for the following substances, determine the reaction enthalpy for the following reaction. 2N2H4(g) + 2NO2(g) → 3N2(g) + 4H2O(g) AHrxn ? kJ Substance AH in kJ/mol N2H4(g) +95.4 NO2(g) +33.1 H2O(g) -241.8arrow_forward
- If 7.3 kJ of energy are required to change the temperature of water from 5.0 to 70.0, what was the volume of water? (cs = 4.184 J/(g ⋅ ), d = 1.00 g/mL)arrow_forwardBALANCE CHEMICAL REACTIONarrow_forwardPredict the product(s) of the following reactions. If no reaction, write "NR". a) Cl₂ FeCl3 e) HNO3 H2SO4 b) NO2 CI. HNO3 f) Br Br2 OH H2SO4 HO3S. FeBr3 c) Cl2 g) FeCl3 F d) O₂N Br2 FeBr3 O₂N OH HNO3 CH3 H2SO4arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
