
Concept explainers
Keller Construction is considering two new investments. Project E calls for the purchase of earthmoving equipment. Project H represents an investment in a hydraulic lift. Keller wishes to use a
a. Determine the net present value of the projects based on a zero percent discount rate.
b. Determine the net present value of the projects based on a 9 percent discount rate.
c. The
d. If the two projects are not mutually exclusive, what would your acceptance or rejection decision be if the cost of capital (discount rate) is 8 percent? (Use the net present value profile for your decision; no actual numbers are necessary.)
e. If the two projects are mutually exclusive (the selection of one precludes the selection of the other), what would be your decision if the cost of capital is (1) 6 percent, (2) 13 percent, (3) 18 percent? Once again, use the net present value profile for your answer.
a.
To calculate: The NPV of the projects by using zero discount rate for Keller Construction Company.
Introduction:
Net present value (NPV):
It is the difference between the PV (present value) of cash inflows and the PV of cash outflows. It is used in capital budgeting and planning of investment to assess the benefits and losses of any project or investment.
Answer to Problem 23P
The NPV of the project E is $8,000 and project H is $5,000 based on zero discount rate for Keller Construction Company.
Explanation of Solution
The calculation of NPV of project E:
The calculation of NPV of project H:
Working Notes:
The calculation of inflows for project E:
The calculation of inflows for project H:
b.
To calculate: The NPV of the projects by using 9% discount rate for Keller Construction Company.
Introduction:
Net present value (NPV):
It is the difference between the PV (present value) of cash inflows and the PV of cash outflows. It is used in capital budgeting and planning of investment to assess the benefits and losses of any project or investment.
Present value (PV):
The current value of an investment or an asset is termed as its present value. It is calculated by discounting the future value of the investment or asset.
Answer to Problem 23P
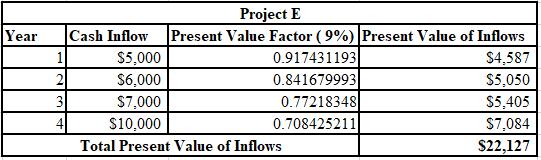
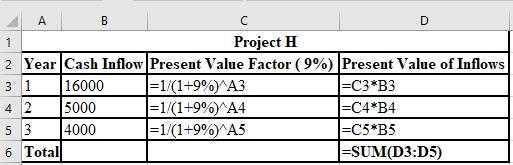
The calculation of PV of inflows for Project E at 9%:
The calculation of PV of inflows for Project H at 9%:
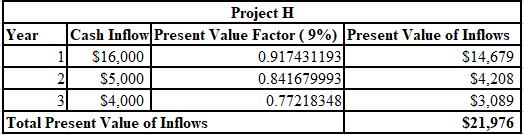
Thus, the NPV of project E is $2,127 and project H is $1,976.
Explanation of Solution
The calculation of NPV of project E:
The calculation of NPV of project H:
The formulae used for the calculation of PV of inflows for Project E:
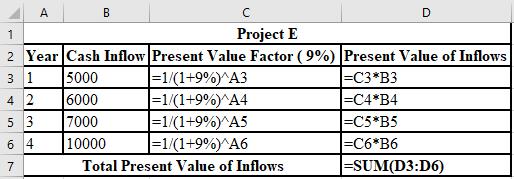
The formulae used for the calculation of PV of inflows for Project E:
c.
To plot: The graph for the NPV of the project according to the Fig. 12-3 for the Keller Construction Company.
Introduction:
Internal rate of return (IRR):
A method of capital budgeting that is used to measure the profitability of potential projects or investments. It is a discount that makes the NPV equals to zero for a specific project.
Answer to Problem 23P
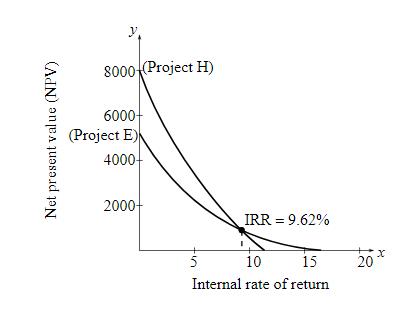
The graph for the NPV of the project according to the Fig. 12-3 for the Keller Construction Company:
Explanation of Solution
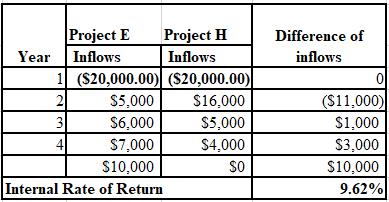
Calculation of IRR:
Working Note:
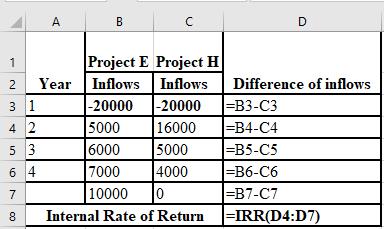
The formulae used in the calculation of IRR:
d.
To determine: The decision regarding the acceptance or the rejection of the projects, if the projects are mutually exclusive and discount rate of the cost of capital is 8% for the Keller Construction Company.
Introduction:
Net present value (NPV):
It is the difference between the PV (present value) of cash inflows and the PV of cash outflows. It is used in capital budgeting and planning of investment to assess the benefits and losses of any project or investment.
Present value (PV):
The current value of an investment or an asset is termed as its present value. It is calculated by discounting the future value of the investment or asset.
Answer to Problem 23P
The calculation of PV of project E and project H at 8%:
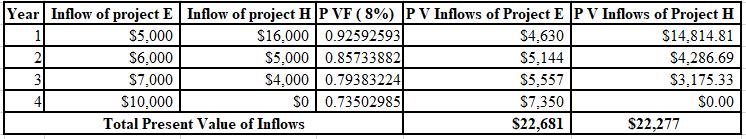
The NPV of project E is $2,681 and project H is $2,277. Thus, the NPV of project E is higher than the project H. Therefore, project E must be accepted as it is more profitable than the project H.
Explanation of Solution
The calculation of NPV of project E:
The calculation of NPV of project H:
The formulae used in the calculation of PV of project E and H at 8% are shown below:
e.
To determine: The decision regarding the acceptance or rejection of the projects, if the projects are mutually exclusive and discount rates of cost of capital are 6%, 13%, and 18% for the Keller Construction Company.
Introduction:
Net present value (NPV):
It is the difference between the PV (present value) of cash inflows and the PV of cash outflows. It is used in capital budgeting and planning of investment to assess the benefits and losses of any project or investment.
Present value (PV):
The current value of an investment or an asset is termed as its present value. It is calculated by discounting the future value of the investment or asset.
Answer to Problem 23P
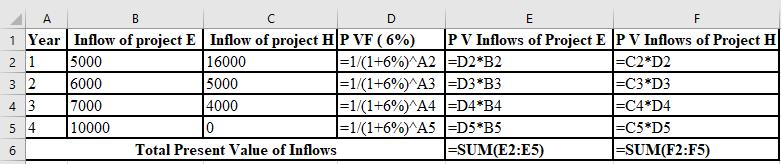
The calculation of PV of project E and project H at 6%:
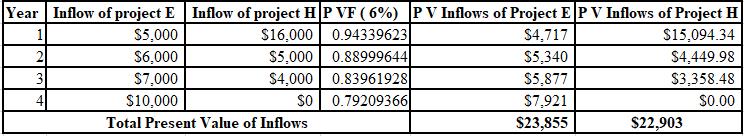
The NPV of project E is $3,855 and project H is $2,903. Thus, the NPV of project E is higher than the project H, So, project E must be accepted at 6% discount rate as it is superior to the project H.
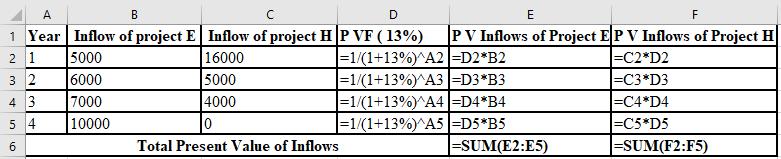
The calculation of PV of project E and project H at 13%:
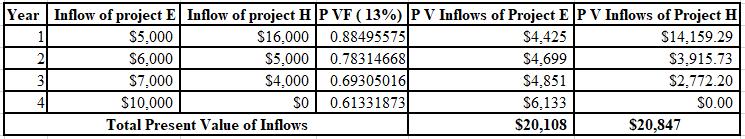
The NPV of project E is $108 and project H is $847. Thus, the NPV of project H is higher than the project E, So, project H must be accepted at 13% discount rate as it is superior to the project E.
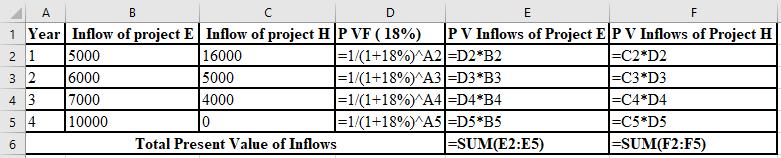
The calculation of PV of project E and project H at 18%:
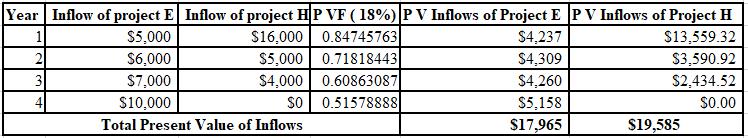
The NPV of project E is ($2,035) and project H is ($415). Thus, both projects must be rejected at 18% discount rate as NPV of both projects are negative.
Explanation of Solution
The calculation of NPV of project E at 6%:
The calculation of NPV of project H at 6%:
The calculation of NPV of project E at 13%:
The calculation of NPV of project H at 13%:
The calculation of NPV of project E at 18%:
The calculation of NPV of project H at 18%:
The formulae used in the calculation of PV of project E and H at 6% are shown below:
The formulae used in the calculation of PV of project E and H at 13% are shown below:
The formulae used in the calculation of PV of project E and H at 18% are shown below:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
EBK FOUNDATIONS OF FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
- How can the book value still serve as a useful metric for investors despite the dominance of market value?arrow_forwardHow do you think companies can practically ensure that stakeholder interests are genuinely considered, while still prioritizing the financial goal of maximizing shareholder equity? Do you think there’s a way to measure and track this balance effectively?arrow_forward$5,000 received each year for five years on the first day of each year if your investments pay 6 percent compounded annually. $5,000 received each quarter for five years on the first day of each quarter if your investments pay 6 percent compounded quarterly. Can you show me either by hand or using a financial calculator please.arrow_forward
- Can you solve these questions on a financial calculator: $5,000 received each year for five years on the last day of each year if your investments pay 6 percent compounded annually. $5,000 received each quarter for five years on the last day of each quarter if your investments pay 6 percent compounded quarterly.arrow_forwardNow suppose Elijah offers a discount on subsequent rooms for each house, such that he charges $40 for his frist room, $35 for his second, and $25 for each room thereafter. Assume 30% of his clients have only one room cleaned, 25% have two rooms cleaned, 30% have three rooms cleaned, and the remaining 15% have four rooms cleaned. How many houses will he have to clean before breaking even? If taxes are 25% of profits, how many rooms will he have to clean before making $15,000 profit? Answer the question by making a CVP worksheet similar to the depreciation sheets. Make sure it works well, uses cell references and functions/formulas when appropriate, and looks nice.arrow_forward1. Answer the following and cite references. • what is the whole overview of Green Markets (Regional or Sectoral Stock Markets)? • what is the green energy equities, green bonds, and green financing and how is this related in Green Markets (Regional or Sectoral Stock Markets)? Give a detailed explanation of each of them.arrow_forward
- Could you help explain “How an exploratory case study could be goodness of work that is pleasing to the Lord?”arrow_forwardWhat are the case study types and could you help explain and make an applicable example.What are the 4 primary case study designs/structures (formats)?arrow_forwardThe Fortune Company is considering a new investment. Financial projections for the investment are tabulated below. The corporate tax rate is 24 percent. Assume all sales revenue is received in cash, all operating costs and income taxes are paid in cash, and all cash flows occur at the end of the year. All net working capital is recovered at the end of the project. Year 0 Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Investment $ 28,000 Sales revenue $ 14,500 $ 15,000 $ 15,500 $ 12,500 Operating costs 3,100 3,200 3,300 2,500 Depreciation 7,000 7,000 7,000 7,000 Net working capital spending 340 390 440 340 ?arrow_forward
- What are the six types of alternative case study compositional structures (formats)used for research purposes, such as: 1. Linear-Analytical, 2. Comparative, 3. Chronological, 4. Theory Building, 5. Suspense and 6. Unsequenced. Please explainarrow_forwardFor an operating lease, substantially all the risks and rewards of ownership remain with the _________. QuestFor an operating lease, substantially all the risks and rewards of ownership remain with the _________: A) Tenant b) Lessee lessor none of the above tenant lessee lessor none of the aboveLeasing allows the _________ to acquire the use of a needed asset without having to make the large up-front payment that purchase agreements require Question 4 options: lessor lessee landlord none of the abovearrow_forwardHow has AirBnb negatively affected the US and global economy? How has Airbnb negatively affected the real estate market? How has Airbnb negatively affected homeowners and renters market? What happened to Airbnb in the Tax Dispute in Italy?arrow_forward
- Principles of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT  Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning





