
Label the parts of this kidney and nephron.
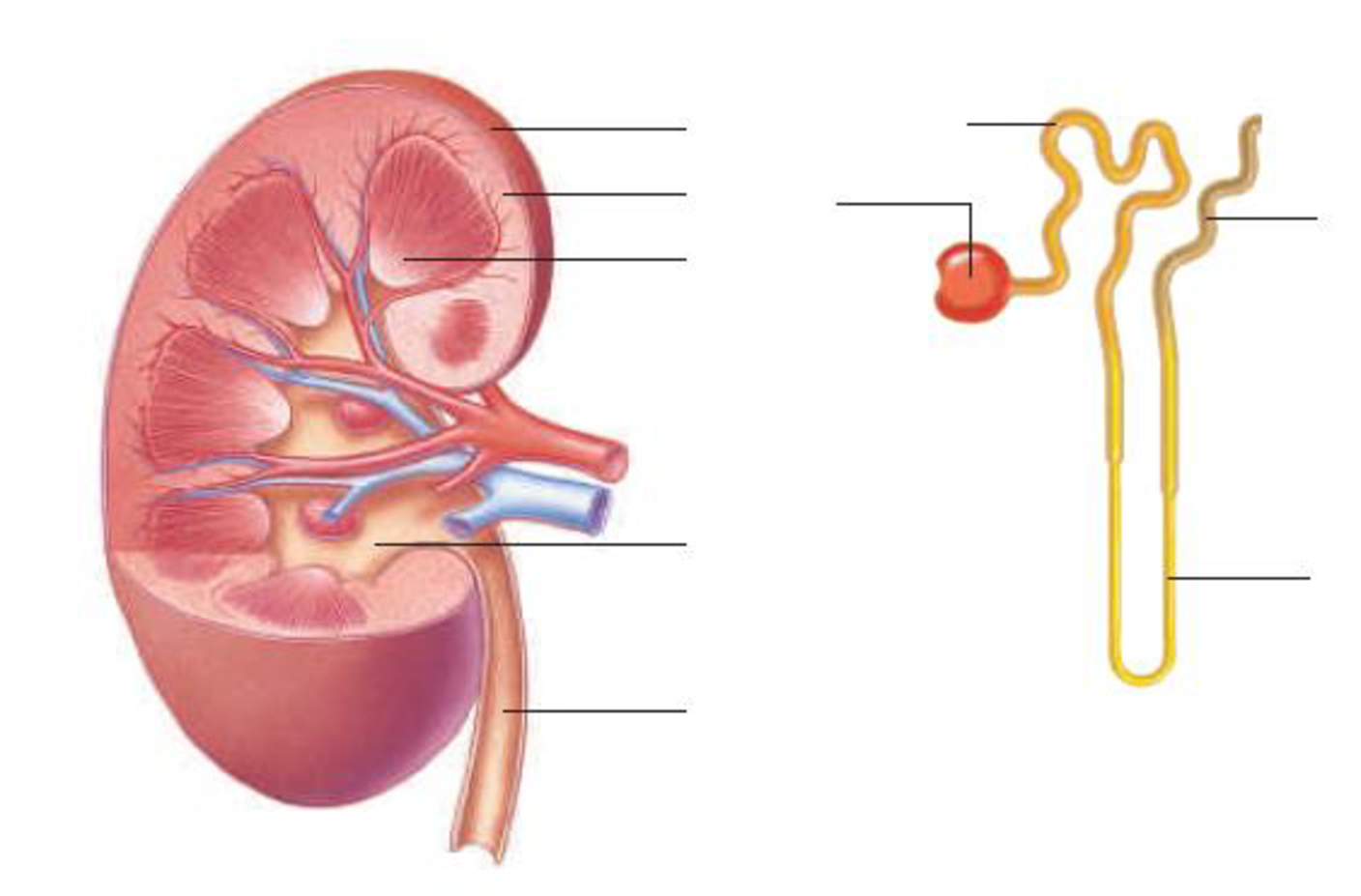
To label: The parts of the kidney and nephron.
Introduction: The kidney is an important organ of the excretory system, and nephron is the basic structural unit of the kidney. As blood passes through the kidneys, it filters the nitrogenous waste to form urine. It maintains homeostasis of the body.
Answer to Problem 1RQ
Pictorial representation: Fig.1 shows the parts of the kidney, and Fig.2 shows the parts of the nephron.
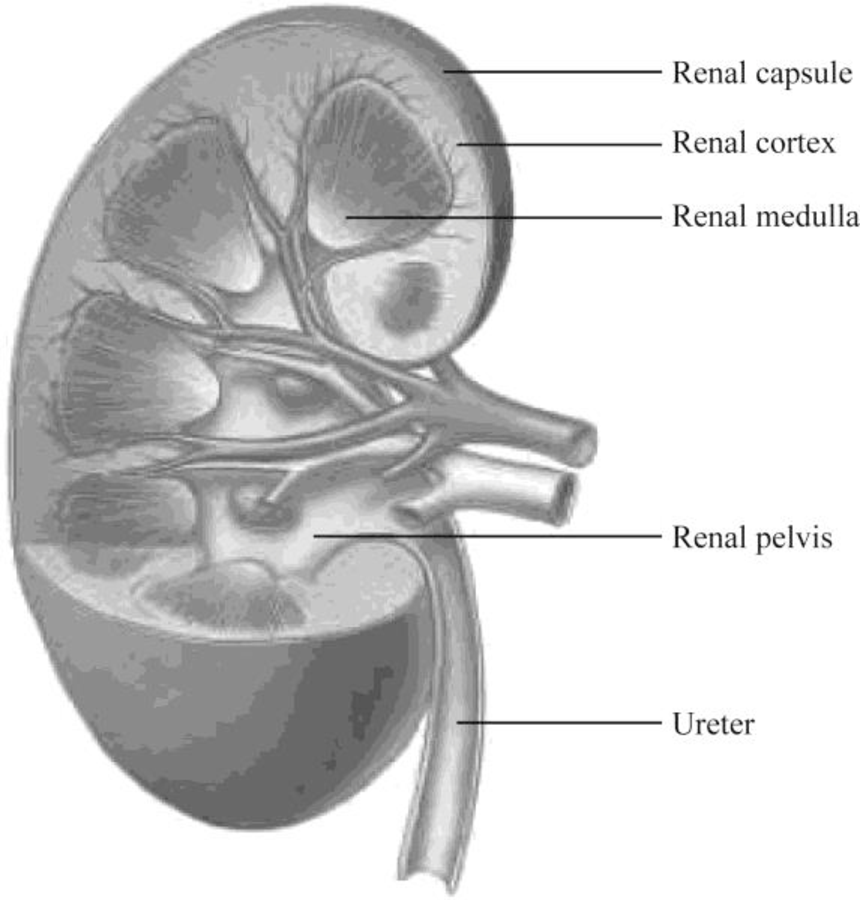
Fig.1: Kidney
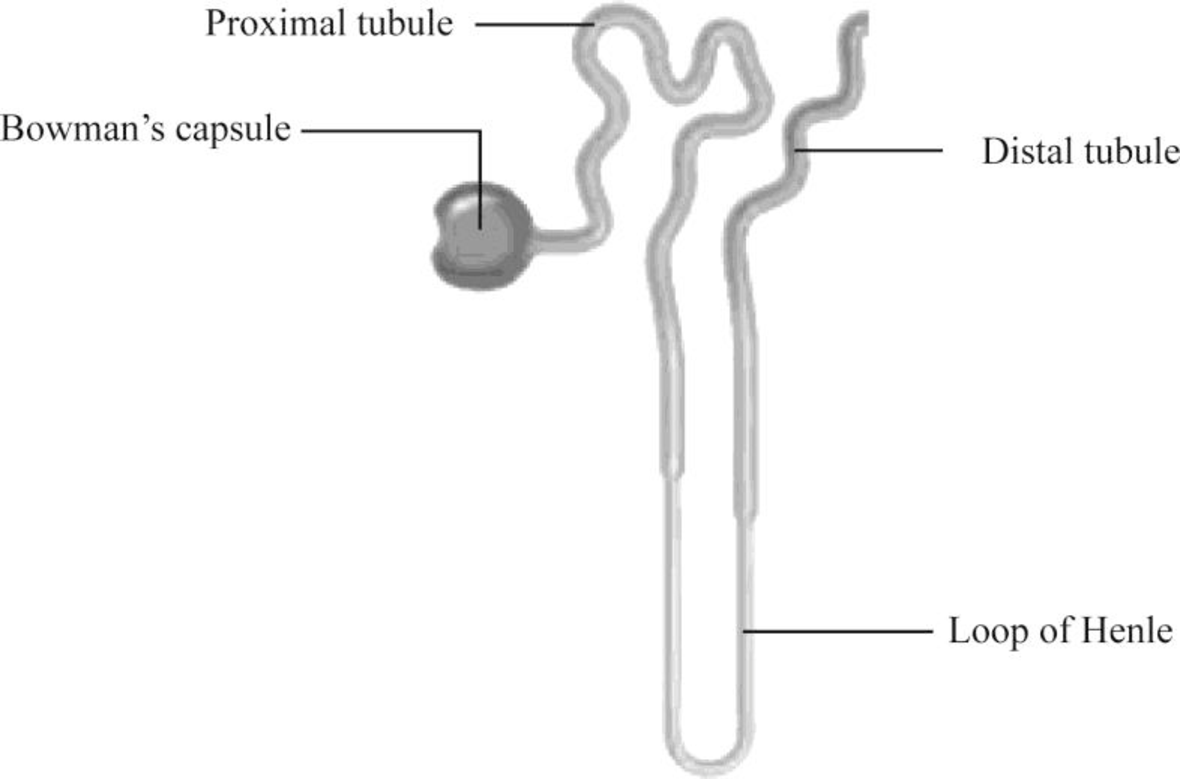
Fig.2: Nephron
Explanation of Solution
Structure of a kidney:
The kidney has two zones namely renal cortex and renal medulla. Renal cortex is the outer part of kidney. It consists of blood vessels that are connected to nephrons. Renal medulla is the inner part of the kidney containing 8–12 renal pyramids consisting of collecting tubules. Each kidney has a medially located space called renal sinus. This space is the urine drainage area. It is organized into minor calyces, major calyces, and a renal pelvis. There are 8 to 15 funnel-shaped minor calyces that are associated with the renal pyramid. Several minor calyces merge to form large major calyces. There are two to three major calyces in each kidney. The major calyces merge to form a large renal pelvis. Renal pelvis merges with the ureter at the medial edge of the kidneys.
Structure of a nephron:
Nephron is the functional filtration unit of kidney. It is microscopic in nature. Nephron has divided into renal corpuscle and renal tubule. Renal tubule is composed of simple epithelium that rests on the basement membrane. Renal tubule extends from the glomerular capsule (also called Bowman's capsule. It collects the material obtained from glomeruli) and ends at the collecting duct. It consists of three continuous sections. They are as follows:
- • The proximal convoluted tubule
- • The nephron loop
- • The distal convoluted tubule
The convoluted tubules reside in the cortex, but the nephron loop usually extends into the medulla from the cortex.
The proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) is the first region of the renal tubule that is originated from the tubular pole of renal capsule. It consists of simple cuboidal epithelium and is marked by tall, apical microvilli that increase its surface area and reabsorption capacity. Under light microscope, the lumen of the proximal convoluted tubule looks fuzzy due to microvilli.
The nephron loop originates at the sharp bend in the proximal convoluted tubules. Each nephron has two limbs, namely descending limb and ascending limb. Both limbs are continuous at a hairpin within the medulla. From the proximal convoluted tubule, the descending limb extends medially to the tip of the nephron loop. Ascending limb of the nephron loop returns to the renal cortex and terminates at the distal convoluted tubule. Some parts of these limbs are classified as thick or thin according to the epithelia composing them. Thick segments of each limb have a simple cuboidal epithelium lining, whereas the thin segments of each limb have a simple squamous epithelium.
The distal convoluted tubule (DCT) originates in the renal cortex at the end of the nephron loop’s thick ascending limb and extends to a collecting tubule. DCT is composed of simple cuboidal epithelium. DCT is smaller and has only sparse, short, apical microvilli. DCT does not look fuzzy when viewed under the light microscope.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)
- calculate the questions showing the solution including variables,unit and equations all the questiosn below using the data a) B1, b) B2, c) hybrid rate constant (1) d) hybrid rate constant (2) e) t1/2,dist f) t1/2,elim g) k10 h) k12 i) k21 j) initial concentration (C0) k) central compartment volume (V1) l) steady-state volume (Vss) m) clearance (CL) AUC (0→10 min) using trapezoidal rule n) AUC (20→30 min) using trapezoidal rule o) AUCtail (AUC360→∞) p) total AUC (using short cut method) q) volume from AUC (VAUC)arrow_forwardQUESTION 8 For the following pedigree, assume that the mode of inheritance is X-linked recessive, and that the trait has full penetrance and expressivity and occurs at a very low frequency in the hum population. Using XA for the dominant allele and Xa for the recessive allele, assign genotypes for the following individuals (if it is not possible to figure out the second allele of a genotype, that with an underscore): 2 m 1 2 1 2 4 5 6 7 8 9 IV 1 2 3 5 6 7 8 CO 9 10 12 13 V 1, 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 a. Il-1: b. 11-2: c. III-3: d. III-4: e. If individuals IV-11 and IV-12 have another child, what is the probability that they will have a boy with the disorder?arrow_forwardAnswerrarrow_forward
- please,show workings ahd solutions calculate the questions showing the solution including variables,unit and equations all the questiosn below using the data a) B1, b) B2, c) hybrid rate constant (1) d) hybrid rate constant (2) e) t1/2,dist f) t1/2,elim g) k10 h) k12 i) k21 j) initial concentration (C0) k) central compartment volume (V1) l) steady-state volume (Vss) m) clearance (CL) AUC (0→10 min) using trapezoidal rule n) AUC (20→30 min) using trapezoidal rule o) AUCtail (AUC360→∞) p) total AUC (using short cut method) q) volume from AUC (VAUC)arrow_forwardQuestion about consensus and the relationship to transcriptional activityarrow_forwardQuestion about archaea and eukaryotic general transcription homologsarrow_forward
- Question about general transcription factors and their relationship to polymerasesarrow_forwardIdentify the indicated structure?arrow_forwardrewrite: Problem 1 (Mental Health): The survivor victim is dealing with acute stress and symptoms of a post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) due to their traumatic experience during the January 2025 wildfire. Goal 1: To alleviate the client's overall level, frequency, and intensity of anxiety and PTSD symptoms so that daily functioning remains unimpaired. Objective 1: The client will learn and regularly use at least two anxieties management techniques to reduce anxiety symptoms to less than three episodes per week. Intervention 1: The therapist will provide psychoeducation about anxiety and PTSD, including their symptoms and triggers. The therapist will also teach and assist the client in adopting relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing exercises and progressive muscle relaxation, to better manage anxiety and lessen PTSD symptoms.arrow_forward
- O Macmillan Learning You have 0.100 M solutions of acetic acid (pKa = 4.76) and sodium acetate. If you wanted to prepare 1.00 L of 0.100 M acetate buffer of pH 4.00, how many milliliters of acetic acid and sodium acetate would you add? acetic acid: mL sodium acetate: mLarrow_forwardHow does the cost of food affect the nutritional choices people make?arrow_forwardBiopharmaceutics and Pharmacokinetics:Two-Compartment Model Zero-Order Absorption Questions SHOW ALL WORK, including equation used, variables used and each step to your solution, report your regression lines and axes names (with units if appropriate) :Calculate a-q a) B1, b) B2, c) hybrid rate constant (1) d) hybrid rate constant (2) e) t1/2,dist f) t1/2,elim g) k10 h) k12 i) k21 j) initial concentration (C0) k) central compartment volume (V1) l) steady-state volume (Vss) m) clearance (CL) AUC (0→10 min) using trapezoidal rule n) AUC (20→30 min) using trapezoidal rule o) AUCtail (AUC360→∞) p) total AUC (using short cut method) q) volume from AUC (VAUC)arrow_forward
 Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax





