
Concept explainers
Imagine you have found a small quantity of DNA. Fill in the following diagram, which outlines a series of DNA technology experiments you could perform to study this DNA.
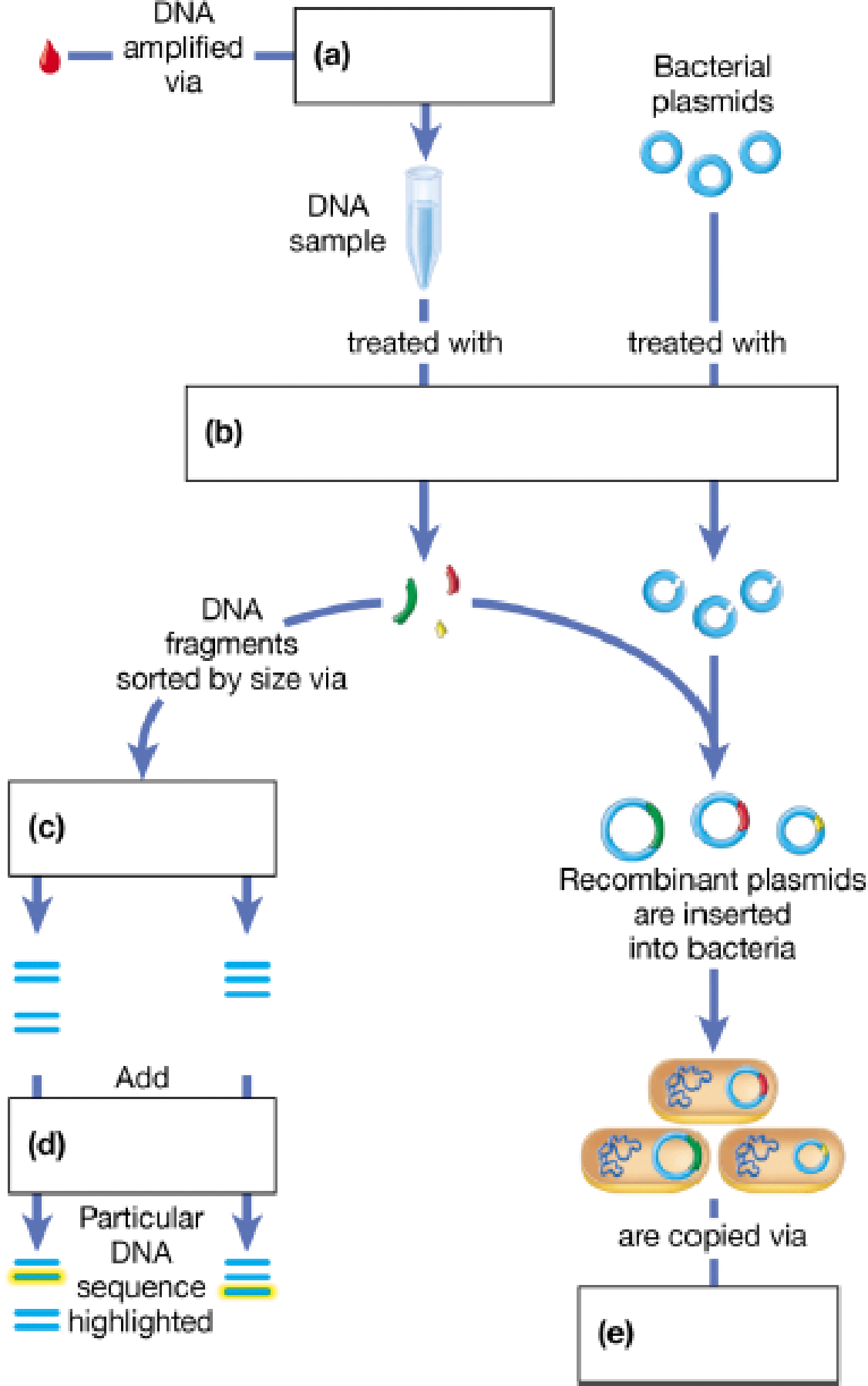
To complete: The given map showing the steps involved in recombinant DNA (rDNA) technology.
Introduction: Recombinant DNA technology is a technique used to produce novel genetic combinations by combining the genes from two different organisms and introduces them inside a host in order to proliferate and grow.
Answer to Problem 1CC
Pictorial representation: Fig. 1 shows the completed map of the steps involved in recombinant DNA technology.
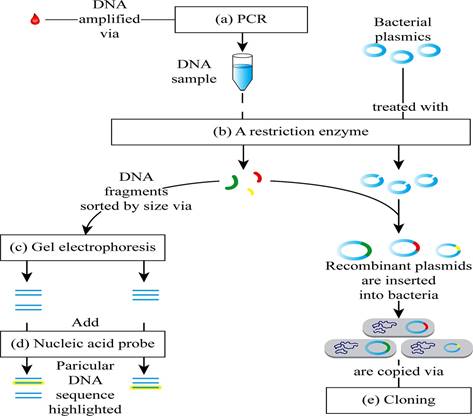
Fig. 1 The steps involved in recombinant DNA (rDNA) technology.
Explanation of Solution
(a)
Correct answer: PCR
Explanation: The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is used to get multiple copies of DNA within a short period. In PCR, for synthesizing multiple copies of a specific DNA fragment, DNA nucleotide primers are used. Hence, the correct answer is PCR.
(b)
Correct answer: A restriction enzyme
Explanation: Restriction enzymes are a group of enzymes used to cut the DNA by binding to certain specific DNA sequence sites called as restriction sites. It forms single-stranded ends called as sticky ends. The sticky ends help the DNA to bind with the other DNA fragment that has the same single-stranded ends by complementary base pairing. Hence, the correct answer is a restriction enzyme.
(c)
Correct answer: Gel electrophoresis
Explanation: Electrophoresis is used to separate the molecules based on their size and charge in the presence of an electric field. Hence, the correct answer is Gel electrophoresis.
(d)
Correct answer: Nucleic acid probe
Explanation: Nucleic acid probe is used for the analysis of the probe, which can specifically bind to the complementary DNA strand. Hence, the correct answer is nucleic acid probe.
(e)
Correct answer: Cloning
Explanation: The process of production of identical copies of the parent cell is called as cloning. Cloning vectors are used in the rDNA technology for the propagation of the desired gene. Hence, the correct answer is cloning.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
CAMPBEL BIOLOGY:CONCEPTS & CONNECTIONS
- Use the following information to answer the question(s) below. Martin Wikelski and L. Michael Romero (Body size, performance and fitness in Galápagos marine iguanas, Integrative and Comparative Biology 43 [2003]:376-86) measured the snout-to-vent (anus) length of Galápagos marine iguanas and observed the percent survival of different-sized animals, all of the same age. The graph shows the log snout-vent length (SVL, a measure of overall body size) plotted against the percent survival of these different size classes for males and females. Survival (%) 100- 80- 60- 40- 20- 0+ 1.9 T 2 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 Log SVL (mm) 19) Examine the figure above. What type of selection for body size appears to be occurring in these marine iguanas? A) directional selection B) stabilizing selection C) disruptive selection D) You cannot determine the type of selection from the above information. 3arrow_forward24) Use the following information to answer the question below. Researchers studying a small milkweed population note that some plants produce a toxin and other plants do not. They identify the gene responsible for toxin production. The dominant allele (T) codes for an enzyme that makes the toxin, and the recessive allele (t) codes for a nonfunctional enzyme that cannot produce the toxin. Heterozygotes produce an intermediate amount of toxin. The genotypes of all individuals in the population are determined (see table) and used to determine the actual allele frequencies in the population. TT 0.49 Tt 0.42 tt 0.09 Refer to the table above. Is this population in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium? A) Yes. C) No; there are more homozygotes than expected. B) No; there are more heterozygotes than expected. D) It is impossible to tell.arrow_forward30) A B CDEFG Refer to the accompanying figure. Which of the following forms a monophyletic group? A) A, B, C, and D B) C and D C) D, E, and F D) E, F, and Garrow_forward
- Molecular Biology Question. Please help with step solution and explanation. Thank you: The Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) reaction consists of three steps denaturation, hybridization, and elongation. Please describe what occurs in the annealing step of the PCR reaction. (I think annealing step is hybridization). What are the other two steps of PCR, and what are their functions? Next, suppose the Tm for the two primers being used are 54C for Primer A and 67C for Primer B. Regarding annealing step temperature, I have the following choices for the temperature used during the annealing step:(a) 43C (b) 49C (c) 62C (d) 73C Which temperature/temperatures should I choose? What is the corresponding correct explanation, and why would I not use the other temperatures? Have a good day!arrow_forwardUsing the data provided on the mean body mass and horn size of 4-year-old male sheep, draw a scatterplot graph to examine how body mass and horn size changed over time.arrow_forwardPlease write a 500-word report about the intake of saturated fat, sodium, alcoholic beverages, or added sugar in America. Choose ONE of these and write about what is recommended by the Dietary Guidelines for Americans (guideline #4) and why Americans exceed the intake of that nutrient. Explain what we could do as a society and/or individuals to reduce our intake of your chosen nutrient.arrow_forward
 Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax





