
Concept explainers
Lysozyme is an enzyme that cleaves bacterial cell walls. A sample of lysozyme extracted from egg white has a molar mass of 13,930 g. A quantity of 0.100 g of this enzyme is dissolved in 150 g of water at 25°C. Calculate the vapor-pressure lowering, the depression in freezing point, the elevation in boiling point, and the osmotic pressure of this solution. (The vapor pressure of water at 25°C is 23.76 mmHg.)
Interpretation:
For given solution vapor pressure lowering, freezing point depression, boiling point elevation and osmotic pressures to be calculated.
Concept introduction
Boiling point elevation
Where,
Freezing point depression
Where,
Osmotic pressure is the pressure that is needed to stop osmosis. Osmotic pressure of the solution is directly proportional to the concentration of the solution. We can calculate osmotic pressure by using this formula is given by,
Where,
Vapor pressure lowering: Vapor pressure lowering is one of the colligative properties. Pure solvent has higher vapour pressure than its solution have non-volatile liquid. Thus vapour pressure lowering guide boiling point elevation.
Where,
Answer to Problem 12.83QP
Vapour pressure lowering of the solution = 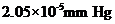
Freezing point elevation = 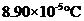
Boiling point elevation = 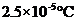
Osmotic pressure = 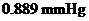
Explanation of Solution
Given data
Molar mass of egg white =
Amount of enzyme which is dissolved in water =
Amount of water =
Vapor pressure of water =
Calculation of number of moles in lysozyme and water
Molecular mass of water =
By plugging in the value of amount of Isozyme and molar mass of egg white, mole of Isozyme has calculated. Similarly, by plugging in the value of amount of water and molar mass of water, mole of water has calculated.
Calculation of vapour pressure lowering of the solution
By plugging in the values of mole fraction of Isozyme and vapour pressure of water, vapour pressure lowering of the solution has calculated.
Calculation freezing point depression of the solution
Molal freezing point depression constant =
By plugging in the values of molal freezing point depression constant and molality of the solution, freezing point depression of the solution has calculated.
Calculation of boiling point elevation of the solution
Boiling point elevation constant =
By plugging in the values of boiling point elevation constant and molality of the solution, boiling point elevation of the solution has calculated.
Calculation of osmotic pressure of the solution
As known above, we assume the density of the solution is
By plugging in the values of molarity of the solution, ideal gas constant and temperature in Kelvin, the osmotic pressure of the solution has calculated.
Vapour pressure lowering of the solution was calculated as
Freezing point elevation has calculated as
Boiling point elevation has calculated as
Osmotic pressure has calculated as
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
AVC LOOSELEAF CHEMISTRY W/CONNECT 2 SEM
- B 1 of 2 Additional problems in preparation to Midterm #1: 1.) How can the following compounds be prepared using Diels-Alder reaction: CH3 O CN (a) (b) CN CH3 2.) What is the missing reagent in the shown reaction? H3C + ? H3C H3C CN H3C ''CN (၁) H 3.) Write the products 1,2-addition and 1,4-addition of DBr to 1,3-cyclohexadiene. Remember, D is deuterium, a heavy isotope of hydrogen. It reacts exactly like hydrogen. 4.) In the shown reaction, which will be the kinetic product and which will be the thermodynamic product? H3C CI H3C HCI H3C + 5.) Which of the following molecules is aromatic? (a) (b) (c) H 6.) Which of the following molecules is aromatic? (a) (b) (c) 7.) Write the mechanism for the shown reaction. + Ха AICI 3 CI 8.) Suggest reagents that would convert benzene into the shown compounds. CI NO2 -8-6-6-8-a (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (a) SO3H Brarrow_forwardThe number of 2sp^2 hybridized atoms in is: A. 8; B. 6; C.4; D.2; E.0;arrow_forwardThe highest boiling compound from among the following isA. 2-methylheptane; B. 3-methylheptane; C. 2,2-dimethylhexane;D. octane; E. 2,2,3-trimethylpentanearrow_forward
- Which of the following features are found in the most stable structure ofCH5NO that does not have a CO bond?w. a π bond, x. two NH bonds, y. one OH bond, z. 3 lone pairsA. w, x; B. x, y; C. y, z; D. x, y, z; E. all of them.arrow_forwardWhich one of the following functional groups is not present in thecompound shownA. amine; B. aldehyde, C. ether; D. amide. E. ketonearrow_forwardWhich of the following formulas correspond to at least one compound inwhich resonance is important?w. C2H5N x. C3H5Br; y. C3H4; z. C4H6.A. w, x, y; B. x, y, z; C. w, x, z; D. w, y, z; E. all of themarrow_forward
- Predict the product(s) that are formed after each step for reactions 1-4. In each case, consider formation of any chiral center(s) and draw all expected stereoisomers. 1) OH 1) HBr (SN2) 2) NaOH, heat 3) BH3, THF 4) H2O2, NaOH 2) OH 1) SOCI 2, py 2) NaOEt 3) Br2, H₂O 3) OH 1) H2SO4 conc. 2) HBr, ROOR 3) KOtBu 4) OH 1) TsCl, py 2) NaOEt 3) 03 4) DMSarrow_forwardWhich of the following rings has the least strain in its most stableconformation?A. Cyclobutane; B. Cyclopentane; C. Cyclohexane; D. Cycloheptane;E. Cyclooctanearrow_forwardThe number of different carbon skeletons that have a main chain of 9carbons and an ethyl branch isA 3; B. 4; C. 5; D. 6; E. 7arrow_forward
- Q5: Classify the following pair of molecules as constitutional isomers, enantiomers, diastereomers, the same molecule, or completely different molecules. Br O CI Br OH OH 111 Br .!!!/Br F OH and ...m Br Br OH CI Br OH ་་་་་" ། ་arrow_forwardConsidering only rotation around the 1-2 bond, how many differentstaggered conformations are there of 1,2-dibromo-1,2-dichloropropane?A: 2; B. 3; C. 4; D. 6; E. more than 6.arrow_forwardcan you help me solve thisarrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning





