
(Learning Objectives 4, 5: Calculate and analyze ratios and earnings quality for a company in the restaurant industry)
Note: This case is part of The Cheesecake Factory serial case contained in every chapter in this textbook.
To follow are The Cheesecake Factory Incorporated's financial statements from its 2016 Form 10-K.
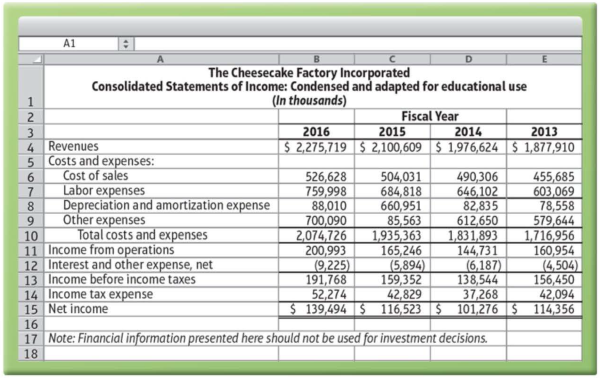
Data from the US. Securities and Exchange Commission EDGAR Company filings, www.sec.gov
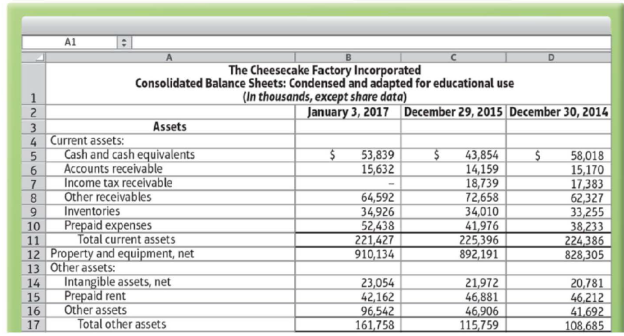
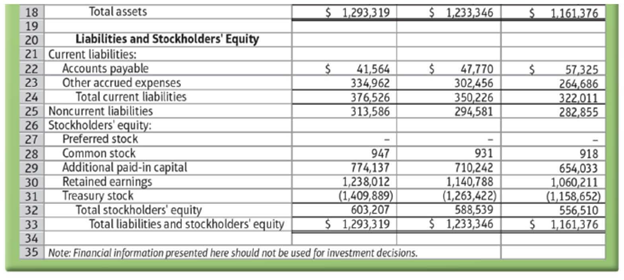
Data from the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission EDGAR Company filings, www.sec.gov
The preceding financial statements have been condensed and adapted for educational use and should not be used for investment decisions.
Requirements
1. Calculate The Cheesecake Factory’s net
2. Calculate The Cheesecake Factory’s
3. Calculate The Cheesecake Factory’s quick ratio for 2015 and 2016. Did the quick ratio improve or deteriorate?
4. How would you assess The Cheesecake Factory’s overall ability to pay its current liabilities? Explain.
5. Calculate inventory turnover for 2016. Next, calculate days' inventory outstanding. What does this number mean?
6. Calculate
7. Calculate accounts payable turnover for 2016. Next. calculate days’ payable outstanding. What does this number mean?
8. Calculate the cash conversion cycle (in days). Explain what this cash conversion cycle number means.
9. Calculate the debt ratio for 2016 and for 2015. Has the debt ratio increased or decreased?
10. Calculate the times-interest-earned ratio for 2016. Use “interest and other expense, net” as interest expense. What does this ratio mean?
11. Calculate the following profitability ratios for 2016:
- a. Gross margin percentage
- b. Operating income percentage
- c.
Rate of return on sales - d. Rate of return on assets
12. Comment on The Cheesecake Factory’s profitability in 2016 based on the profitability ratios you just calculated.
13. How would you evaluate the company’s earnings quality?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 12 Solutions
MyLab Accounting with Pearson eText -- Access Card -- for Financial Accounting
- Provide correct answerarrow_forwardFor the system shown in figure below, the per unit values of different quantities are E-1.2, V 1, X X2-0.4. Xa-0.2 Determine whether the system is stable for a sustained fault. The fault is cleared at 8-60°. Is the system stable? If so find the maximum rotor swing. Find the critical clearing angle. E25 G X'd 08 CB X2 F CB V28 Infinite busarrow_forwardGeisner Inc. has total assets of $1,000,000 and total liabilities of $600,000. The industry average debt-to-equity ratio is 1.20. Calculate Geisner's debt-to-equity ratio and indicate whether the company's default risk is higher or lower than the average of other companies in the industry.arrow_forward
- Hy expert give me solution this questionarrow_forwardBaker's Market began the current month with inventory costing $35,250, then purchased additional inventory at a cost of $78,400. The perpetual inventory system indicates that inventory costing $82,500 was sold during the month for $88,250. An inventory count at month-end shows that inventory costing $29,000 is actually on hand. What amount of shrinkage occurred during the month? a) $350 b) $1,150 c) $1,750 d) $2,150arrow_forwardA pet store sells a pet waste disposal system for $60 each. The cost per unit, including the system and enzyme digester, is $42.50. What is the contribution margin per unit? A. $15.00 B. $17.50 C. $12.25 D. $19.00arrow_forward
- Narchie sells a single product for $40. Variable costs are 80% of the selling price, and the company has fixed costs that amount to $152,000. Current sales total 16,000 units. What is the break-even point in units?arrow_forwardA company sells 32,000 units at $25 per unit. The variable cost per unit is $20.50, and fixed costs are $52,000. (a) Determine the contribution margin ratio. (b) Determine the unit contribution margin. (c) Determine the income from operations.arrow_forwardhello tutor provide solutionarrow_forward
- Gerry Co. has a gross profit of $990,000 and $290,000 in depreciation expenses. Selling and administrative expense is $129,000. Given that the tax rate is 37%, compute the cash flow for Gerry Co. a. $700,000 b. $128,963 c. $649,730 d. $652,230arrow_forwardProvide correct answer this financial accounting questionarrow_forwardWhat are the revenues for division l?arrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis...FinanceISBN:9781285190907Author:James M. Wahlen, Stephen P. Baginski, Mark BradshawPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis...FinanceISBN:9781285190907Author:James M. Wahlen, Stephen P. Baginski, Mark BradshawPublisher:Cengage Learning- Century 21 Accounting Multicolumn JournalAccountingISBN:9781337679503Author:GilbertsonPublisher:Cengage
 Fundamentals of Financial Management, Concise Edi...FinanceISBN:9781305635937Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Financial Management, Concise Edi...FinanceISBN:9781305635937Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning





