
(a)
Interpretation: The diagrams analogous to crystalline solids and amorphous solids are to be predicted.
Concept introduction: The solids can be classified into two forms on the basis of the arrangement of their constituent particles. These forms of solid are,
- Crystalline solids
- Amorphous solids
In crystalline solids the constituent particles are arranged in an organized manner in their given space and the crystals of crystalline solids have definite geometry.
On other hand in amorphous solids the constituent particles are arranged in an unorganized manner that is all the constituent particles are arranged randomly in the space provided to them and do not have definite geometry.
To determine: The drawing given in the stated figure is to be classified as being analogous to a crystalline solid or an amorphous solid.
Answer to Problem 12.1VP
Solution
The given diagramof constituent particlesis analogous to a crystalline solid.
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
The given figure is,
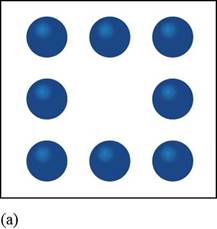
Figure 1
In the given figure, the constituent particles are arranged in an organized specific manner in the space provided to them and have definite geometry.
Therefore, the given diagram of constituent particles is analogous to a crystalline solid.
(b)
To determine: The drawing given in the stated figure is to be classified as being analogous to a crystalline solid or an amorphous solid.
(b)
Answer to Problem 12.1VP
Solution
The given diagram of constituent particles is analogous to a crystalline solid.
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
In the given figure, the constituent particles are arranged in an organized specific manner in the space provided to them and have definite geometry
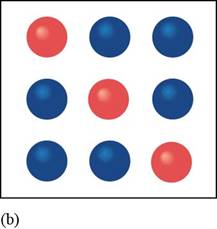
Figure
Therefore, the given diagram of constituent particles is analogous to a crystalline solid.
(c)
To determine: The drawing given in the stated figure is to be classified as being analogous to a crystalline solid or an amorphous solid..
(c)
Answer to Problem 12.1VP
Solution
The given diagram of constituent particles is analogous to an amorphous solid.
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
In the given figure, the constituent particles are not arranged in an organized manner in the space provided to them and do not have definite geometry
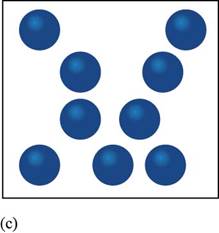
Figure
Therefore, the given diagram of constituent particles is analogous to an amorphous solid.
(d)
To determine: The drawing given in the stated figure is to be classified as being analogous to a crystalline solid or an amorphous solid..
(d)
Answer to Problem 12.1VP
Solution
The given diagram of constituted particles is analogous to an amorphous solid.
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
In the given figure, the constituent particles are not arranged in an organized manner in the space provided to them that is they are randomly arranged.
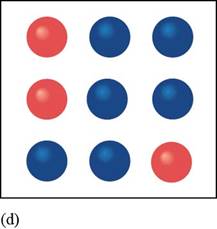
Figure
Therefore, the given diagram of constituted particles is analogous to an amorphous solid.
Conclusion
The conclusions are,
- a) The given diagram of constituent particles is analogous to a crystalline solid.
- b) The given diagram of constituent particles is analogous to a crystalline solid.
- c) The given diagram of constituent particles is analogous to an amorphous solid.
- d) The given diagram of constituent particles is analogous to an amorphous solid.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Chemistry: The Science in Context (Fifth Edition)
- Can I please get help with this?arrow_forwardUse the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation to calculate pH of a buffer containing 0.050M benzoic acidand 0.150M sodium benzoate. The Ka of benzoic acid is 6.5 x 10-5arrow_forwardA. Draw the structure of each of the following alcohols. Then draw and name the product you would expect to produce by the oxidation of each. a. 4-Methyl-2-heptanol b. 3,4-Dimethyl-1-pentanol c. 4-Ethyl-2-heptanol d. 5,7-Dichloro-3-heptanolarrow_forward
- What is the pH of a 1.0 L buffer made with 0.300 mol of HF (Ka = 6.8 × 10⁻⁴) and 0.200 mol of NaF to which 0.160 mol of NaOH were added?arrow_forwardCan I please get help with this.arrow_forwardDetermine if the following salt is neutral, acidic or basic. If acidic or basic, write the appropriate equilibrium equation for the acid or base that exists when the salt is dissolved in aqueous solution. If neutral, simply write only NR. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. N₂H₅ClO₄arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





