
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Whether the
Concept introduction:
Those compounds which have the same molecular formula but have different arrangements of atoms are known as isomers. The phenomenon is called isomerism. The isomers are generally classified as structural isomers and stereoisomers. Stereoisomers are further divided into two categories diastereomers and enantiomers.
Answer to Problem 12.18E
The alkene
Explanation of Solution
The alkene is
A compound shows cis-trans isomerism when the substituent groups on the carbon atoms that are connected via double bond are different. The alkene has the same substituted groups on a carbon atom that is on the right-hand side of the double bond. Therefore; it will not have cis-trans isomerism.
The alkene
(b)
Interpretation:
Whether the alkene
Concept introduction:
Those compounds which have the same molecular formula but have different arrangements of atoms are known as isomers. This phenomenon is called isomerism. The isomers are generally classified as structural isomers and stereoisomers. Stereoisomers are further divided into two categories diastereomers and enantiomers.
Answer to Problem 12.18E
The alkene
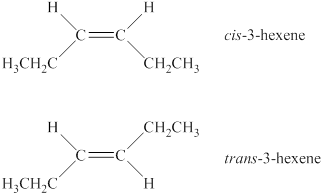
Explanation of Solution
The alkene is
A compound shows cis-trans isomerism when the substituents groups on the carbon atoms that are connected via double bond are different. The alkene has two different substituted groups on carbon atoms that are connected via a double bond. Therefore, it will show cis-trans isomerism. In the cis isomer, same substituted groups are on the same side of a ring or double bonds, whereas in the trans isomer same substituted groups are on a different side of a ring or double bond. Therefore, the structures of cis-trans isomers of the alkene are shown below.

Figure 1
The alkene
(c)
Interpretation:
Whether the alkene
Concept introduction:
Those compounds which have the same molecular formula but have different arrangements of atoms are known as isomers. The phenomenon is called isomerism. The isomers are generally classified as structural isomers and stereoisomers. Stereoisomers are further divided into two categories diastereomers and enantiomers.
Answer to Problem 12.18E
The alkene
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the alkene
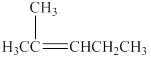
Figure 2
A compound shows cis-trans isomerism when the substituents groups on the carbon atoms that are connected via double bond are different. The alkene has the same substituted groups on a carbon atom that is on the left-hand side of the double bond. Therefore, it will not have cis-trans isomerism.
The alkene
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Chemistry For Today: General, Organic, And Biochemistry, Loose-leaf Version
- Based on the chart Two similarities between the molecule with alpha glycosidic linkages. Two similarities between the molecules with beta glycosidtic linkages. Two differences between the alpha and beta glycosidic linkages.arrow_forwardplease help fill in the tablearrow_forwardAnswer F pleasearrow_forward
- 4. Refer to the data below to answer the following questions: The octapeptide saralasin is a specific antagonist of angiotensin II. A derivative of saralasin is used therapeutically as an antihypertensive. Amino acid analysis of saralasin show the presence of the following amino acids: Ala, Arg, His, Pro, Sar, Tyr, Val, Val A.Sar is the abbreviation for sarcosine, N-methyl aminoethanoic acid. Draw the structure of sarcosine. B. N-Terminal analysis by the Edman method shows saralasin contains sarcosine at the N-terminus. Partial hydrolysis of saralasin with dilute hydrochloric acid yields the following fragments: Tyr-Val-His Sar-Arg-Val His-Pro-Ala Val-Tyr-Val Arg-Val-Tyr What is the structure of saralasin?arrow_forwardWhat is the structure of the DNA backbone?arrow_forwardPLEASE PLEASE PLEASE use hand drawn structures when possarrow_forward
- . M 1- MATCH each of the following terms to a structure from the list below. There is only one correct structure for each term and structures may be used more than once. Place the letter of the structure in the blank to the left of the corresponding term. A. Sanger dideoxy method C. Watson-Crick B. GAUCGUAAA D. translation E. HOH2C OH OH G. transcription I. AUGGCUGAG 0 K. OPOH2C 0- OH N- H NH2 F. -OPOH2C 0- OH OH H. Maxam-Gilbert method J. replication N L. HOH2C a. b. C. d. e. f. g. B M. AGATCGCTC a pyrimidine nucleoside RNA base sequence with guanine at the 3' end. DNA base sequence with cytosine at the 3' end. a purine nucleoside DNA sequencing method for the human genome 2'-deoxyadenosine 5'-phosphate process by which mRNA directs protein synthesis OH NH2arrow_forwardPlease use hand drawn structures when neededarrow_forwardB. Classify the following amino acid. Atoms other than carbon and hydrogen are labeled. a. acidic b. basic C. neutral C. Consider the following image. Which level of protein structure is shown here? a. primary b. secondary c. tertiary d. quaternary D. Consider the following image. H RH H HR H R HR HR RH Which level of protein structure is shown in the box? a. primary b. secondary R c. tertiary d. quaternary コー Rarrow_forward
- Briefly answer three from the followings: a. What are the four structures of the protein? b. Why is the side chain (R) attached to the alpha carbon in the amino acids is important for the function? c. What are the types of amino acids? And how is it depend on the (R) structure? d. Write a reaction to prepare an amino acid. prodarrow_forwardAnswe Answer A and B pleasearrow_forward3. Refer to the data below to answer the following questions: Isoelectric point Amino Acid Arginine 10.76 Glutamic Acid 3.22 Tryptophan 5.89 A. Define isoelectric point. B. The most basic amino acid is C. The most acidic amino acid is sidizo zoarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning





