
(a)
Interpretation:
The Lewis structure for given acetone and carbon disulfide molecules should be determined and the deviation from ideal behavior should be explained using intermolecular forces.
Concept Introduction:
- The Lewis structure is based on the concept of the octet rule so that the electrons shared in each atom should have 8 electrons in its outer shell.
- Sometimes the
chemical bonding of a molecule cannot be represented using a single Lewis structure. In these cases, the chemical bonding are described by delocalization of electrons and is known as resonance.
Lewis structure for any molecule is drawn by using the following steps,
First the skeletal structure for the given molecule is drawn then the total number of valence electrons for all atoms present in the molecule is determined
The next step is to subtract the electrons present in the total number of bonds present in the skeletal structure of the molecule with the total valence electrons such that considering each bond contains two electrons with it.
Finally, the electrons which got after subtractions have to be equally distributed such that each atom contains eight electrons in its valence shell.
Intermolecular force: The attractive force that withholds two molecules is called as intermolecular force. The influence of intermolecular forces depends on molar mass and the
Types and strength of intermolecular forces in decreasing order:
Polar molecule: Polar molecules have large dipole moments.
Non-Polar molecules: Non-polar molecules have bonded atoms with similar electronegativity results to have zero dipole moments.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
The Lewis structures are as follows,
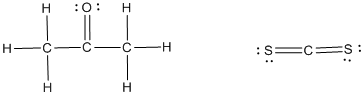
The given molecule acetone is polar whereas the molecule carbon disulfide is nonpolar molecule.
According to Like dissolves like principle, the attraction between acetone and
Due to weak attractions the molecules will leave the solution that result in increased vapor pressure of the solution than the sum of vapor pressures by Raoutl’s law.
(b)
Interpretation:
The vapor pressure of the solution under ideal condition should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Raoult’s law: Raoult’s law states that solvent partial pressure over a solution is equal to vapor pressure of pure solvent multiplied with mole fraction of the solvent.
Where,
The solution that obeys Raoult’s law is defined as ideal solution.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
The ideal solution should obey Raoult’s law.
Partial pressure for A is as follows,
Partial pressure for B is as follows,
The ideal pressure of the solution is
(c)
Interpretation:
The sign of
Concept Introduction:
Enthalpy
Enthalpy is the amount energy absorbed or released in a process.
The enthalpy change in a system
Where,
(c)
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule acetone is polar whereas the molecule carbon disulfide is nonpolar molecule.
According to Like dissolves like principle, the attraction between acetone and
Due to weak attractions the molecules will leave the solution that result in increased vapor pressure of the solution than the sum of vapor pressures by Raoutl’s law.
Therefore, the solution deviates positively from Raoutl’s law which says that heat of solution is positive that means mixing is an endothermic process (heat is absorbed by the system).
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
ALEKS 360; 18WKS F/ GEN. CHEMISTRY >I<
- What would you expect to be the major product obtained from the following reaction? Please explain what is happening here. Provide a detailed explanation and a drawing showing how the reaction occurs. The correct answer to this question is V.arrow_forwardPlease answer the question for the reactions, thank youarrow_forwardWhat is the product of the following reaction? Please include a detailed explanation of what is happening in this question. Include a drawing showing how the reagent is reacting with the catalyst to produce the correct product. The correct answer is IV.arrow_forward
- Please complete the reactions, thank youarrow_forwardConsider the synthesis. What is compound Y? Please explain what is happening in this question. Provide a detailed explanation and a drawing to show how the compound Y creates the product. The correct answer is D.arrow_forwardWhat would be the major product of the following reaction? Please include a detailed explanation of what is happening in this question. Include steps and a drawing to show this reaction proceeds and how the final product is formed. The correct answer is B. I put answer D and I don't really understand what is going on in the question.arrow_forward
- What is the product of the following reaction? Please explain what is happening in this question. Provide a detailed explanation and a drawing showing how the reagent is reacting with the catalysts to product the correct product. The correct answer is B.arrow_forwardWhat is the missing intermediate 1 and the final product 2. Please include a detailed explanation explaining the steps of malonic ester synthesis. Please include drawings of the intermediate and how it occurs and how the final product is former.arrow_forwardWhat would be the reagents and conditions above and below the arrow that will complete the proposed acetoacetic ester synthesis? If it cannot be done efficiently, then I will choose that answer. There could be 2 or 4 reagents involved. Please provide a detailed explanation and drawings showing how it would proceed with the correct reagents.arrow_forward
- For benzene, the ∆H° of vaporization is 30.72 kJ/mol and the ∆S° of vaporization is 86.97 J/mol・K. At 1.00 atm and 228.0 K, what is the ∆G° of vaporization for benzene, in kJ/mol?arrow_forwardThe reaction Q(g) + R(g) → Z(l) is shown to be exothermic. Which of the following is true concerning the reaction. it is spontaneous only at High T, it is spontaneous at low T it is nonspontaneous at all T it is spontanrous at all T. it is non spontaneous only at low T.arrow_forwardThe reaction Q(g) + R(g) → Z(l) is shown to be exothermic. Which of the following is true concerning the reactionarrow_forward
- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning  Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning





