
EBK MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
7th Edition
ISBN: 8220100257063
Author: BEER
Publisher: YUZU
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 11.9, Problem 92P
For the beam and loading shown, determine the deflection of point A. Use E = 29 × 106 psi.
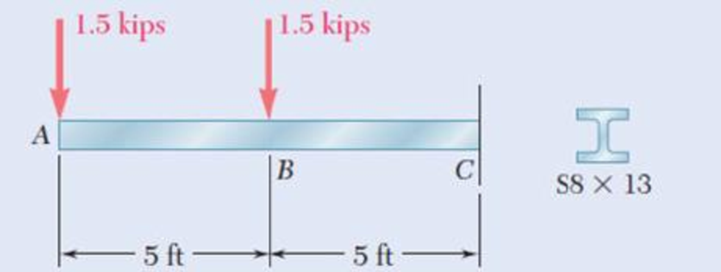
Fig. P11.91 and P11.92
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
CE-112 please solve this problem step by step and give me the correct answer
CE-112 please solve this problem step by step and give me the correct answer
CE-112 solve this problem step by step and give me the correct answer please
Chapter 11 Solutions
EBK MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
Ch. 11.3 - Determine the modulus of resilience for each of...Ch. 11.3 - Determine the modulus of resilience for each of...Ch. 11.3 - Determine the modulus of resilience for each of...Ch. 11.3 - Determine the modulus of resilience for each of...Ch. 11.3 - The stress-strain diagram shown has been drawn...Ch. 11.3 - The stress-strain diagram shown has been drawn...Ch. 11.3 - Prob. 7PCh. 11.3 - Prob. 8PCh. 11.3 - Using E = 29 106 psi, determine (a) the strain...Ch. 11.3 - Using E = 200 GPa, determine (a) the strain energy...
Ch. 11.3 - A 30-in. length of aluminum pipe of...Ch. 11.3 - A single 6-mm-diameter steel pin B is used to...Ch. 11.3 - Prob. 13PCh. 11.3 - Prob. 14PCh. 11.3 - The assembly ABC is made of a steel for which E =...Ch. 11.3 - Show by integration that the strain energy of the...Ch. 11.3 - Prob. 17PCh. 11.3 - Prob. 18PCh. 11.3 - Prob. 19PCh. 11.3 - 11.18 through 11.21 In the truss shown, all...Ch. 11.3 - Prob. 21PCh. 11.3 - Each member of the truss shown is made of aluminum...Ch. 11.3 - Each member of the truss shown is made of aluminum...Ch. 11.3 - 11.24 through 11.27 Taking into account only the...Ch. 11.3 - Prob. 25PCh. 11.3 - 11.24 through 11.27 Taking into account only the...Ch. 11.3 - 11.24 through 11.27 Taking into account only the...Ch. 11.3 - Prob. 28PCh. 11.3 - Prob. 29PCh. 11.3 - Prob. 30PCh. 11.3 - 11.30 and 11.31 Using E = 200 GPa, determine the...Ch. 11.3 - Assuming that the prismatic beam AB has a...Ch. 11.3 - Prob. 33PCh. 11.3 - The design specifications for the steel shaft AB...Ch. 11.3 - Show by integration that the strain energy in the...Ch. 11.3 - The state of stress shown occurs in a machine...Ch. 11.3 - Prob. 37PCh. 11.3 - The state of stress shown occurs in a machine...Ch. 11.3 - Prob. 39PCh. 11.3 - Prob. 40PCh. 11.3 - Prob. 41PCh. 11.5 - A 5-kg collar D moves along the uniform rod AB and...Ch. 11.5 - The 18-lb cylindrical block E has a horizontal...Ch. 11.5 - The cylindrical block E has a speed v0 =16 ft/s...Ch. 11.5 - Prob. 45PCh. 11.5 - Prob. 46PCh. 11.5 - The 48-kg collar G is released from rest in the...Ch. 11.5 - Prob. 48PCh. 11.5 - Prob. 49PCh. 11.5 - Prob. 50PCh. 11.5 - Prob. 51PCh. 11.5 - The 2-kg block D is dropped from the position...Ch. 11.5 - The 10-kg block D is dropped from a height h = 450...Ch. 11.5 - Prob. 54PCh. 11.5 - A 160-lb diver jumps from a height of 20 in. onto...Ch. 11.5 - Prob. 56PCh. 11.5 - A block of weight W is dropped from a height h...Ch. 11.5 - 11.58 and 11.59 Using the method of work and...Ch. 11.5 - 11.58 and 11.59 Using the method of work and...Ch. 11.5 - 11.60 and 11.61 Using the method of work and...Ch. 11.5 - 11.60 and 11.61 Using the method of work and...Ch. 11.5 - 11.62 and 11.63 Using the method of work and...Ch. 11.5 - 11.62 and 11.63 Using the method of work and...Ch. 11.5 - Using the method of work and energy, determine the...Ch. 11.5 - Using the method of work and energy, determine the...Ch. 11.5 - The 20-mm diameter steel rod BC is attached to the...Ch. 11.5 - Torques of the same magnitude T are applied to the...Ch. 11.5 - Prob. 68PCh. 11.5 - The 20-mm-diameter steel rod CD is welded to the...Ch. 11.5 - The thin-walled hollow cylindrical member AB has a...Ch. 11.5 - 11.71 and 11.72 Each member of the truss shown has...Ch. 11.5 - 11.71 and 11.72 Each member of the truss shown has...Ch. 11.5 - Each member of the truss shown is made of steel...Ch. 11.5 - Each member of the truss shown is made of steel....Ch. 11.5 - Each member of the truss shown is made of steel...Ch. 11.5 - The steel rod BC has a 24-mm diameter and the...Ch. 11.9 - 11.77 and 11.78 Using the information in Appendix...Ch. 11.9 - 11.77 and 11.78 Using the information in Appendix...Ch. 11.9 - 11.79 through 11.82 For the beam and loading...Ch. 11.9 - 11.79 through 11.82 For the beam and loading...Ch. 11.9 - 11.79 through 11.82 For the beam and loading...Ch. 11.9 - 11.79 through 11.82 For the beam and loading...Ch. 11.9 - 11.83 through 11.85 For the prismatic beam shown,...Ch. 11.9 - 11.83 through 11.85 For the prismatic beam shown,...Ch. 11.9 - 11.83 through 11.85 For the prismatic beam shown,...Ch. 11.9 - 11.86 through 11.88 For the prismatic beam shown,...Ch. 11.9 - 11.86 through 11.88 For the prismatic beam shown,...Ch. 11.9 - 11.86 through 11.88 For the prismatic beam shown,...Ch. 11.9 - For the prismatic beam shown, determine the slope...Ch. 11.9 - For the prismatic beam shown, determine the slope...Ch. 11.9 - For the beam and loading shown, determine the...Ch. 11.9 - For the beam and loading shown, determine the...Ch. 11.9 - 11.93 and 11.94 For the beam and loading shown,...Ch. 11.9 - 11.93 and 11.94 For the beam and loading shown,...Ch. 11.9 - For the beam and loading shown, determine the...Ch. 11.9 - For the beam and loading shown, determine the...Ch. 11.9 - Prob. 97PCh. 11.9 - For the beam and loading shown, determine the...Ch. 11.9 - 11.99 and 11.100 For the truss and loading shown,...Ch. 11.9 - 11.99 and 11.100 For the truss and loading shown,...Ch. 11.9 - 11.101 and 11.102 Each member of the truss shown...Ch. 11.9 - 11.101 and 11.102 Each member of the truss shown...Ch. 11.9 - 11.103 and 11.104 Each member of the truss shown...Ch. 11.9 - 11.103 and 11 104 Each member of the truss shown...Ch. 11.9 - A uniform rod of flexural rigidity EI is bent and...Ch. 11.9 - For the uniform rod and loading shown and using...Ch. 11.9 - For the beam and loading shown and using...Ch. 11.9 - Two rods AB and BC of the same flexural rigidity...Ch. 11.9 - Three rods, each of the same flexural rigidity EI,...Ch. 11.9 - Three rods, each of the same flexural rigidity EI,...Ch. 11.9 - 11.111 through 11.115 Determine the reaction at...Ch. 11.9 - 11.111 through 11.115 Determine the reaction at...Ch. 11.9 - 11.111 through 11.115 Determine the reaction at...Ch. 11.9 - 11.111 through 11.115 Determine the reaction at...Ch. 11.9 - 11.111 through 11.115 Determine the reaction at...Ch. 11.9 - For the uniform beam and loading shown, determine...Ch. 11.9 - 11.117 through 11.120 Three members of the same...Ch. 11.9 - 11.117 through 11.120 Three members of the same...Ch. 11.9 - 11.117 through 11.120 Three members of the same...Ch. 11.9 - 11.117 through 11.120 Three members of the same...Ch. 11.9 - 11.121 and 11.122 Knowing that the eight members...Ch. 11.9 - 11.121 and 11.122 Knowing that the eight members...Ch. 11 - Rod AB is made of a steel for which the yield...Ch. 11 - Each member of the truss shown is made of steel...Ch. 11 - The ship at A has just started to drill for oil on...Ch. 11 - Collar D is released from rest in the position...Ch. 11 - Each member of the truss shown is made of steel...Ch. 11 - A block of weight W is placed in contact with a...Ch. 11 - Two solid steel shafts are connected by the gears...Ch. 11 - A 160-lb diver jumps from a height of 20 in. onto...Ch. 11 - For the prismatic beam shown, determine the slope...Ch. 11 - A disk of radius a has been welded to end B of the...Ch. 11 - A uniform rod of flexural rigidity EI is bent and...Ch. 11 - The steel bar ABC has a square cross section of...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Please do not use any AI tools to solve this question. I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor. No AI-generated responses, please.arrow_forwardPlease do not use any AI tools to solve this question. I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor. No AI-generated responses, please.arrow_forwardCE-112 please solve this problem step by step and give me the correct answerarrow_forward
- CE-112 please solve this problem step by step and give me the correct asnwerarrow_forwardthis is an old practice exam, the answer is Ax = -4, Ay = -12,Az = 32.5, Bx= 34, Bz = 5, By = 0 but how?arrow_forwardThis is an old practice exam, the answer is Ax = Az = 0, Ay = 2000, TDE = 4750, Cx = 2000, Cy = 2000, Cz = -800 but how?arrow_forward
- this is an old practice exam, the answer is Fmin = 290.5lb but howarrow_forwardThis is an exam review question. The answer is Pmin = 622.9 lb but whyarrow_forwardPlease do not use any AI tools to solve this question. I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor. No AI-generated responses, please.arrow_forward
- Please do not use any AI tools to solve this question. I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor. No AI-generated responses, please.arrow_forwardPlease do not use any AI tools to solve this question. I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor. No AI-generated responses, please.arrow_forwardThis is an old practice exam. Fce = 110lb and FBCD = 62 lb but whyarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L Automotive Technology: A Systems Approach (MindTa...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781133612315Author:Jack Erjavec, Rob ThompsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Automotive Technology: A Systems Approach (MindTa...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781133612315Author:Jack Erjavec, Rob ThompsonPublisher:Cengage Learning Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Technology (Mi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305578296Author:John Tomczyk, Eugene Silberstein, Bill Whitman, Bill JohnsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Technology (Mi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305578296Author:John Tomczyk, Eugene Silberstein, Bill Whitman, Bill JohnsonPublisher:Cengage Learning

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:CENGAGE L

Automotive Technology: A Systems Approach (MindTa...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781133612315
Author:Jack Erjavec, Rob Thompson
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305387102
Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Technology (Mi...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305578296
Author:John Tomczyk, Eugene Silberstein, Bill Whitman, Bill Johnson
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanical SPRING DESIGN Strategy and Restrictions in Under 15 Minutes!; Author: Less Boring Lectures;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dsWQrzfQt3s;License: Standard Youtube License