
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780137605521
Author: HIBBELER
Publisher: RENT PEARS
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 11.2, Problem 42P
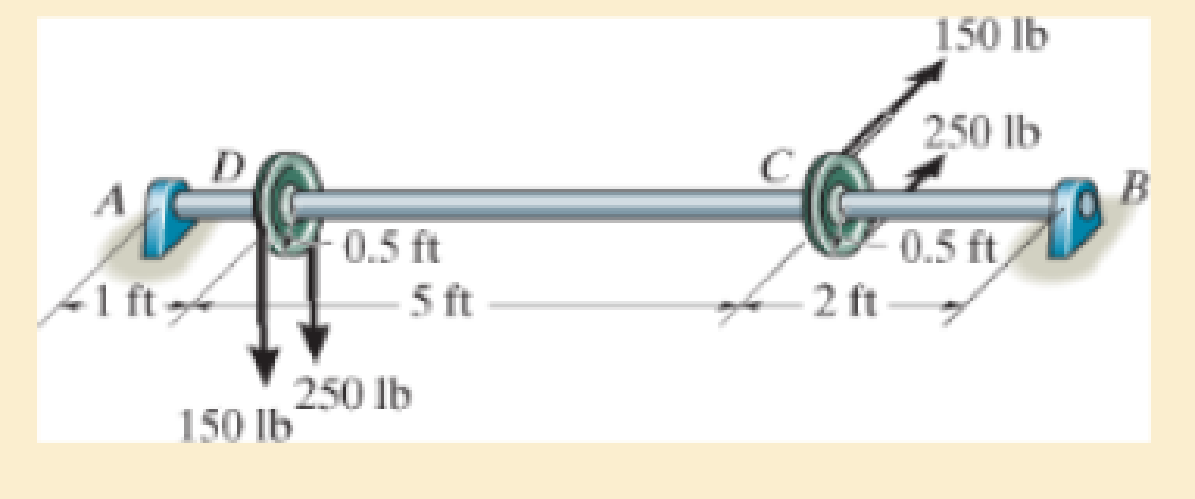
The pulleys fixed to the shaft are loaded as shown. If the journal bearings at A and B exert only horizontal and vertical forces on the shaft, determine the required diameter of the shaft to the nearest
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Solve this problem and show all of the work
Practice
L[sin at]
Find the Hertzian stresses and the maximum shear stress for the wheel.
Chapter 11 Solutions
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
Ch. 11.2 - Determine the minimum dimension a to the nearest...Ch. 11.2 - of the rod to safely support the load. The rod is...Ch. 11.2 - The wood has an allowable normal stress of allow =...Ch. 11.2 - of the beam's cross section to safely support the...Ch. 11.2 - Determine the minimum dimension b to the nearest...Ch. 11.2 - The beam is made of steel having an allowable...Ch. 11.2 - Determine the minimum width of the beam to the...Ch. 11.2 - if P=10 kip.Ch. 11.2 - The beam has an allowable normal stress of allow...Ch. 11.2 - If each beam is to be designed to carry 90 lb/ft...
Ch. 11.2 - Determine its height h so that it simultaneously...Ch. 11.2 - to safely support the load. The wood has an...Ch. 11.2 - and the wood has an allowable normal stress of...Ch. 11.2 - if allow = 30 ksi and allow = 15 ksi. The journal...Ch. 11.2 - if allow = 30 ksi and allow = 15 ksi. The journal...Ch. 11.2 - The tapered beam supports a uniform distributed...Ch. 11.2 - Determine the variation in the depth d of a...Ch. 11.2 - Prob. 41PCh. 11.2 - The pulleys fixed to the shaft are loaded as...Ch. 11.2 - Prob. 43PCh. 11.2 - Prob. 44PCh. 11 - The cantilevered beam has a circular cross...Ch. 11 - Select the lightest-weight wide-flange overhanging...Ch. 11 - Prob. 3RPCh. 11 - Determine the shaft's diameter to the nearest...Ch. 11 - Select the lightest-weight wide-flange beam from...Ch. 11 - The simply supported joist is used in the...Ch. 11 - The simply supported joist is used in the...Ch. 11 - by 4-in. pieces of wood braced as shown. If the...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Can I get help on this question?arrow_forwardDuring some actual expansion and compression processes in piston–cylinder devices, the gases have been observed to satisfy the relationship PVn = C, where n and C are constants. Calculate the work done when a gas expands from 350 kPa and 0.03 m3 to a final volume of 0.2 m3 for the case of n = 1.5. The work done in this case is kJ.arrow_forwardCarbon dioxide contained in a piston–cylinder device is compressed from 0.3 to 0.1 m3. During the process, the pressure and volume are related by P = aV–2, where a = 6 kPa·m6. Calculate the work done on carbon dioxide during this process. The work done on carbon dioxide during this process is kJ.arrow_forward
- The volume of 1 kg of helium in a piston–cylinder device is initially 5 m3. Now helium is compressed to 3 m3 while its pressure is maintained constant at 130 kPa. Determine the initial and final temperatures of helium as well as the work required to compress it, in kJ. The gas constant of helium is R = 2.0769 kJ/kg·K. The initial temperature of helium is K. The final temperature of helium is K. The work required to compress helium is kJ.arrow_forwardA piston-cylinder device initially contains 0.4 kg of nitrogen gas at 160 kPa and 140°C. Nitrogen is now expanded isothermally to a pressure of 80 kPa. Determine the boundary work done during this process. The properties of nitrogen are R= 0.2968 kJ/kg-K and k= 1.4. N₂ 160 kPa 140°C The boundary work done during this process is KJ.arrow_forward! Required information An abrasive cutoff wheel has a diameter of 5 in, is 1/16 in thick, and has a 3/4-in bore. The wheel weighs 4.80 oz and runs at 11,700 rev/min. The wheel material is isotropic, with a Poisson's ratio of 0.20, and has an ultimate strength of 12 kpsi. Choose the correct equation from the following options: Multiple Choice о σmax= (314) (4r2 — r²) - о σmax = p² (3+) (4r² + r²) 16 σmax = (314) (4r² + r²) σmax = (314) (4² - r²)arrow_forward
- I don't know how to solve thisarrow_forwardI am not able to solve this question. Each part doesn't make sense to me.arrow_forwardExercises Find the solution of the following Differential Equations 1) y" + y = 3x² 3) "+2y+3y=27x 5) y"+y=6sin(x) 7) y"+4y+4y = 18 cosh(x) 9) (4)-5y"+4y = 10 cos(x) 11) y"+y=x²+x 13) y"-2y+y=e* 15) y+2y"-y'-2y=1-4x³ 2) y"+2y' + y = x² 4) "+y=-30 sin(4x) 6) y"+4y+3y=sin(x)+2 cos(x) 8) y"-2y+2y= 2e* cos(x) 10) y+y-2y=3e* 12) y"-y=e* 14) y"+y+y=x+4x³ +12x² 16) y"-2y+2y=2e* cos(x)arrow_forward
- Qu. 15 What are the indices for the Plane 1 drawn in the following sketch? Qu. 16 What are the Miller indices for the Plane shown in the following cubic unit cell? this is material engineering please show all workarrow_forwardI do not understand how to approach this question. I tried to answer it but I kept getting it incorrect.arrow_forward(read image)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Power Transmission; Author: Terry Brown Mechanical Engineering;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YVm4LNVp1vA;License: Standard Youtube License