
The tournament sort is a sorting algorithm that works by building an ordered binary tree. We represent the elements to be sorted by vertices that sill become the leaves. We build up the tree one level at a time we would construct the tree representing the winners of matches in a tournament Working left to right, we compare pairs of consecutive elements, adding a parent vertex labeled with the larger of the two elements under comparison. We make similar comparisons between labels of vertices at each level until we reach the root of the tree that is labeled with the largest element. The tree constructed by the tournament sort of , 8.14,17,3,9,27,11 is ilinstrated in part(a)ef the figure. Once the argestelementhbeendetermined. The leaf with this labelisrelabeled by -s,which is definedtobelessthanevery element The labels of all vertices on the path from this vertex up to the root of the tree are recalculated, as shown in part (b) of the figure.
This produces the second largest element This process continues until the entire list has been sorted.
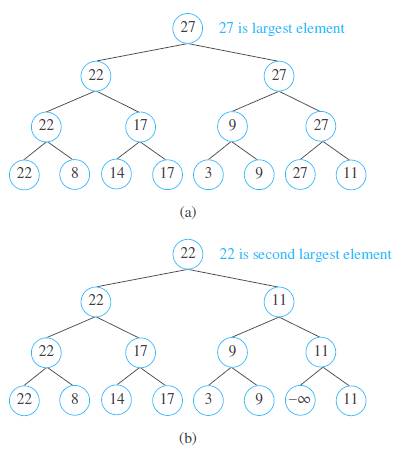
18. Show that the tournament sort requires (3(n log n) comparisons to sort a list of n elements. [Hint: By iierting the appropriate number of dummy elements defined to be smaller than all integers, such as -z, assume that n = 2k for some positive integer k.]
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 11 Solutions
DISCRETE MATHEMATICS LOOSELEAF
- Use the critical path algorithm to create a priority list for the digraph below. T4 (5) Т6 (11) T1 (8) End T2 (10) T5 (6) T7 (7) ТЗ (12) Priority list: Give the priority as a list of task numbers. For example, you'd enter something like: 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10arrow_forwardComplete the tree diagram by filling in the missing entries below.arrow_forwardCreate a tree diagram to show the possible answer combinations of the first three questions on the take-home assignment.arrow_forward
- Use the critical path algorithm to create a priority list for the digraph below. T1 (2) T4 (12) Т6 (5) End T2 (7) T5 (4) T7 (11) Т3 (9) Priority list: Give the priority as a list of task numbers. For example, you'd enter something like: 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10arrow_forwardDiagram the recursive tree in a number of paths method: numPath(row: 3, col: 3) starting location: 0,0 please draw the recursive tree that goes up to 3, 3 in the numPath call method.arrow_forwardCoordinates for a clipping window and a line are given in the following figure. Use Liang- Q1. Barsky algorithm to clip this line with respect to the clipping window. Show your steps and calculations clearly. Ymax=20- Po(8, 12) Ymin=10 P1(30,6) Xmin=10 Xmax=20arrow_forward
- John discovered that he also has a pair of boots and a pair of dress shoes in his closet. Make a tree diagram showing all of the possible shirt, pant, and shoe combinations.arrow_forwardChess is a board game, where the board is made up of 64 squares arranged in an 8-by-8 grid. One of the pieces is a rook, which can move from its current square any number of spaces either vertically or horizontally (but not diagonally) in a single turn. Discuss how you could use graphs to show that a rook can get from its current square to any other square on the board in at most two turns. You’re encouraged to utilize relevant graph definitions, problems, and algorithms where appropriate.arrow_forwardA box contains 3 black spheres and 4 white spheres. Draw a tree diagram to represent the procedure of selecting 3 spheres from the box WITHOUT replacement.arrow_forward
- Explain the step by step procedure of Dijktra’s algorithm to find the shortest path between any two vertices?arrow_forwardPlease help me with these questions. I am having trouble understanding what to do. Please show all your work Thank youarrow_forwardConstruct a KD tree for the following points. (17, 15)(2, 7)(13, 15)(9, 1)(6, 12)(3, 6)(10, 19)arrow_forward
 Discrete Mathematics and Its Applications ( 8th I...MathISBN:9781259676512Author:Kenneth H RosenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Discrete Mathematics and Its Applications ( 8th I...MathISBN:9781259676512Author:Kenneth H RosenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Mathematics for Elementary Teachers with Activiti...MathISBN:9780134392790Author:Beckmann, SybillaPublisher:PEARSON
Mathematics for Elementary Teachers with Activiti...MathISBN:9780134392790Author:Beckmann, SybillaPublisher:PEARSON
 Thinking Mathematically (7th Edition)MathISBN:9780134683713Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON
Thinking Mathematically (7th Edition)MathISBN:9780134683713Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON Discrete Mathematics With ApplicationsMathISBN:9781337694193Author:EPP, Susanna S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Discrete Mathematics With ApplicationsMathISBN:9781337694193Author:EPP, Susanna S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Pathways To Math Literacy (looseleaf)MathISBN:9781259985607Author:David Sobecki Professor, Brian A. MercerPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Pathways To Math Literacy (looseleaf)MathISBN:9781259985607Author:David Sobecki Professor, Brian A. MercerPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





