
Concept explainers
(a)
The accelerations of A
(a)
Answer to Problem 11.60P
The accelerations of A
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The relative change in position of block C with respect to block A
The relative velocity of collar B with respect to block A
The displacement of A
The displacement of B
Calculation:
Show the length and position of the cables as in Figure (1).
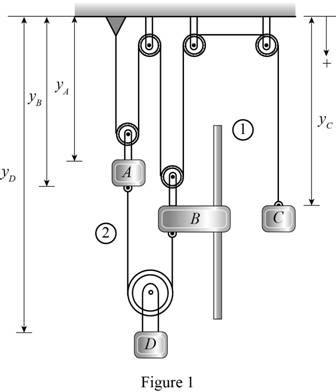
Choose the coordinate downward positive and right side positive.
Write the express for total lengths of cables 1:
Differentiate the above equation with respective to time (t).
Denotes
Differentiate the equation (2) with respective to time (t).
Denotes
Write the express for total lengths of cables 2:
Differentiate the above equation with respective to time (t).
Denotes
Differentiate the equation (3) with respective to time (t).
Denotes
At time (t) 0 sec the velocity (v) is zero.
Then, the initial position of cable A, cable B and cable C is equal.
Calculate the position
Here,
Substitute 0 for
Calculate the position
Here,
Substitute 0 for
Calculate the position
Here,
Substitute 0 for
Write the expression for relative change in position of block C with respect to block A:
Substitute
Write the equation for acceleration
Substitute
Calculate the acceleration of block A:
Substitute
Calculate the velocity
Substitute 0 for
Calculate the velocity
Substitute 0 for
Write the equation for relative velocity of block B with respect to block A
Substitute
Substitute
Modify the equation (5).
Substitute
Modify the equation (7).
Substitute
Calculate the time (t):
Substrate equation (13) and (12).
Substitute
Calculate the acceleration
Substitute 4 sec for t in equation (12).
Therefore, the accelerations of A
(b)
The change in position
(b)
Answer to Problem 11.60P
The change in position
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The relative change in position of block C with respect to block A
The relative velocity of collar B with respect to block A
The displacement of A
The displacement of B
The velocity
Calculation:
Calculate the acceleration
Substitute
Calculate the acceleration
Substitute
Calculate the time (t) using the relation below;
Here,
Substitute 0 for
Calculate the change in positon
Here,
Substitute 0 for
Therefore, the change in position
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
<LCPO> VECTOR MECH,STAT+DYNAMICS
- arch Moving to año Question 5 The head-vs-capacity curves for two centrifugal pumps A and B are shown below: Which of the following is a correct statement at a flow rate of 600 ft3/min? Assuming a pump efficiency of 80%. Head [ft] 50 45. 40 CHE 35. 30 25 20 PR 64°F Cloudy 4arrow_forwardI need help with a MATLAB code. I am trying to implement algorithm 3 and 4 as shown in the image. I am getting some size errors. Can you help me fix the code. clc; clear all; % Define initial conditions and parameters r0 = [1000, 0, 0]; % Initial position in meters v0 = [0, 10, 0]; % Initial velocity in m/s m0 = 1000; % Initial mass in kg z0 = log(m0); % Initial mass logarithm a0 = [0, 0, 1]; % Initial thrust direction in m/s^2 (thrust in z-direction) sigma0 = 0.1; % Initial thrust magnitude divided by mass % Initial state vector x0 = [r0, v0, z0] x0 = [r0, v0, z0]; % Initial control input u0 = [a0, sigma0] u0 = [a0, sigma0]; % Time span for integration t0 = 0; % Initial time tf = 10; % Final time N = 100; % Number of time steps dt = (tf - t0) / N; % Time step size t_span = linspace(t0, tf, N); % Discretized time vector % Solve the system of equations using ode45 [t, Y] = ode45(@(t, Y) EoMwithDiscreteMatrix(t, Y, u0, x0, t0, tf), t_span, x0); % Compute the matrices A_k,…arrow_forwardQ2) Determine the thickness of weld (h) for the figure shown below. when the Su= 410 MPa and factor of safety of 2. COR 50 200 60 F=2000Narrow_forward
- Please draw front, top and side view, in AutoCAD both of themarrow_forwardQuestion 7 A well is pumped from a confined aquifer at a constant rate of 1000 gallons per minute (gpm). The following data were collected during the pumping test: . Distance from the well to the observation well (r) = 150 feet Differential drawdown (Ah) in the observation well at this distance = 2.5 feet Aquifer properties: Transmissivity (T) = 25,000 gpd/ft • Storativity (S)- 0.0005 (dimensionless) Pumping time (t) = 5 hours Watch your units !! Using the above information, calculate the drawdown (h) in feet in the observation well at a distance of 150 feet after 5 hours of pumping. (Use the powerpoint slides for approximations for the well function W(u).arrow_forwardQu 2 Calcium oxide (CaO) a white, caustic, alkaline solid that reacts vigorously with water to produce calcium hydroxide, releasing heat in the process. It is used in various industrial applications, including cement production and water treatment. FA= 41{0 The ionic radii of the ions are: TCa2+= 0.100 nm and roz-= 0.140 nm. On the basis of this information answer the following questions: 1. What is the type of bonding that exists in CaO crystal? 2.Calculate attractive (Fs) force in [N] between a Ca'* iron and O* ifon that is separated by an equilibrium distance ro. Calculate repulsive (FR) force in [N] between a Ca?* iron and O? iron that is separated by an equilibrium distance ro. What is the magnitude of the net force FN?arrow_forward
- Show work if any equations or calculations are used.What is the main alloying element and carbon percentage of SAE-AISI 4621 Steel?arrow_forwardThe particle has a mass of 0.5 kg and is confined to move along the smooth horizontal slot due to the rotation of the arm OA. Determine the force of the rod on the particle and the normal force of the Isot on the particle when 0 = 30°. The rod is rotating with a angular velocity of ė = 2rad/s and an angular acceleration of = 3rad/s². Assume the particle only contacts one side of the slot at any instant. To check your answer, please enter the normal force of the slot onto the particle in Newtons. A * = 2 rad/s -0- 0.5 marrow_forwardSolve, use engineering economic tablesarrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





