
(a)
Interpretation:
The acyl chloride and carboxylate ion that could be used to form the given mixed anhydride have to be found.
Concept Introduction:
Mixed anhydrides are unsymmetrical anhydrides which have different alkyl groups.
Example:
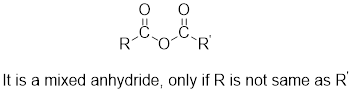
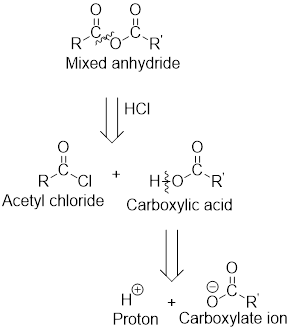
The acetyl chloride and carboxylate ion that could be used to form any given mixed anhydride can be analysed using the simple retro analysis as shown here:
(b)
Interpretation:
The other reagents that could be used to form the given mixed anhydride have to be found.
Concept Introduction:
Mixed anhydrides are unsymmetrical anhydrides which have different alkyl groups.
Example:
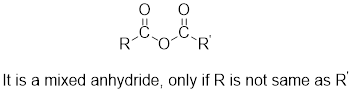
Any anhydride can be obtained using the following two pairs of reagents:
- 1. Acetyl chloride and a carboxylate ion.
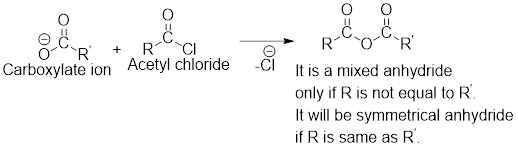
- 2. Two different carboxylic acids if mixed or unsymmetrical anhydride has to be formed or two same carboxylic acids if symmetrical anhydride has to be formed.
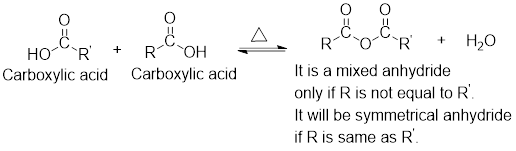
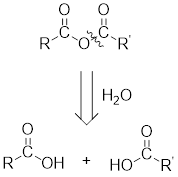
For any simple anhydride, the two carboxylic acids from which it has been formed can be found by the simple retro analysis as shown here:
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 11 Solutions
Essential Organic Chemistry Study Guide & Solution Manual, Books a la Carte Edition
- Which one? Ca2^- Na2^+ Si2^+ Mg2^- AI2^-arrow_forwardIn general, which is more polar, the stationary phase or the mobile phase? The stationary phase is always more polar The mobile phase is always more polar It depends on our choices for both stationary and mobile phase Their polarity doesn't really matter so we never consider itarrow_forwardPlease helparrow_forward
- Draw the mechanism of aspirin synthesis in an basic medium and in a neutral medium, showing the attacks and the process for the formation of the product.arrow_forwardNa :S f. F NO2arrow_forwardQ1: For each molecule, assign each stereocenter as R or S. Circle the meso compounds. Label each compound as chiral or achiral. + CI OH woཡི།༠w Br H مه D CI ပ။ Br H, Br Br H₂N OMe R IN Ill N S H CI Br CI CI D OH H 1/111arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning


