
a)
To find:the slope of the graph of the function at the indicated point using the limit of definition of the derivative.
The slope of the graph of the function at the point
Given information:
Formula used:
The derivative of the function
The derivative of a function at a point can be viewed geometrically as the slope of the line tangent to the curve
Calculation:
Calculate the derivative of the function
Calculate
Therefore,the slope of the graph of the function at the point
b)
To find: an equation of the tangent line at that point.
The equation of the tangent line at point
Given information:
Formula used:
Let
Calculation:
It is given that
Calculate
The tangent is passing through point
Compute the equation of the tangent line at point
Therefore, the equation of the tangent line at point
c)
To sketch:a graph of the curve near the point without using a grapher.
The graph is a parabola.
Given information:
Formula used:
The derivative of the function
The derivative of a function at a point can be viewed geometrically as the slope of the line tangent to the curve
Calculation:
Sketch the graph of
Prepare a table of points for
Plot the above points and connect them.
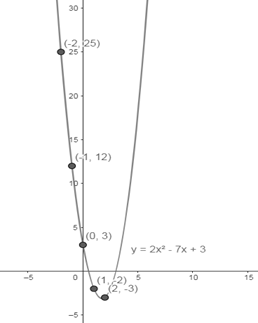
Therefore, it can be observed that the graph is a parabola.
Chapter 11 Solutions
PRECALCULUS:GRAPHICAL,...-NASTA ED.
- Find the maximum volume of a rectangular box whose surface area is 1500 cm² and whose total edge length is 200 cm. cm³arrow_forwardFind the minimum cost of a rectangular box of volume 120 cm³ whose top and bottom cost 6 cents per cm² and whose sides cost 5 cents per cm². Round your answer to nearest whole number cents. Cost = cents.arrow_forwardEarly Monday morning, the temperature in the lecture hall has fallen to 40°F, the same as the temperature outside. At 7:00 A.M., the janitor turns on the furnace with the thermostat set at 72°F. The time constant for the building is = 3 hr and that for the building along with its heating system is 1 K A.M.? When will the temperature inside the hall reach 71°F? 1 = 1 hr. Assuming that the outside temperature remains constant, what will be the temperature inside the lecture hall at 8:30 2 At 8:30 A.M., the temperature inside the lecture hall will be about (Round to the nearest tenth as needed.) 1°F.arrow_forward
- Find the absolute extrema of the function f(x, y) = x² + y² - 3x-3y+3 on the domain defined by x² + y² <9. Round answers to 3 decimals or more. Absolute Maximum: Absolute Minimum:arrow_forwardFind the maximum and minimum values of the function f(x, y) = e² subject to ï³ + y³ = 128 Please show your answers to at least 4 decimal places. Enter DNE if the value does not exist. Maximum value:arrow_forwardA chemical manufacturing plant can produce x units of chemical Z given p units of chemical P and 7 units of chemical R, where: z = 140p0.6,0.4 Chemical P costs $300 a unit and chemical R costs $1,500 a unit. The company wants to produce as many units of chemical Z as possible with a total budget of $187,500. A) How many units each chemical (P and R) should be "purchased" to maximize production of chemical Z subject to the budgetary constraint? Units of chemical P, p = Units of chemical R, r = B) What is the maximum number of units of chemical Z under the given budgetary conditions? (Round your answer to the nearest whole unit.) Max production, z= unitsarrow_forward
- A firm manufactures a commodity at two different factories, Factory X and Factory Y. The total cost (in dollars) of manufacturing depends on the quantities, and y produced at each factory, respectively, and is expressed by the joint cost function: C(x, y) = x² + xy +4y²+400 A) If the company's objective is to produce 1,900 units per month while minimizing the total monthly cost of production, how many units should be produced at each factory? (Round your answer to whole units, i.e. no decimal places.) To minimize costs, the company should produce: units at Factory X and units at Factory Y B) For this combination of units, their minimal costs will be enter any commas in your answer.) Question Help: Video dollars. (Do notarrow_forwarduse Lagrange multipliers to solvearrow_forwardSuppose a Cobb-Douglas Production function is given by the following: P(L,K)=80L0.75 K-0.25 where L is units of labor, K is units of capital, and P(L, K) is total units that can be produced with this labor/capital combination. Suppose each unit of labor costs $400 and each unit of capital costs $1,600. Further suppose a total of $384,000 is available to be invested in labor and capital (combined). A) How many units of labor and capital should be "purchased" to maximize production subject to your budgetary constraint? Units of labor, L = Units of capital, K = B) What is the maximum number of units of production under the given budgetary conditions? (Round your answer to the nearest whole unit.) Max production = unitsarrow_forward
- Suppose a Cobb-Douglas Production function is given by the function: P(L, K) = 7L0.0 K0.4 Furthemore, the cost function for a facility is given by the function: C(L, K) = 100L +400K Suppose the monthly production goal of this facility is to produce 15,000 items. In this problem, we will assume L represents units of labor invested and K represents units of capital invested, and that you can invest in tenths of units for each of these. What allocation of labor and capital will minimize total production Costs? Units of Labor L = Units of Capital K = (Show your answer is exactly 1 decimal place) (Show your answer is exactly 1 decimal place) Also, what is the minimal cost to produce 15,000 units? (Use your rounded values for L and K from above to answer this question.) The minimal cost to produce 15,000 units is $ Hint: 1. Your constraint equation involves the Cobb Douglas Production function, not the Cost function. 2. When finding a relationship between L and K in your system of equations,…arrow_forwardFind the absolute maximum and minimum of f(x, y) = x + y within the domain x² + y² ≤ 4. Please show your answers to at least 4 decimal places. Enter DNE if the value does not exist. 1. Absolute minimum of f(x, y) isarrow_forwardSuppose that one factory inputs its goods from two different plants, A and B, with different costs, 3 and 7 each respective. And suppose the price function in the market is decided as p(x, y) = 100 - x - y where I and y are the demand functions and 0 < x,y. Then as x = y = the factory can attain the maximum profit,arrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





