
In Figure 11.5, we show three combinations of main effects and interactions for a 2 × 2 factorial design. Using the same 2 × 2 structure, with factor A defining the rows and factor B defining the columns, create a set of means that produce each of the following patterns:
a. A main effect for factors A and B, but no interaction.
b. A main effect for factor A and an interaction, but no main effect for factor B.
c. A main effect for both factors and an interaction.
FIGURE 11.5
Three Possible Combinations of Main Effects and Interactions in a Two-Factor Experiment.
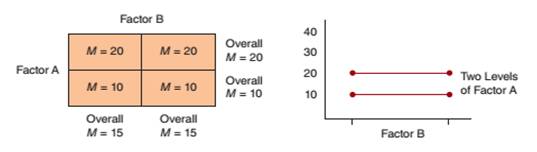
(a) Data showing a main effect for factor A but no main effect for factor B and no interaction.
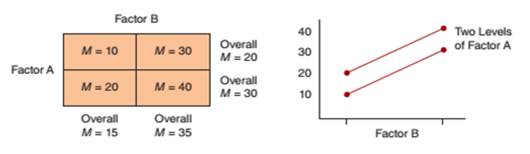
(b) Data showing main effects for both factor A and factor B but no interaction.
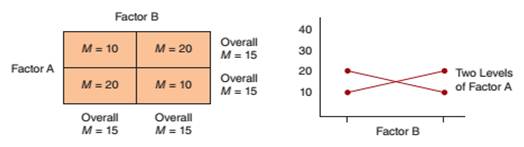
(c) Data showing no main effect for either factor, but an interaction.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 11 Solutions
RESEARCH METHODS F/ BEHAV.(LL)-W/MINTAP
- 19. Let X be a non-negative random variable. Show that lim nE (IX >n)) = 0. E lim (x)-0. = >arrow_forward(c) Utilize Fubini's Theorem to demonstrate that E(X)= = (1- F(x))dx.arrow_forward(c) Describe the positive and negative parts of a random variable. How is the integral defined for a general random variable using these components?arrow_forward
- 26. (a) Provide an example where X, X but E(X,) does not converge to E(X).arrow_forward(b) Demonstrate that if X and Y are independent, then it follows that E(XY) E(X)E(Y);arrow_forward(d) Under what conditions do we say that a random variable X is integrable, specifically when (i) X is a non-negative random variable and (ii) when X is a general random variable?arrow_forward
 College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning
