
Concept explainers
For each of the following independent Cases A and B, fill in the missing information. The company budgets and applies production
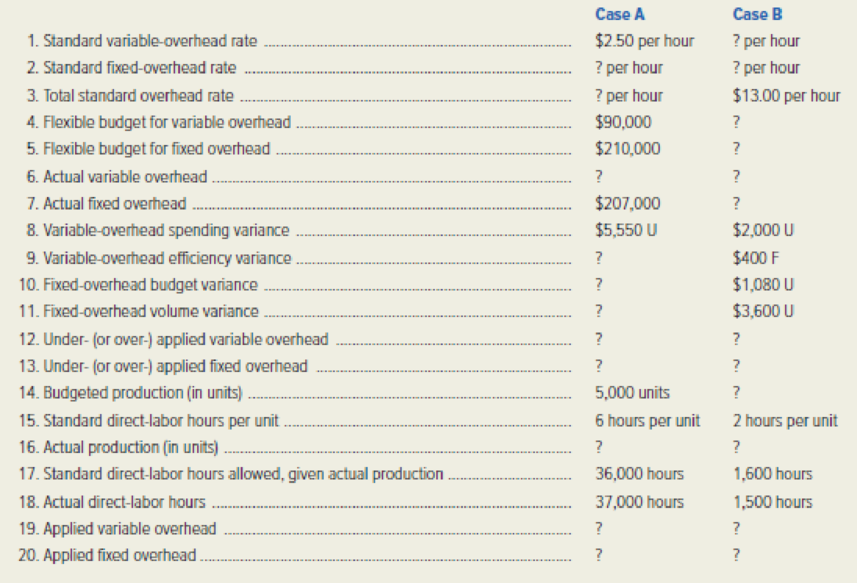
Calculate the missing amount for each of the given independent case A and B.
Explanation of Solution
Flexible Budget: A flexible budget is a budget that is prepared for different levels of the output. In other words, it is a budget that adjusts according to the changes in the volume of the activity. The main purpose of preparing flexible budget is to determine the differences among standard and actual result.
Calculate the missing amount for each of the given independent case A and B as follows:
| Particulars | Case A | Case B |
| 1. Standard variable overhead rate | $2.50 per hour |
$4.00 per hour (13) |
| 2. Standard fixed overhead rate |
$7.00 per hour (2) |
$9.00 per hour (14) |
| 3. Total standard overhead rate |
$9.50 per hour (3) | $13.00 per hour |
| 4. Flexible budget for variable overhead | $ 90,000 |
$ 6,400 (15) |
| 5. Flexible budget for fixed overhead | $ 210,000 |
$ 18,000 (16) |
| 6. Actual variable overhead |
$ 98,050 (4) |
$ 8,000 (17) |
| 7. Actual fixed overhead | $ 207,000 |
$ 19,080 (18) |
| 8. Variable overhead spending variance | $5,550 U | $2,000 U |
| 9. Variable overhead efficiency variance |
$2,500 U (5) | $400 F |
| 10. Fixed overhead budget variance |
$3,000 F (6) | $1,080 U |
| 11. Fixed overhead volume variance |
-$42,000 (7) | $3,600 U |
| 12. Under (over) applied variable overhead | $8,050 Under applied (8) | $1,600 Under applied (19) |
| 13. Under (over) applied fixed overhead | $45,000 over applied (9) | $4,680 under applied (21) |
| 14. Budgeted production (in units) | 5,000 units | 1,000 units (22) |
| 15. Standard direct labor hours per unit | 6 hours per unit | 2 hours per unit |
| 16. Actual production (in units) | 6,000 units (10) | 800 units (23) |
| 17. Standard direct labor hours allowed for actual production | 36,000 hours | 1,600 hours |
| 18. Actual direct labor hours | 37,000 hours | 1,500 hours |
| 19. Applied variable overhead | $ 90,000 (11) | $ 6,400 (24) |
| 20. Applied fixed overhead | $ 252,000 (12) | $ 14,400 (25) |
Table (1)
Working note (1):
Calculate the budgeted direct labor hours for Case A.
Working note (2):
Calculate the standard fixed overhead rate for Case A.
Working note (3):
Calculate the total standard overhead rate for Case A.
Working note (4):
Calculate the actual variable overhead for Case A.
Working note (5):
Calculate the variable overhead efficiency variance for Case A.
Working note (6):
Calculate the fixed overhead budget variance for Case A.
Working note (7):
Calculate the fixed overhead volume variance for Case A.
Working note (8):
Calculate the under applied variable overhead for Case A.
Working note (9):
Calculate the over applied fixed overhead for Case A.
Working note (10):
Calculate the actual production for Case A.
Working note (11):
Calculate the applied variable overhead for Case A.
Working note (12):
Calculate the applied fixed overhead for Case A.
Working note (13):
Calculate the variable overhead efficiency variance for Case B.
Working note (14):
Calculate the standard fixed overhead rate for Case B.
Working note (15):
Calculate the flexible budget for variable overhead for Case B.
Working note (16):
Calculate the flexible budget for fixed overhead for Case B.
Working note (17):
Calculate the actual variable overhead for Case B.
Working note (18):
Calculate the actual fixed overhead for Case B.
Working note (19):
Calculate the under applied variable overhead for Case B.
Working note (20):
Calculate the under applied fixed overhead for Case B.
Working note (21):
Calculate the budgeted direct labor hours for Case B:
Working note (22):
Calculate the budgeted production for Case B:
Working note (23):
Calculate the actual production for Case B:
Working note (24):
Calculate the applied variable overhead for Case B:
Working note (25):
Calculate the applied fixed overhead for Case B:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Managerial Accounting: Creating Value in a Dynamic Business Environment
- what is the variable cost per minute?arrow_forwardI want to know how to solve these 2 questions and what the answers are 1. Stella Motors has $50m in assets, which is financed with 40% debt and 60% common equity. The company’s beta is currently 1.25 and its tax rate is 30%. Find Stella’s unlevered beta. 2. Sugar Corp. uses no debt. The weighted average cost of capital is 7.9%. If the current market value of the equity is $15.6 million and there are no taxes, what is the company’s EBIT?arrow_forwardI don't need ai answer general accounting questionarrow_forward
- Can you help me with accounting questionsarrow_forwardCariveh Co sells automotive supplies from 25 different locations in one country. Each branch has up to 30 staff working there, although most of the accounting systems are designed and implemented from the company's head office. All accounting systems, apart from petty cash, are computerised, with the internal audit department frequently advising and implementing controls within those systems. Cariveh has an internal audit department of six staff, all of whom have been employed at Cariveh for a minimum of five years and some for as long as 15 years. In the past, the chief internal auditor appoints staff within the internal audit department, although the chief executive officer (CEO) is responsible for appointing the chief internal auditor. The chief internal auditor reports directly to the finance director. The finance director also assists the chief internal auditor in deciding on the scope of work of the internal audit department. You are an audit manager in the internal audit…arrow_forwardCariveh Co sells automotive supplies from 25 different locations in one country. Each branch has up to 30 staff working there, although most of the accounting systems are designed and implemented from the company's head office. All accounting systems, apart from petty cash, are computerised, with the internal audit department frequently advising and implementing controls within those systems. Cariveh has an internal audit department of six staff, all of whom have been employed at Cariveh for a minimum of five years and some for as long as 15 years. In the past, the chief internal auditor appoints staff within the internal audit department, although the chief executive officer (CEO) is responsible for appointing the chief internal auditor. The chief internal auditor reports directly to the finance director. The finance director also assists the chief internal auditor in deciding on the scope of work of the internal audit department. You are an audit manager in the internal audit…arrow_forward
- Principles of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,  Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial & Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337119207Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial & Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337119207Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial & Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781285866307Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial & Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781285866307Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning





