
Concept explainers
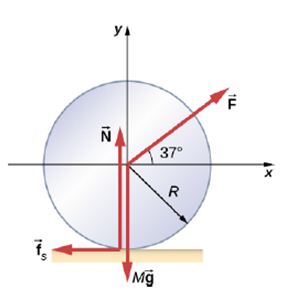
A solid cylindrical wheel of mass
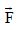 applied to the center of the wheel at
applied to the center of the wheel at
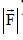 ? The coefficients of static and kinetic friction are
? The coefficients of static and kinetic friction are
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 11 Solutions
University Physics Volume 1
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
- Find the net torque on the wheel in Figure P10.23 about the axle through O, taking a = 10.0 cm and b = 25.0 cm. Figure P10.23arrow_forwardThe wheels, axle, and handles of a wheelbarrow weigh W = 57 N. The load chamber and its contents weigh W₁ = 563 N. The drawing shows these two forces in two different wheelbarrow designs. To support the wheelbarrow in equilibrium, the man's hands apply a force to the handles that is directed vertically upward. Consider a rotational axis at the point where the tire contacts the ground, directed perpendicular to the plane of the paper. Find the magnitude of the man's force for both designs. F F (a) F = (b) F = i i W 0.400 m ¹0.700 m 0.200 m (a) > > 0.600 m' 0.700 (b)arrow_forwardA 65 kg student is in a car traveling at 25 m/s on a hill of radius 110 m. When the car is at the top of the hill, what upward force does the seat exert on the student? A 4.2 m long uniform post is supported by a cable having a tension of 1 700 N. What is the mass of this post?arrow_forward
- A grindstone in the shape of a solid disk with diameter 0.520 m and a mass of 50.0 kg is rotating at 810 rev/min. You press an ax against the rim with a normal force of 190 N, and the grindstone comes to rest in 7.10 s. Find the coefficient of friction between the ax and the grindstone. You can ignore friction in the bearings.arrow_forwardThe wheels, axle, and handles of a wheelbarrow weigh W = 58 N. The load chamber and its contents weigh WL = 580 N. The drawing shows these two forces in two different wheelbarrow designs. To support the wheelbarrow in equilibrium, the man’s hands apply a force to the handles that is directed vertically upward. Consider a rotational axis at the point where the tire contacts the ground, directed perpendicular to the plane of the paper. Find the magnitude of the man’s force for both designs.arrow_forwardRound off 2 decimal places. Input magnitude only. The block on a smooth inclined plane is moving down with a constant acceleration of 4 m/s2 m, m2 The block on the inclined plane is 49 kg and the hanging mass is 23 kg. The radius of the pulley is 0.42 m. The angle theta is 26 degress. Determine the moment of inertia of the pulley.arrow_forward
- The bolts on the cylinder head of an engine require tightening to a torque of 76 m⋅N. If a wrench is 28 cm long, what force perpendicular to the wrench must the mechanic exert at its end? Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units. Answer is 270 N. If the six-sided bolt head is 15 mm across, estimate the force applied near each of the six points by a socket wrench. Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units.arrow_forwardA block of mass 4 kg slides down an inclined plane at an angle of 45° with a massless tether attached to a pulley with mass 2 kg and radius 0.6 m at the top of the incline (see the following figure). The pulley can be approximated as a disk. The coefficient of kinetic friction on the plane is 0.2. What is the acceleration of the block (in m/s2)? (Enter the magnitude.) 45 m/s2 tarrow_forwardThe wheels, axle, and handles of a wheelbarrow weigh 60.0 N. The load chamber and its contents weigh 525 N. The drawing shows these two forces in two different wheelbarrow designs. To support the wheel- barrow in equilibrium, the man’s hands apply a force F to the handles that is directed vertically upward. Consider a rotational axis at the point where the tire contacts the ground, directed perpendicular to the plane of the paper. Find the magnitude of the man’s force for both designs.arrow_forward
- The wheels, axle, and handles of a wheelbarrow weigh 60.0 N. The load chamber and its contents weigh 525 N. The drawing shows these two forces in two different wheelbarrow designs. To support the wheel- barrow in equilibrium, the man’s hands apply a force F to the handles that is directed vertically upward. Consider a rotational axis at the point where the tire contacts the ground, directed perpendicular to the plane of the paper. Find the magnitude of the man’s force for both designs.arrow_forwardConsider the setup shown below. The blocks have masses 3.6 kg and 24 kg. The pulley has mass 7.4 kg, and is a uniform disc with radius 0.23 m. Assume the pulley to be fric- tionless, but the coefficient of friction between the block and the surface is 0.36. a T2 3.6 kg T1 = 0.36 22° 24 kg What is the acceleration of the blocks? As- sume the 24 kg mass is descending with accel- erațion a. The moment of inertia of the disk is - M R? and the acceleration of gravity is 2 9.8 m/s?. Answer in units of m/s?.arrow_forwardA circular-shaped object of mass 9 kg has an inner radius of 7 cm and an outer radius of 28 cm. Three forces (acting perpendicular to the axis of rotation) of magnitudes 13 N, 22 N, and 13 N act on the object, as shown. The force of magnitude 22 N acts 33◦ below the horizontal. Find the magnitude of the net torque (units Nm) on the wheel about the axle through the center of the object.arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

