
Chemistry (OER)
19th Edition
ISBN: 9781947172623
Author: OpenStax
Publisher: OpenStax College
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 11, Problem 22E
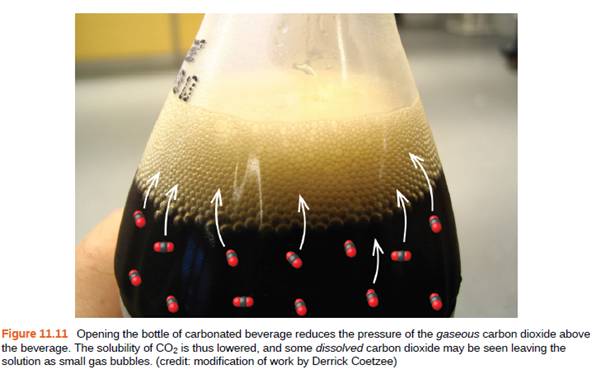
Refer to Figure 11.11.
(a) How did the concentration of dissolved CO2 in the beverage change when the bottle was opened?
(b) What caused this change?
(c) Is the beverage unsaturated, saturated, or supersaturated with CO2?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Using the following two half-reactions, determine the pH range in which $NO_2^-\ (aq)$ cannot be found as the predominant chemical species in water.* $NO_3^-(aq)+10H^+(aq)+8e^-\rightarrow NH_4^+(aq)+3H_2O(l),\ pE^{\circ}=14.88$* $NO_2^-(aq)+8H^+(aq)+6e^-\rightarrow NH_4^+(aq)+2H_2O(l),\ pE^{\circ}=15.08$
Indicate characteristics of oxodec acid.
What is the final product when hexanedioic acid reacts with 1º PCl5 and 2º NH3.
Chapter 11 Solutions
Chemistry (OER)
Ch. 11 - How do solutions differ from compounds? From other...Ch. 11 - Which of the principal characteristics of...Ch. 11 - When KNO3 is dissolved in water, the resulting...Ch. 11 - Give an example of each of the following types of...Ch. 11 - Indicate the most important types of...Ch. 11 - Predict whether each of the following substances...Ch. 11 - Heat is released when some solutions form; heat is...Ch. 11 - Solutions of hydrogen in palladium may be formed...Ch. 11 - Explain why the ions Na+ and CI- are strongly...Ch. 11 - Explain why solutions of HBr in benzene (a...
Ch. 11 - Consider the solutions presented: (a) Which of the...Ch. 11 - Compare the processes that occur when methanol...Ch. 11 - What is the expected electrical conductivity of...Ch. 11 - Why are most solid ionic compounds electrically...Ch. 11 - Indicate the most important type of intermolecular...Ch. 11 - Suppose you are presented with a clear solution of...Ch. 11 - Supersaturated solutions of most solids in water...Ch. 11 - Suggest an explanation for the observations that...Ch. 11 - Calculate the percent by mass of KBr in a...Ch. 11 - Which of the following gases is expected to be...Ch. 11 - At 0 C and 1.00 atm, as much as 0.70 g of O2 can...Ch. 11 - Refer to Figure 11.11. (a) How did the...Ch. 11 - The Henry's law constant for CO2 is 3.4102 M/atm...Ch. 11 - The Henry's law constant for O2 is 1.3103M /atm at...Ch. 11 - How many liters of HCI gas, measured at 30.0 C and...Ch. 11 - Which is are part of the macroscopic domain of...Ch. 11 - What is the microscopic explanation for the...Ch. 11 - Sketch a qualitative graph of the pressure versus...Ch. 11 - A solution of potassium nitrate, an electrolyte,...Ch. 11 - What are the mole fractions of H3PO4 and water in...Ch. 11 - What are the mole fractions of HNO3 and water in a...Ch. 11 - Calculate the mole fraction of each solute and...Ch. 11 - Calculate the mole fraction of each solute and...Ch. 11 - Calculate the mole fractions of methanol, CH3OH;...Ch. 11 - What is the difference between a 1 M solution and...Ch. 11 - What is the molality of phosphoric acid, H3PO4, in...Ch. 11 - What is the molality of nitric acid in a...Ch. 11 - Calculate the molality of each of the following...Ch. 11 - Calculate the molality of each of the following...Ch. 11 - The concentration of glucose, C6H12O6, in normal...Ch. 11 - A 13.0% solution of K2CO3 by mass has a density of...Ch. 11 - Why does 1 mol of sodium chloride depress the...Ch. 11 - What is the boiling point of a solution of 115.0 g...Ch. 11 - What is the boiling point of a solution of 9.04 g...Ch. 11 - What is the freezing temperature of a solution of...Ch. 11 - What is the freezing point of a solution of 9.04 g...Ch. 11 - What is the osmotic pressure of an aqueous...Ch. 11 - What is osmotic pressure of a solution of bovine...Ch. 11 - What is the molar mass of a solution of 5.00 g of...Ch. 11 - A sample of an organic compound (a nonelectrolyte)...Ch. 11 - A 1.0 m solution of HCI in benzene has a freezing...Ch. 11 - A solution contains 5.00 g of urea, CO(NH2)2, a...Ch. 11 - A 12.0-g sample of a nonelectrolyte is dissolved...Ch. 11 - Arrange the following solutions in order by their...Ch. 11 - Calculate the boiling point elevation of 0.100 kg...Ch. 11 - How could you prepare a 3.08 m aqueous solution of...Ch. 11 - A sample of sulfur weighing 0.210 g was dissolved...Ch. 11 - In a significant experiment performed many years...Ch. 11 - Lysozyme is an enzyme that cleaves cell walls. A...Ch. 11 - The osmotic pressure of a solution containing 7.0...Ch. 11 - The osmotic pressure of human blood is 7.6 atm at...Ch. 11 - What is the freezing point of a solution of...Ch. 11 - What is the boiling point of a solution of NaCI in...Ch. 11 - The sugar fructose contains 40.0% C, 6.7% H, and...Ch. 11 - The vapor pressure of methanol, CH3OH, is 94 torr...Ch. 11 - The triple point of air-free water is defined as...Ch. 11 - Meat can be classified as fresh (not frozen) even...Ch. 11 - An organic compound has a composition of 93.46% C...Ch. 11 - A sample of HgCI2 weighing 9.41 g is dissolved in...Ch. 11 - A salt is known to be an alkali metal fluoride. A...Ch. 11 - Identify the dispersed phase and the dispersion...Ch. 11 - Distinguish between dispersion methods and...Ch. 11 - How do colloids differ from solutions with regard...Ch. 11 - Explain the cleansing action of soap.Ch. 11 - How can it be demonstrated that colloidal...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
How is a mailing address analogous to biologys hierarchical classification system?
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
1. An object is subject to two forces that do not point in opposite directions. Is it possible to choose their ...
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
72. Name each molecular compound.
a.
b.
C.
d.
e.
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
8. A 1000 kg car pushes a 2000 kg truck that has a dead battery. When the driver steps on the accelerator, the ...
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
Raw Oysters and Antacids: A Deadly Mix? The highly acidic environment of the stomach kills most bacteria before...
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (5th Edition)
4. What five specific threats to biodiversity are described in this chapter? Provide an example of each.
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- What is the final product when D-galactose reacts with hydroxylamine?arrow_forwardIndicate the formula of the product obtained by reacting methyl 5-chloro-5-oxopentanoate with 1 mole of 4-penten-1-ylmagnesium bromide.arrow_forwardIn the two chair conformations of glucose, the most stable is the one with all the OH groups in the equatorial position. Is this correct?arrow_forward
- please help me with my homeworkarrow_forwardhelparrow_forwardThe temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forward
- QUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forwardpressure (atm) 3 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 0 0 200 temperature (K) 400 аarrow_forwarder your payment details | bar xb Home | bartleby x + aleksogi/x/isl.exe/1o u-lgNskr7j8P3jH-1Qs_pBanHhviTCeeBZbufuBYT0Hz7m7D3ZcW81NC1d8Kzb4srFik1OUFhKMUXzhGpw7k1 O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 1 3- 0- 0 200 Explanation Check temperature (K) 400 X Q Search L G 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved Terms of Use Privacy Cearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning

General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285853918
Author:H. Stephen Stoker
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079243
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:9780534420123
Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Intermolecular Forces and Boiling Points; Author: Professor Dave Explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=08kGgrqaZXA;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY