
Concept explainers
Distinguish between unstable, stable, and neutral equilibrium.
To Distinguish: Among the unstable, stable and neutral equilibrium.
Explanation of Solution
Introduction:
When body is said to be in equilibrium, there is no change in the state of the body. Vector sum of the all the forces acting on body is zero. Equilibrium can be classified as:
- Stable equilibrium
- Unstable equilibrium
- Neutral equilibrium.
Stable equilibrium:
When body is in stable equilibrium, force/torque acting on the body is in the opposite direction to its displacement when body is moved from its equilibrium point.In stable equilibrium, body always tries to attain the stable equilibrium point. In this case net torque acting on the body is zero.Below figure shows the marble in circular vessel. Point O is the equilibrium point. When marble moved, force is acting on the marble in the reverse direction to its displacement so that it again reaches to its initial position O.Therefore, in this case acceleration of marble is zero.
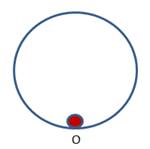
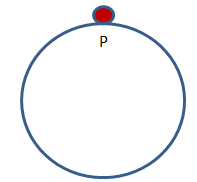
Unstable equilibrium:
In case of unstable equilibrium, when body is acted upon by the force, it accelerates in the direction of displacement. The net force acting on the body is in the direction of the force. Consider the following figure. Initially marble is at point P. When force isapplied on marble from any direction it slides down. So, in this case, the net force acting on the marble is in the direction of the displacement. In this case, marble accelerates in the downward direction.
Neutral equilibrium:
Neutral equilibrium is the state where equilibrium does not depend on the displacement of the body. So, after the displacement, body remains in the state of new position. Consider the marble from below figure. Marble is at rest initially. When force is applied on marble, displacement of the marble in the direction of force and it will not come to its original position.

Conclusion: Therefore, in stable equilibrium net force acting on the body is zero and displacement is opposite to the direction of force. In case of unstable equilibrium, net force acting on the body is non-zero and displacement and force in the same direction. While in neutral equilibrium, equilibrium does not depend on the displacement of the body.
Chapter 11 Solutions
EP CONCEPTUAL PHYSICS-ONLINE ACCESS
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (5th Edition)
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
- The force of the quadriceps (Fq) and force of the patellar tendon (Fp) is identical (i.e., 1000 N each). In the figure below angle in blue is Θ and the in green is half Θ (i.e., Θ/2). A) Calculate the patellar reaction force (i.e., R resultant vector is the sum of the horizontal component of the quadriceps and patellar tendon force) at the following joint angles: you need to provide a diagram showing the vector and its components for each part. a1) Θ = 160 degrees, a2) Θ = 90 degrees. NOTE: USE ONLY TRIGNOMETRIC FUNCTIONS (SIN/TAN/COS, NO LAW OF COSINES, NO COMPLICATED ALGEBRAIC EQUATIONS OR ANYTHING ELSE, ETC. Question A has 2 parts!arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- Solve and answer the question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forward་ The position of a particle is described by r = (300e 0.5t) mm and 0 = (0.3t²) rad, where t is in seconds. Part A Determine the magnitude of the particle's velocity at the instant t = 1.5 s. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. v = Value Submit Request Answer Part B ? Units Determine the magnitude of the particle's acceleration at the instant t = 1.5 s. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. a = Value A ? Unitsarrow_forwardSolve and answer the question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forward
- Solve and answer the question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forwardA spiral transition curve is used on railroads to connect a straight portion of the track with a curved portion. (Figure 1) Part A v = v₁ft/s 600 ft y = (106) x³ If the spiral is defined by the equation y = (106)³, where x and y are in feet, determine the magnitude of the acceleration of a train engine moving with a constant speed of v₁ = 30 ft/s when it is at point x = 600 ft. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. ? a = Value Unitsarrow_forwardsolve and answer the problem correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forward
- Solve and answer the question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forwardSolve and answer the question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forwardWhen the motorcyclist is at A, he increases his speed along the vertical circular path at the rate of = (0.3t) ft/s², where t is in seconds. Take p = 360 ft. (Figure 1) Part A 60° Ρ B If he starts from rest at A, determine the magnitude of his velocity when he reaches B. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. v = Value Submit Request Answer ་ Part B ? Units If he starts from rest at A, determine the magnitude of his acceleration when he reaches B. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. 11 ? a = Value Unitsarrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





