
Earlier in this section, we looked at the parametric equations for a cycloid, which is the path a point on the edge of a wheel traces as the wheel rolls along a straight path. In this project we look at two different variations of the cycloid. called the curtate and prolate cycloids.
First. let’s revisit the derivation of the parametric equations for a cycloid. Recall that we considered a tenacious ant trying to get home by hanging onto the edge of a bicycle tire. We have assumed the ant climbed onto the tire at the very edge, where the tire touches the ground. As the wheel rolls, the ant moves with the edge of the tire (Figure 1.13).
As we have discussed, we have a lot of flexibility when parameterizing a curve. In this case we let our parameter c represent the angle the tire has rotated through. Looking at Figure 1.13, we see that after the tire has rotated through an angle of t, the Position of the center of the wheel,
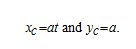
Furthermore, letting
Then
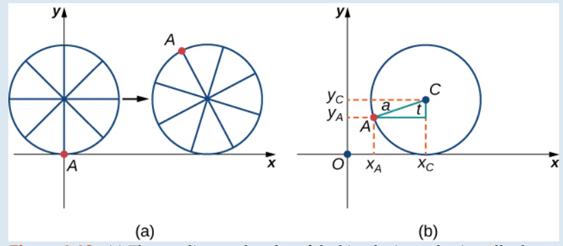
Figure 1.13 (a) The ant clings to die edge of the bicycle tile as the tire rolls along the ground. (b) Using geometry to determine the position of the ant after the tire has rotated through an angle of t.
Note that these are the same parametric representations we had before, but we have now assigned a physical meaning to the parametric variable t.
After a while the am is getting dizzy from going round and round on the edge of the tire. So he climbs up one of the spokes toward the center of the wheel. By climbing toward the center of the wheel. the ant has changed his path of motion. The new path has less up-and-down motion and is called a mutate cycloid (Figure 1.14). As shown in the figure. we let b denote the distance along the spoke flow the center of the wheel to the ant. As before, we let t represent the angle the fire has rotated through. Additionally, we let
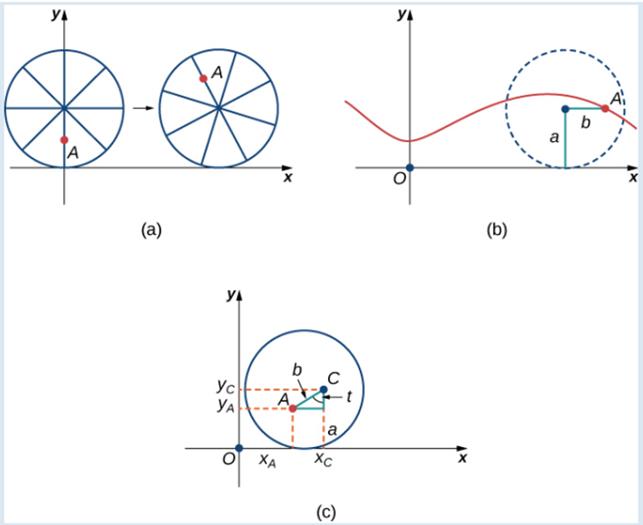
Figure 1.14 (a) The ant climbs up one of the spokes toward the center of the wheel. (b) The ant's path of motion after he climbs closer to the center of the wheel. This is called a mutate cycloid. (c) The new Setup, now that the ant has moved closer to the center of the wheel.
4. Using the same approach you used in parts 1- 3. find the parametric equations for the path of motion of the ant.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 1 Solutions
CALCULUS,VOLUME 3 (OER)
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Thinking Mathematically (6th Edition)
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
Elementary and Intermediate Algebra: Concepts and Applications (7th Edition)
Elementary Statistics (13th Edition)
A Problem Solving Approach To Mathematics For Elementary School Teachers (13th Edition)
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
- Calculus III May I please have some elaborations on Example 2 part a? Thank you.arrow_forward26.1. Locate and determine the order of zeros of the following functions: (a). e2z – e*, (b). z2sinhz, (c). z*cos2z, (d). z3 cosz2.arrow_forwardWrite 7. √49 using rational exponents. ○ A. 57 47 B. 7 O C. 47 ○ D. 74arrow_forward
- 31.5. Let be the circle |+1| = 2 traversed twice in the clockwise direction. Evaluate dz (22 + 2)²arrow_forwardThe details of the clock sales at a supermarket for the past 6 weeks are shown in the table below. The time series appears to be relatively stable, without trend, seasonal, or cyclical effects. The simple moving average value of k is set at 2. Calculate the value of the simple moving average mean absolute percentage error. Round to two decimal places. Week Units sold 1 88 2 44 3 54 4 65 5 72 6 85 Part 1 A. 14.39 B. 25.56 C. 23.45 D. 20.90arrow_forwardThe accompanying data shows the fossil fuels production, fossil fuels consumption, and total energy consumption in quadrillions of BTUs of a certain region for the years 1986 to 2015. Complete parts a and b. Year Fossil Fuels Production Fossil Fuels Consumption Total Energy Consumption1949 28.748 29.002 31.9821950 32.563 31.632 34.6161951 35.792 34.008 36.9741952 34.977 33.800 36.7481953 35.349 34.826 37.6641954 33.764 33.877 36.6391955 37.364 37.410 40.2081956 39.771 38.888 41.7541957 40.133 38.926 41.7871958 37.216 38.717 41.6451959 39.045 40.550 43.4661960 39.869 42.137 45.0861961 40.307 42.758 45.7381962 41.732 44.681 47.8261963 44.037 46.509 49.6441964 45.789 48.543 51.8151965 47.235 50.577 54.0151966 50.035 53.514 57.0141967 52.597 55.127 58.9051968 54.306 58.502 62.4151969 56.286…arrow_forward
- Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
 Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305071742Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305071742Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning  Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL



