
Concept explainers
Problem 10.16 projected financial statements for Walmart for Years +1 through +5. The following data for Walmart include the actual amounts for 2012 and the projected amounts for Years +1 through +5 for comprehensive income and common shareholders’ equity, assuming it will use implied dividends as the financial flexible account to balance the
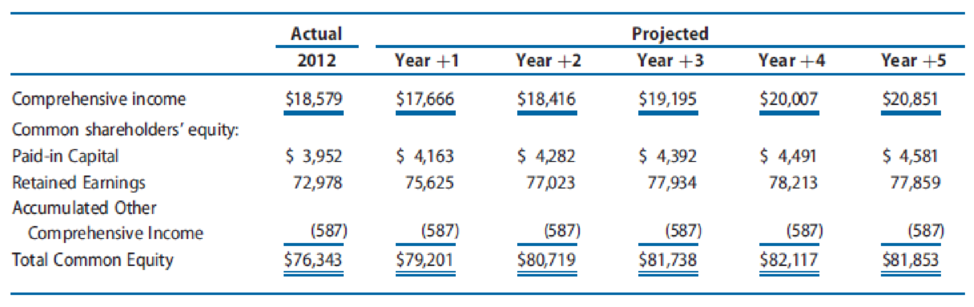
Assume that the market equity beta for Walmart at the end of 2012 was 1.00. Assume that the risk-free interest rate was 3.0% and the market risk premium was 6.0%. Also assume that Walmart had 3,314 million shares outstanding at the end of 2012, and share price was $69.09.
REQUIRED
- a. Use the
CAPM to compute the requiredrate of return on common equity capital for Walmart. - b. Compute the weighted-average cost of capital for Walmart as of the start of Year +1. At the end of 2012, Walmart had $48,222 million in outstanding interest-bearing debt on the balance sheet and no preferred stock. Assume that the balance sheet value of Walmart’s debt is approximately equal to the market value of the debt. Assume that at the start of Year +1, it will incur interest expense of 4.2% on debt capital and that its average tax rate will be 32.0%. Walmart also had $5,395 million in equity capital from noncontrolling interests. Assume that this equity capital carries a 15.0% required rate of return. (For our forecasts, we assume noncontrolling interests are similar to
preferred shares and receive dividends equal to the required rate of return each year.) - c. Use the clean surplus accounting approach to derive the projected dividends for common shareholders for Years +1 through +5 based on the projected comprehensive income and shareholders’ equity amounts. (Throughout this problem, you can ignore dividends to noncontrolling interests.)
- d. Use the clean surplus accounting approach to project the continuing dividend to common shareholders in Year +6. Assume that the steady-state long-run growth rate will be 3% in Years +6 and beyond.
- e. Using the required rate of return on common equity from Requirement a as a discount rate, compute the sum of the
present value of dividends to common shareholders for Walmart for Years +1 through +5. - f. Using the required rate of return on common equity from Requirement a as a discount rate and the long-run growth rate from Requirement d, compute the continuing value of Walmart as of the beginning of Year +6 based on its continuing dividends in Years +6 and beyond. After computing continuing value, bring continuing value back to present value at the start of Year +1.
- g. Compute the value of a share of Walmart common stock, as follows:
- (1) Compute the sum of the present value of dividends including the present value of continuing value.
- (2) Adjust the sum of the present value using the midyear discounting adjustment factor.
- (3) Compute the per-share value estimate.
- h. Using the same set of
forecast assumptions as before, recompute the value of Walmart shares under two alternative scenarios. To quantify the sensitivity of your share value estimate for Walmart to these variations in growth and discount rates, compare (in percentage terms) your value estimates under these two scenarios with your value estimate from Requirement g.- Scenario 1: Assume that Walmart’s long-run growth will be 2%, not 3% as before, and assume that its required rate of
return on equity is 1 percentage point higher than the rate you computed using the CAPM in Requirement a. - Scenario 2: Assume that Walmart’s long-run growth will be 4%, not 3% as before, and assume that its required rate of return on equity is 1 percentage point lower than the rate you computed using the CAPM in Requirement a.
- Scenario 1: Assume that Walmart’s long-run growth will be 2%, not 3% as before, and assume that its required rate of
- i. What reasonable range of share values would you expect for Walmart common stock? Where is the current price for Walmart shares relative to this range? What do you recommend?
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 11 Solutions
Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis and Valuation
- What are the six types of alternative case study compositional structures (formats)used for research purposes, such as: 1. Linear-Analytical, 2. Comparative, 3. Chronological, 4. Theory Building, 5. Suspense and 6. Unsequenced. Please explainarrow_forwardFor an operating lease, substantially all the risks and rewards of ownership remain with the _________. QuestFor an operating lease, substantially all the risks and rewards of ownership remain with the _________: A) Tenant b) Lessee lessor none of the above tenant lessee lessor none of the aboveLeasing allows the _________ to acquire the use of a needed asset without having to make the large up-front payment that purchase agreements require Question 4 options: lessor lessee landlord none of the abovearrow_forwardHow has AirBnb negatively affected the US and global economy? How has Airbnb negatively affected the real estate market? How has Airbnb negatively affected homeowners and renters market? What happened to Airbnb in the Tax Dispute in Italy?arrow_forward
- How has AirBnb positively affected the US and global economy? How has Airbnb positively affected the real estate market? How has Airbnb positively affected homeowners and renters market?arrow_forwardD. (1) Consider the following cash inflows of a financial product. Given that the market interest rate is 12%, what price would you pay for these cash flows? Year 0 1 2 3 4 Cash Flow 160 170 180 230arrow_forwardExplain why financial institutions generally engage in foreign exchange tradingactivities. Provide specific purposes or motivations behind such activities.arrow_forward
- A. In 2008, during the global financial crisis, Lehman Brothers, one of the largest investment banks, collapsed and defaulted on its corporate bonds, causing significant losses for bondholders. This event highlighted several risks that investors in corporate bonds might face. What are the key risks an investor would encounter when investing in corporate bonds? Explain these risks with examples or academic references. [15 Marks]arrow_forwardTwo companies, Blue Plc and Yellow Plc, have bonds yielding 4% and 5.3%respectively. Blue Plc has a credit rating of AA, while Yellow Plc holds a BB rating. If youwere a risk-averse investor, which bond would you choose? Explain your reasoning withacademic references.arrow_forwardB. Using the probabilities and returns listed below, calculate the expected return and standard deviation for Sparrow Plc and Hawk Plc, then justify which company a risk- averse investor might choose. Firm Sparrow Plc Hawk Plc Outcome Probability Return 1 50% 8% 2 50% 22% 1 30% 15% 2 70% 20%arrow_forward
 Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis...FinanceISBN:9781285190907Author:James M. Wahlen, Stephen P. Baginski, Mark BradshawPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis...FinanceISBN:9781285190907Author:James M. Wahlen, Stephen P. Baginski, Mark BradshawPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781285867977Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781285867977Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Financial Management, Concise Edi...FinanceISBN:9781285065137Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Financial Management, Concise Edi...FinanceISBN:9781285065137Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Financial Management, Concise Edi...FinanceISBN:9781305635937Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Financial Management, Concise Edi...FinanceISBN:9781305635937Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning





