
(a)
Interpretation:
The systematic name of the compound
Concept Introduction:
Rules for naming compound:
- 1) The carbon atoms in the longest chain have to be counted.
- 2) The substituents and multiple bonds have to be identified and counted and the suffix “-ene” is added.
- 3) The backbone carbon atoms have to be numbered by assigning the lowest number from the starting end that contains the double bond.
Rules for naming compound:
- 1) The carbon atoms in the longest chain have to be counted.
- 2) The substituents and multiple bonds have to be identified and counted and the suffix “-yne” is added.
- 3) The backbone carbon atoms have to be numbered by assigning the lowest number from the starting end that contains the double bond.
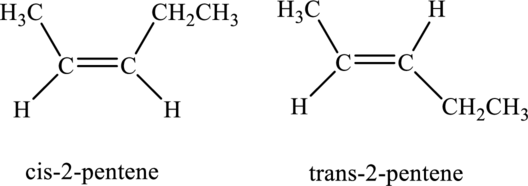
Geometrical isomers: In geometrical isomers, atoms have different arrangements on either side of a double bond above or below the ring of a cycloalkane or cycloalkane. If the atoms are present on the same side of the double bond, then it is cis-isomer and if they are present on the opposite side of the double bond, then it is trans-isomer.
(a)
Answer to Problem 11.8E
The systematic name of the compound
Cis-
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is,
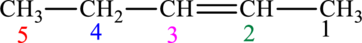
The compound is identified as alkene. The parent chain of the compound is pentane and a double bond is seen at the carbon second position. Hence, the systematic name of the compound is
Cis-
(b)
Interpretation:
The systematic name of the compound
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(b)
Answer to Problem 11.8E
The systematic name of the compound
The geometrical isomers are not possible in
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is,
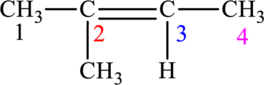
The compound is identified as alkene. The parent chain of the compound is butane. One methyl group is present in the carbon second position and a double bond is seen at the carbon second position. Hence, the systematic name of the compound is
No geometrical isomers are possible in
(c)
Interpretation:
The systematic name of the compound
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(c)
Answer to Problem 11.8E
The systematic name of the compound
No geometrical isomers are possible in
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is,
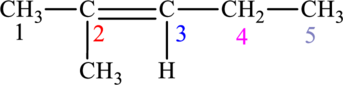
The compound is identified as alkene. The parent chain of the compound is pentane. One methyl group is present in the carbon second position and a double bond is seen at the carbon second position. Hence, the systematic name of the compound is
No geometrical isomers are possible in
(d)
Interpretation:
The systematic name of the compound
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(d)
Answer to Problem 11.8E
The systematic name of the compound
No geometrical isomers are possible in
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is,
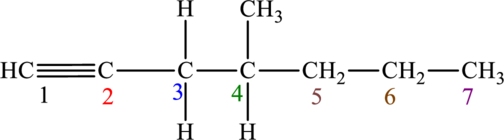
The compound is identified as alkyne. The parent chain of the compound is heptane. One triple bond is present in carbon first position and one methyl substituent is present in carbon fourth position. Hence, the systematic name of the compound is
Geometrical isomers are not possible because triple bond has only one substituent each.
(e)
Interpretation:
The systematic name of the compound
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(e)
Answer to Problem 11.8E
The systematic name of the compound
No geometrical isomers are possible in
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is,
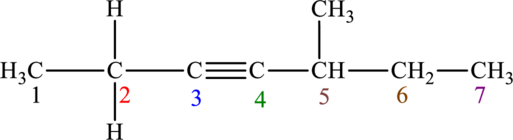
The compound is identified as alkyne. The parent chain of the compound is heptane. One triple bond is present in carbon third position and one methyl substituent is present in carbon fifth position. Hence, the systematic name of the compound is
Geometrical isomers are not possible because triple bond has only one substituent each.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
CHEM PRINCIPLES LL W/ACHIEVE ONE-SEM
- Please help me solve this reaction.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing 2,2-dimethylpropanal with acetaldehyde and sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forwardSynthesize 2-Ethyl-3-methyloxirane from dimethyl(propyl)sulfonium iodide using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- Synthesize 2-Hydroxy-2-phenylacetonitrile from phenylmethanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- If possible, please provide the formula of the compound 3,3-dimethylbut-2-enal.arrow_forwardSynthesize 1,4-dibromobenzene from acetanilide (N-phenylacetamide) using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing (3-oxo-3-phenylpropyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide with sodium hydride.arrow_forward
- We mix N-ethyl-2-hexanamine with excess methyl iodide and followed by heating with aqueous Ag2O. Indicate the major products obtained.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing acetophenone with iodine and NaOH.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing 2-Propanone and ethyllithium and performing a subsequent acid hydrolysis.arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning

