
Concept explainers
(a)
To select:
The pump that runs at the given speed performing the task with efficiency being maximum.
Answer to Problem 11.4CP
The pump that runs at the given speed performing the task with efficiency being maximum is determined below.
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
The given figure,
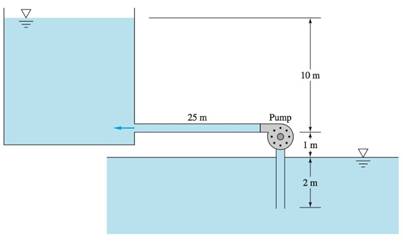
The system delivers 20-degree Celsius water from the sea level reservoir to another iron pipe with diameter 38 cm.
Minor loss before pump entrance
Minor loss after pump entrance
Concept Used:
Velocity of the flow:
Calculation:
According to the figure:
Reynold’s number:
Density
Dynamic Viscosity
Diameter=380mm
Volume=12.24m/s
Substituting the values:
The flow is turbulent.
Friction factor is given as:
Head loss using the friction factor is calculated.
Using equation (1)
Frictional heal loss is calculated using flow rates having different values:
| Q(gal/min) | 4000 | 8000 | 12000 | 16000 | 20000 | 22000 | 24000 |
| |
44 | 66 | 103 | 156 | 223 | 262 | 305 |
From the table and the reference figure at the flow rate of 20,000 gal/min, 88% efficiency. Hence the pump is given as 38 in.
Conclusion:
Thus, the pump that runs at the given speed performing the task with efficiency being maximum is determined.
(b)
To calculate:
The flow rate.
Answer to Problem 11.4CP
The flow rate is given as 20,000 gal/min
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
The given figure:
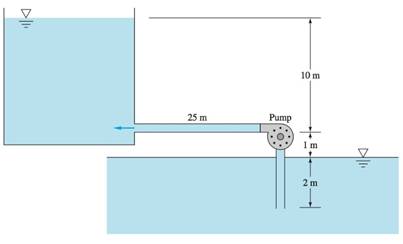
The system delivers 20-degree Celsius water from the sea level reservoir to another iron pipe with diameter 38 cm.
Minor loss before pump entrance
Minor loss after pump entrance
Concept Used:
Velocity of the flow:
Calculation:
Reynold’s number
Density
Dynamic Viscosity
Diameter=380mm
Volume=12.24m/s
Substituting the values:
The flow is turbulent.
Friction factor is given as:
Head loss using the friction factor is calculated:
Using equation (1)
Frictional heal loss is calculated using flow rates having different values:
| Q(gal/min) | 4000 | 8000 | 12000 | 16000 | 20000 | 22000 | 24000 |
| |
44 | 66 | 103 | 156 | 223 | 262 | 305 |
Conclusion:
Thus, the flow rate is determined.
(c)
Brake horse power.
Answer to Problem 11.4CP
Brake horse power=1250hp
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
The given figure,
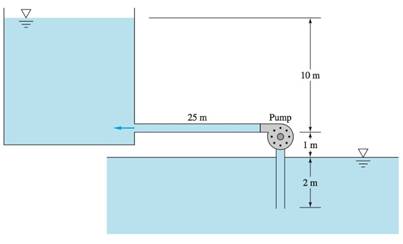
The system delivers 20-degree Celsius water from the sea level reservoir to another iron pipe with diameter 38 cm.
Minor loss before pump entrance
Minor loss after pump entrance
Concept Used:
Calculation:
Substituting we have:
Conclusion:
Thus, the brake horse power is calculated.
(d)
The given pump is safe from cavitation.
Answer to Problem 11.4CP
The pump replacement is needed as the pump will cavitate.
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
The given figure:
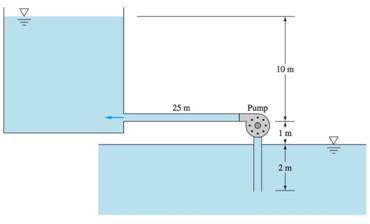
The system delivers 20-degree Celsius water from the sea level reservoir to another iron pipe with diameter 38 cm.
Minor loss before pump entrance
Minor loss after pump entrance
Concept Used:
Calculation:
Substituting we have:
For the flow rate Q=20000gal/min, the NPSH=16m(-0.36m).
So, the pump cavitates.
Conclusion:
Thus, the given pump is safe from cavitation is determined.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Fluid Mechanics
- Ibraheem Super Q3: A boiler as shown in the figure below is producing 2 kg/s saturated steam at 240C. The water enters the boiler at 24C. The boiler efficiency is 80%. Patm=1.05 bar .Determine: (10 Marks) 1- The inlet pressure of the turbine. 2- If a gauge pressure connected to the outlet pipe, what is the reading of this gauge? 3- Calculate the required diesel in [kg/s]. Assume the calorific value of the diesel is 45000 kJ/kgf 4- Calculate the equivalent evaporation of the boiler 5- Keeping the same inlet conditions and fuel consumption, determine the turbine efficiency if the produced steam was saturated at 300C. Steam Cut Hot Gasses Out Ts=240C Boiler FURNACE A Water In C 24 Examiner Head of Department Ahmad. A. M. Alsak laniarrow_forward##2# Superheated steam powers a steam turbine for the production of electrical energy. The steam expands in the turbine and at an intermediate expansion pressure (0.1 Mpa) a fraction is extracted for a regeneration process in a surface regenerator. The turbine has an isentropic efficiency of 90% Design the simplified power plant schematic Analyze it on the basis of the attached figure Determine the power generated and the thermal efficiency of the plant ### Dados in the attached imagesarrow_forward### To make a conclusion for a report of an experiment on rockets, in which the openrocket software was used for the construction and modeling of two rockets: one one-stage and one two-stage. First rocket (single-stage) reached a maximum vertical speed of 100 m/s and a maximum height of 500 m The second rocket (two-stage) reached a maximum vertical speed of 50 m/s and a maximum height of 250 m To make a simplified conclusion, taking into account the efficiency of the software in the study of rocketsarrow_forward
- Determine the coefficients of polynomial for the polynomial function of Cam profile based on the boundary conditions shown in the figure. S a 3 4 5 C₁ (+) Ꮎ В s = q + q { + c f * + q € * + q ( +c+c+c 6 Ꮎ +C5 +C β В В 0 cam angle 0 B 7 (arrow_forward### Superheated steam powers a steam turbine for the production of electrical energy. The steam expands in the turbine and at an intermediate expansion pressure (0.1 Mpa) a fraction is extracted for a regeneration process in a surface regenerator. The turbine has an isentropic efficiency of 90% Design the simplified power plant schematic Analyze it on the basis of the attached figure Determine the power generated and the thermal efficiency of the plant ### Dados in the attached imagesarrow_forwardThe machine below forms metal plates through the application of force. Two toggles (ABC and DEF) transfer forces from the central hydraulic cylinder (H) to the plates that will be formed. The toggles then push bar G to the right, which then presses a plate (p) into the cavity, thus shaping it. In this case, the plate becomes a section of a sphere. If the hydraulic cylinder can produce a maximum force of F = 10 kN, then what is the maximum P value (i.e. Pmax) that can be applied to the plate when θ = 35°? Also, what are the compressive forces in the toggle rods in that situation? Finally, what happens to Pmax and the forces in the rods as θ decreases in magnitude?arrow_forward
- Determine the magnitude of the minimum force P needed to prevent the 20 kg uniform rod AB from sliding. The contact surface at A is smooth, whereas the coefficient of static friction between the rod and the floor is μs = 0.3.arrow_forwardDetermine the magnitudes of the reactions at the fixed support at A.arrow_forwardLet Hill frame H = {i-hat_r, i-hat_θ, i-hat_h} be the orbit frame of the LMO satellite. These base vectors are generally defined as:i-hat_r = r_LM / |r_LM|, i-hat_theta = i-hat_h X i-hat_r, i-hat_h = r_LM X r-dot_LMO /( | r_LM X r-dot_LMO | ) How would you: • Determine an analytic expressions for [HN]arrow_forward
- De Moivre’s Theoremarrow_forwardhand-written solutions only, please.arrow_forwardDetermine the shear flow qqq for the given profile when the shear forces acting at the torsional center are Qy=30Q_y = 30Qy=30 kN and Qz=20Q_z = 20Qz=20 kN. Also, calculate qmaxq_{\max}qmax and τmax\tau_{\max}τmax. Given:Iy=10.5×106I_y = 10.5 \times 10^6Iy=10.5×106 mm4^44,Iz=20.8×106I_z = 20.8 \times 10^6Iz=20.8×106 mm4^44,Iyz=6×106I_{yz} = 6 \times 10^6Iyz=6×106 mm4^44. Additional parameters:αy=0.5714\alpha_y = 0.5714αy=0.5714,αz=0.2885\alpha_z = 0.2885αz=0.2885,γ=1.1974\gamma = 1.1974γ=1.1974. (Check hint: τmax\tau_{\max}τmax should be approximately 30 MPa.)arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





