
COST ACCOUNTING
16th Edition
ISBN: 9781323694008
Author: Horngren
Publisher: PEARSON C
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 11, Problem 11.46P
Closing down divisions. Ainsley Corporation has four operating divisions. The budgeted revenues and expenses for each division for 2017 follows:
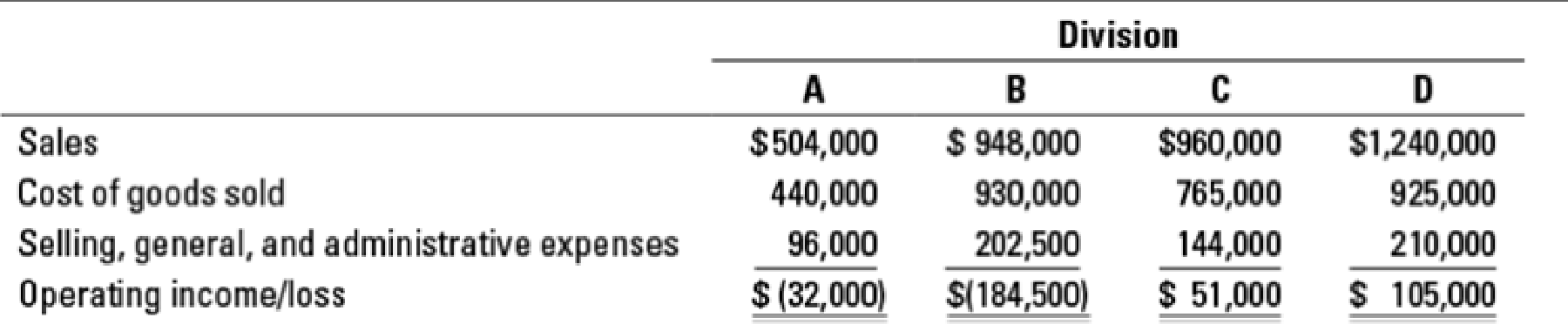
Further analysis of costs reveals the following percentages of variable costs in each division:

Closing down any division would result in savings of 40% of the fixed costs of that division.
Top management is very concerned about the unprofitable divisions (A and B) and is considering closing them for the year.
- 1. Calculate the increase or decrease in operating income if Ainsley closes division A.
Required
- 2. Calculate the increase or decrease in operating income if Ainsley closes division B.
- 3. What other factors should the top management of Ainsley consider before making a decision?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Leslie Corporation uses both ROI and residual income (RI) to measure performance. One of the company's divisions currently has $480,000 of capital invested
in assets and is expected to earn operating income of $120,000 in the current period. The division is considering an investment in new equipment costing
$345,000 that will likely increase its annual operating income by $45,000. The minimum ROI for all divisions within the company is 9%. 1. If the division does
not purchase the equipment, its estimated ROI will be
%. 2. If the division invests in the equipment, its ROI will likely decrease to
%. 3. If the division does not purchase the equipment, its estimated RI will be $
4. If the division invests in the
equipment, its RI will likely increase to $
Please provide answer in text (Without image)
Cop
Chapter 11 Solutions
COST ACCOUNTING
Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.1QCh. 11 - Define relevant costs. Why are historical costs...Ch. 11 - All future costs are relevant. Do you agree? Why?Ch. 11 - Distinguish between quantitative and qualitative...Ch. 11 - Describe two potential problems that should be...Ch. 11 - Variable costs are always relevant, and fixed...Ch. 11 - A component part should be purchased whenever the...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.8QCh. 11 - Managers should always buy inventory in quantities...Ch. 11 - Management should always maximize sales of the...
Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.11QCh. 11 - Cost written off as depreciation on equipment...Ch. 11 - Managers will always choose the alternative that...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.14QCh. 11 - Prob. 11.15QCh. 11 - Qualitative and quantitative factors. Which of the...Ch. 11 - Special order, opportunity cost. Chade Corp. is...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.18MCQCh. 11 - Keep or drop a business segment. Lees Corp. is...Ch. 11 - Relevant costs. Ace Cleaning Service is...Ch. 11 - Disposal of assets. Answer the following...Ch. 11 - Relevant and irrelevant costs. Answer the...Ch. 11 - Multiple choice. (CPA) Choose the best answer. 1....Ch. 11 - Special order, activity-based costing. (CMA,...Ch. 11 - Make versus buy, activity-based costing. The...Ch. 11 - Inventory decision, opportunity costs. Best Trim,...Ch. 11 - Relevant costs, contribution margin, product...Ch. 11 - Selection of most profitable product. Body Image,...Ch. 11 - Theory of constraints, throughput margin, relevant...Ch. 11 - Closing and opening stores. Sanchez Corporation...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.31ECh. 11 - Relevance of equipment costs. Janets Bakery is...Ch. 11 - Equipment upgrade versus replacement. (A. Spero,...Ch. 11 - Special order, short-run pricing. Diamond...Ch. 11 - Short-run pricing, capacity constraints. Fashion...Ch. 11 - International outsourcing. Riverside Clippers Corp...Ch. 11 - Relevant costs, opportunity costs. Gavin Martin,...Ch. 11 - Opportunity costs and relevant costs. Jason Wu...Ch. 11 - Opportunity costs. (H. Schaefer, adapted) The Wild...Ch. 11 - Make or buy, unknown level of volume. (A....Ch. 11 - Make versus buy, activity-based costing,...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.42PCh. 11 - Product mix, special order. (N. Melumad, adapted)...Ch. 11 - Theory of constraints, throughput margin, and...Ch. 11 - Theory of constraints, contribution margin,...Ch. 11 - Closing down divisions. Ainsley Corporation has...Ch. 11 - Dropping a product line, selling more tours....Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.48PCh. 11 - Dropping a customer, activity-based costing,...Ch. 11 - Equipment replacement decisions and performance...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Allocate 2017 fixed costs using the allocation bases suggested by Fisher. What is each division’s operating margin percentage under the new allocation scheme?arrow_forwardColonial Pharmaceuticals is a small firm specializing in new products. It is organized into two divisions, which are based on the products they produce. AC Division is smaller and the life of the products it produces tend to be shorter than those produced by the larger SO Division. Selected financial data for the past year is shown as follows. Divisional investment is as of the beginning of the year. Colonial Pharmaceuticals uses a 9 percent cost of capital and uses beginning-of-the-year investment when computing ROI and residual income. Ignore income taxes. so Division $ 1,500 AC Division $ 630 Allocated corp. overhead Cost of goods sold 3,260 7,600 77,000 Divisional investment 9,600 R&D 4,200 1,875 9,200 Sales 20,600 SG&A 790 1,230 R&D is assumed to have a two-year life in the AC Division and a nine-year life in the SO division. All R&D expenditures are spent at the beginning of the year. Assume there are no current liabilities and (unrealistically) that no R&D investments had taken…arrow_forwardColonial Pharmaceuticals is a small firm specializing in new products. It is organized into two divisions, which are based on the products they produce. AC Division is smaller and the life of the products it produces tend to be shorter than those produced by the larger SO Division. Selected financial data for the past year is shown as follows. Divisional Investment is as of the beginning of the year. Colonial Pharmaceuticals uses a 10 percent cost of capital and uses beginning-of-the-year Investment when computing ROI and residual income. Ignore Income taxes. Allocated corp. overhead Cost of goods sold Divisional investment R&D Sales SG&A AC Division $ 620 3,240 9,400 2,200 8,800 760 SO Division $ 1,600 6,600 78,000 3,400 18,000 1,330 Required: a. Compute divisional Income for the two divisions. b. Calculate the operating margin, which is equivalent to the return on sales, for the two divisions. c. Calculate ROI for the two divisions. d. Compute residual income for the two divisions.arrow_forward
- A study has been conducted to determine if one of the departments in Parry Company should be discontinued. The contribution margin in the department is $40,000 per year. Fixed expenses charged to the department are $65,000 per year. It is estimated that $30,000 of these fixed expenses could be eliminated if the department is discontinued. These data indicate that if the department is discontinued, the company's overall net operating income would: Oa. decrease by $15,000 per year. Ob. decrease by $10,000 per year. c. increase by $10,000 per year. Od. increase by $15,000 per year.arrow_forwardColonial Pharmaceuticals is a small firm specializing in new products. It is organized into two divisions, which are based on the products they produce. AC Division is smaller and the life of the products it produces tend to be shorter than those produced by the larger SO Division. Selected financial data for the past year is shown as follows. Divisional investment is as of the beginning of the year. Colonial Pharmaceuticals uses a 8 percent cost of capital and uses beginning-of-the-year investment when computing ROI and residual income. Ignore income taxes. AC Division so Division $ 1,050 Allocated corp. overhead Cost of goods sold Divisional investment $ 675 3,350 10,500 5,500 72,500 3,600 19,500 R&D 2,750 Sales 11,000 SG&A 925 780 R&D is assumed to have a two-year life in the AC Division and a nine-year life in the SO division. All R&D expenditures are spent at the beginning of the year. Assume there are no current liabilities and (unrealistically) that no R&D investments had taken…arrow_forwardColonial Pharmaceuticals is a small firm specializing in new products. It is organized into two divisions, which are based on the products they produce. AC Division is smaller and the life of the products it produces tend to be shorter than those produced by the larger SO Division. Selected financial data for the past year is shown as follows. Divisional investment is as of the beginning of the year. Colonial Pharmaceuticals uses a 8 percent cost of capital and uses beginning-of-the-year investment when computing ROI and residual income. Ignore income taxes. Allocated corp. overhead Cost of goods sold Divisional investment R&D Sales SG&A AC Division $ 670 3,340 10,400 2,700 10,800 910 SO Division $ 1,100 5,600 73,000 3,600 20,000 830arrow_forward
- The background info is provided in the image attached. Solve the following: e) Recompute the break-even point in units, assuming that variable costs increased by 20% and fixed costs are reduced by $50,625. How will this impact the margin of safety ratio? f) The President of Buggs-Off is under pressure from shareholders to increase operating income by 20% in 2021. Management expects per unit data and total fixed costs to remain the same in 2021. Using the equation method, compute the number of units that would have to be sold in 2021 to reach the shareholder's desired profit level. Is this a realistic goal?arrow_forwardA study has been conducted to determine if one of the departments in Carry Corporation should be discontinued. The contribution margin in the department is $80,000 per year. Fixed expenses charged to the department are $95,000 per year. It is estimated that $50,000 of these fixed expenses could be eliminated if the department is discontinued. These data indicate that if the department is discontinued, the yearly financial advantage (disadvantage) for the company would be: Multiple Choice O ($30,000) ($15,000) $15,000 $30,000arrow_forwardForchen, Inc., provided the following information for two of its divisions for last year: Required: 1. For the Small Appliances Division, calculate: a. Average operating assets b. Margin c. Turnover d. Return on investment (ROI) 2. For the Cleaning Products Division, calculate: a. Average operating assets b. Margin c. Turnover d. Return on investment (ROI) 3. What if operating income for the Small Appliances Division was 2,000,000? How would that affect average operating assets? Margin? Turnover? ROI? Calculate any changed ratios (round to four significant digits).arrow_forward
- The Deluxe Division, a profit center of Riley Manufacturing Company, reported the following data for the first quarter of 2016:Sales $9,000,000Variable costs 6,300,000Controllable direct fixed costs 1,200,000Noncontrollable direct fixed costs 530,000Indirect fixed costs 300,000Instructions(a) Prepare a performance report for the manager of the Deluxe Division.(b) What is the best measure of the manager’s performance? Why?(c) How would the responsibility report differ if the division was an investment center?arrow_forwardhe Pacific Division of Cullumber Industries reported the following data for the current year. Sales $4,179,930 Variable costs 2,625,000 Controllable fixed costs 825,000 Average operating assets 5,034,000 Top management is unhappy with the investment center’s return on investment. It asks the manager of the Pacific Division to submit plans to improve ROI in the next year. The manager believes it is feasible to consider the following independent courses of action. 1. Increase sales by $425,000 with no change in the contribution margin percentage. 2. Reduce variable costs by $145,986. 3. Reduce average operating assets by 4% (a) Compute the return on investment for the current year. (Round answers to 1 decimal place, e.g. 52.7%.) Return on investment enter the return on investment in percentages %arrow_forwardFrieden’s management is considering a major upgrade to the manufacturing equipment, which would result in fixed expenses increasing by $360,000 per month. However, variable expenses would decrease by $9 per unit. Selling price would not change. Prepare two contribution format income statements, one showing current operations and one showing how operations would appear if the upgrade is completed. Show an Amount column, a Per Unit column, and a Percentage column on each statement.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning

Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...
Accounting
ISBN:9781305970663
Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. Mowen
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to Divisional performance measurement - ACCA Performance Management (PM); Author: OpenTuition;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pk8Mzoqr4VA;License: Standard Youtube License