
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The reaction with detailed mechanism for the formation of the given compound from the corresponding
Concept introduction:
The electrophilic addition reaction of an alkene occurs through formation of a more stable carbocation. The electrophilic addition of water across the double bond in an acidic condition produces the alcohol product. The reaction proceeds with proton transfer reaction to form a stable carbocation, followed by the action of water as a nucleophile.
Answer to Problem 11.33P
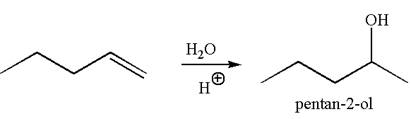
The reaction equation and the detailed mechanism for the formation of
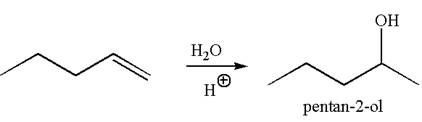
Explanation of Solution
The structure for the given compound
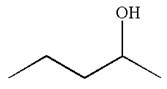
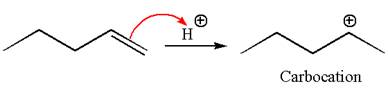
To form the given alcohol by electrophilic addition of water, the double bond must be between the carbon where the
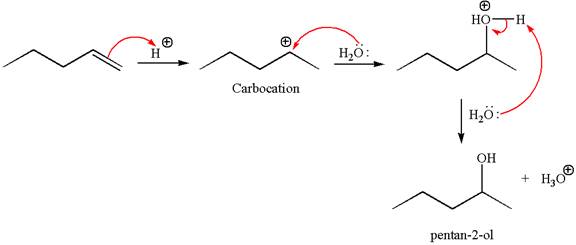
The reaction occurs in acidic condition. Thus the first step is the formation of a secondary carbocation by proton transfer reaction. The proton transfers to the less substituted carbon, forming a more stable carbocation.
In the second step, the water molecule acts as a nucleophile and attacks the carbocation, forming the desired product, followed by deprotonation of the positively charged oxygen.
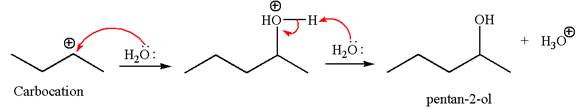
The reaction equation and detailed mechanism are drawn for the formation of
(b)
Interpretation:
The reaction with detailed mechanism for the formation of the given compound from the corresponding alkene by single electrophilic addition reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The electrophilic addition reaction of an alkene occurs through formation of a more stable carbocation. The electrophilic addition of water across the double bond in an acidic condition produces the alcohol product. The reaction proceeds with proton transfer reaction to form a stable carbocation, followed by the action of water as a nucleophile.
Answer to Problem 11.33P
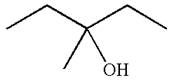
The reaction equation and the detailed mechanism for the formation of
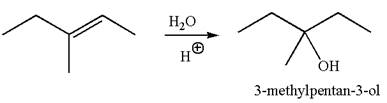
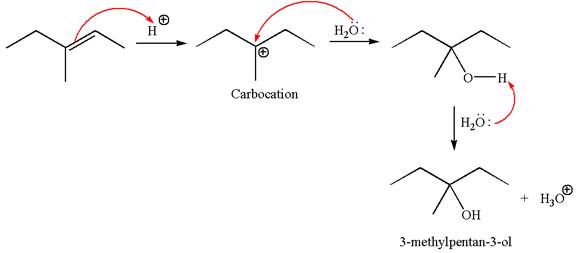
Explanation of Solution
The structure for the given compound
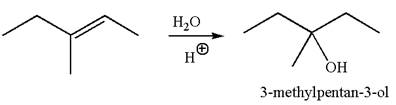
To form the given alcohol by electrophilic addition of water, the double bond must be between the carbon where the
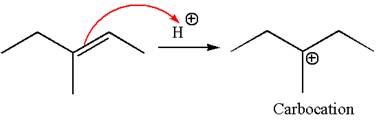
The reaction occurs in acidic condition. Thus the first step is the formation of a tertiary carbocation by proton transfer reaction. The proton transfers to the less substituted carbon, forming a more stable carbocation.
In the second step, the water molecule acts as a nucleophile and attacks the carbocation, forming the desired product, followed by deprotonation of the positively charged oxygen.
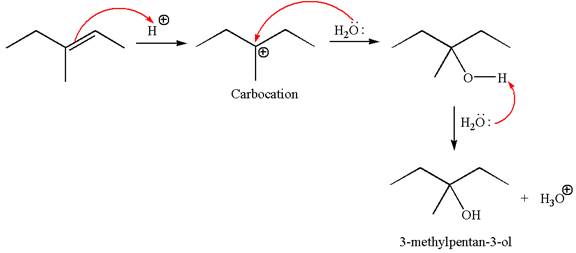
The reaction equation and detailed mechanism are drawn for the formation of
(c)
Interpretation:
The reaction with detailed mechanism for the formation of the given compound from the corresponding alkene by single electrophilic addition reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The electrophilic addition reaction of an alkene occurs through formation of a more stable carbocation. The electrophilic addition of water across the double bond in an acidic condition produces the alcohol product. The reaction proceeds with proton transfer reaction to form a stable carbocation, followed by the action of water as a nucleophile.
Answer to Problem 11.33P
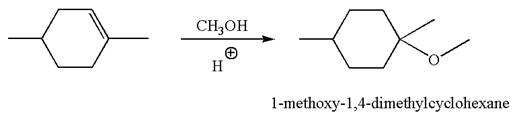
The reaction equation and the detailed mechanism for the formation of
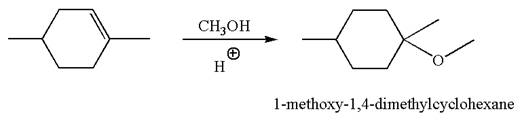
Explanation of Solution
The structure for the given compound
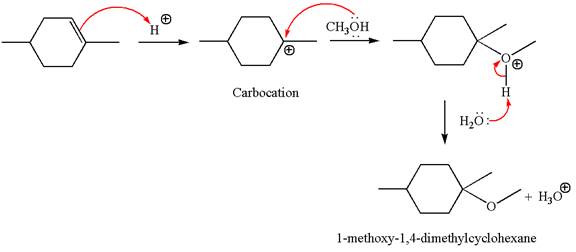
To form the given ether by electrophilic addition of alcohol, the double bond must be between the carbon where the
The reaction occurs in acidic condition. Thus the first step is the formation of a tertiary carbocation by proton transfer reaction. The proton transfers to the less substituted carbon, forming a more stable carbocation.
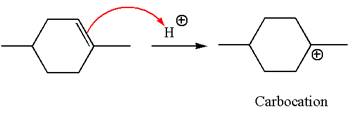
In the second step, the methanol molecule acts as a nucleophile and attacks the carbocation, forming the desired product, followed by deprotonation of the positively charged oxygen.
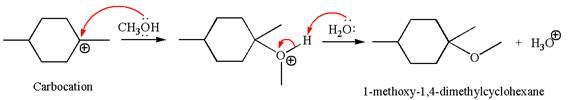
The reaction equation and detailed mechanism are drawn for the formation of
(d)
Interpretation:
The reaction with detailed mechanism for the formation of the given compound from the corresponding alkene by single electrophilic addition reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The electrophilic addition reaction of an alkene occurs through formation of a more stable carbocation. The electrophilic addition of water across the double bond in an acidic condition produces the alcohol product. The reaction proceeds with proton transfer reaction to form a stable carbocation, followed by the action of water as a nucleophile.
Answer to Problem 11.33P
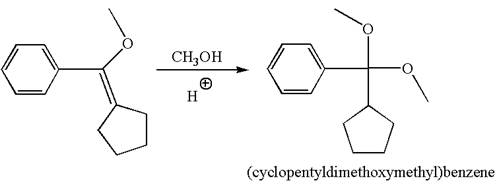
The reaction equation and the detailed mechanism for the formation of (cyclopentyldimethoxymethyl) benzene from alkene are
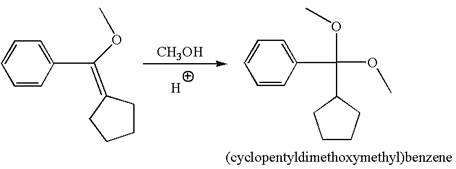
Explanation of Solution
The structure for the given compound (cyclopentyldimethoxymethyl) benzene is
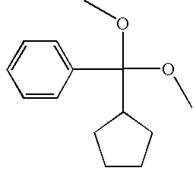
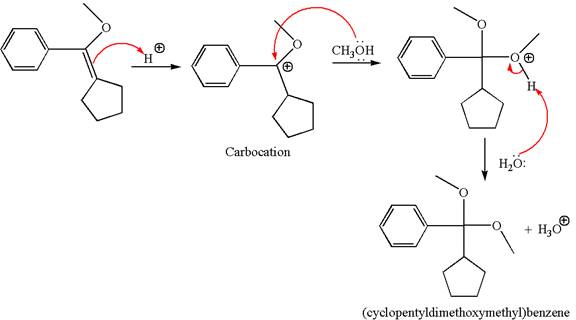
To form the given ether by single electrophilic addition of alcohol, the double bond must be between the carbon where the
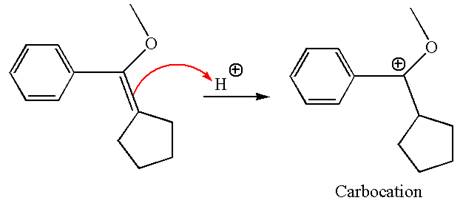
The reaction occurs in acidic condition. Thus the first step is the formation of a tertiary carbocation by proton transfer reaction. The proton transfers to the less substituted carbon, forming a more stable carbocation.
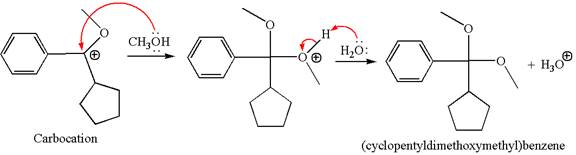
In the second step, the methanol molecule acts as a nucleophile and attacks the carbocation, forming the desired product, followed by deprotonation of the positively charged oxygen.
The reaction equation and detailed mechanism are drawn for the formation of (cyclopentyldimethoxymethyl) benzene by identifying the corresponding alkene.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Get Ready for Organic Chemistry
- Show your work and do something that is reasonable. It does not have to be 100% correct. Just show something that looks good or pretty good as acceptable answers. Something that looks reasonable or correct would be sufficient. If you can get many of them correct that would be great!arrow_forwardShow your work and do something that is reasonable. It does not have to be 100% correct. Just show something that looks good or pretty good as acceptable answers. Something that looks reasonable or correct would be sufficient. If you can get many of them correct that would be great!arrow_forwardTake a look at the following molecule, and then answer the questions in the table below it. (You can click the other tab to see the molecule without the colored regions.) with colored region plain 0= CH2-0-C-(CH2)16-CH3 =0 CH-O-C (CH2)7-CH=CH-(CH2)5-CH3 D CH3 | + OMPLO CH3-N-CH2-CH2-0-P-O-CH2 B CH3 A Try again * 000 Ar 8 0 ?arrow_forward
- Show your work and do something that is reasonable. It does not have to be 100% correct. Just show something that looks good or pretty good as acceptable answers.arrow_forwardShow your work and do something that is reasonable. It does not have to be 100% correct. Just show something that looks good or pretty good as acceptable answers.arrow_forward= 1 = 2 3 4 5 6 ✓ 7 8 ✓ 9 =10 Devise a synthesis to prepare the product from the given starting material. Complete the following reaction scheme. Part 1 of 3 -Br Draw the structure for compound A. Check Step 1 Step 2 A Click and drag to start drawing a structure. × ↓m + OH Save For Later S 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privaarrow_forward
- Predict the products of this organic reduction: 田 Check AP + + H2 Lindlar catalyst Click an drawing 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rigarrow_forward70 Suppose the molecule below is in acidic aqueous solution. Is keto-enol tautomerization possible? • If a keto-enol tautomerization is possible, draw the mechanism for it. Be sure any extra reagents you add to the left-hand sid available in this solution. • If a keto-enol tautomerization is not possible, check the box under the drawing area. : ☐ Add/Remove step Click and drag to st drawing a structure Check Save For Late. 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Usearrow_forwardThe problem will not be graded for correctness, but you have to get a reasonable answer something that is either correct or very closer to the correct answer. The instructor professor wants us to do something that shows the answer but everything does not have to be correct. Ideally, yes, it has to be correct. Give it your best shot.arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
