
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The reaction and complete, detailed mechanism for the reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
A strong Bronsted acid such as
Answer to Problem 11.27P
The overall reaction for the given compound is
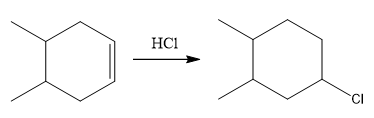
The complete mechanism for the above reaction is
Explanation of Solution
The structure for the given compound
The compound shown above is the alkyl halide compound. This compound is formed by an electrophilic addition reaction of alkene with a strong Bronsted acid
The overall reaction for the given compound is

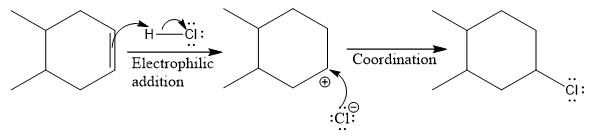
The above reaction completes in two steps. In the first step, the electrophilic addition step, the proton is added to one carbon with C=C bond, forming the carbocation intermediate. The second step is the coordination step in which the nucleophile attacks the carbocation to yield the product.
The complete mechanism for the above reaction is

The reaction and complete, detailed mechanism for the reaction is drawn on the basis of the mechanism of electrophilic addition reaction of alkenes with strong acid.
(b)
Interpretation:
The reaction and complete, detailed mechanism for the reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Alkyl halide is the product of the electrophilic addition reaction of the alkene with a strong Bronsted acid such as
A strong Bronsted acid such as
Answer to Problem 11.27P
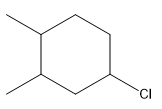
The overall reaction for the given compound is
The complete mechanism for the above reaction is
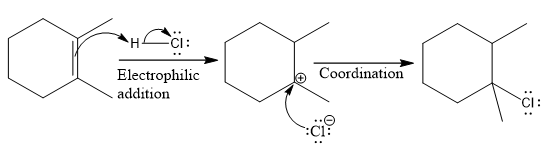
Explanation of Solution
The structure for the given compound
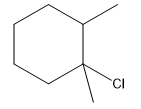
The compound shown above is the alkyl halide compound. This compound is formed by an electrophilic addition reaction of an alkene with a strong Bronsted acid
The overall reaction for the given compound is

The above reaction completes in two steps. In the first step, the electrophilic addition step, the proton is added to one carbon with C=C bond, forming the carbocation intermediate. The second step is the coordination step in which the nucleophile attacks the carbocation to yield the product.
The complete mechanism for the above reaction is

The reaction and complete, detailed mechanism for the reaction is drawn on the basis of the mechanism of electrophilic addition reaction of alkenes with strong acid.
(c)
Interpretation:
The reaction and complete, detailed mechanism for the reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Alkyl halide is the product of the electrophilic addition reaction of the alkene with a strong Bronsted acid such as
A strong Bronsted acid such as
Answer to Problem 11.27P
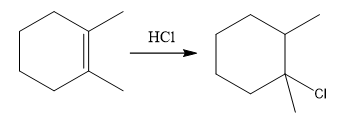
The overall reaction for the given compound is
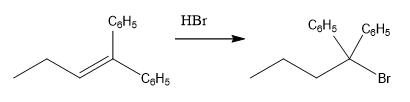
The complete mechanism for the above reaction is
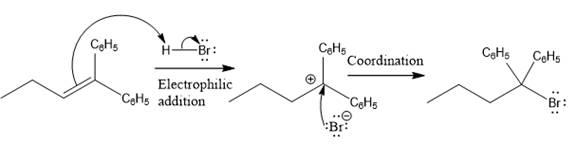
Explanation of Solution
The structure for the given compound
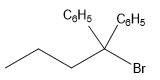
The compound shown above is the alkyl halide compound. This compound is formed by an electrophilic addition reaction of alkene with a strong Bronsted acid
The overall reaction for the given compound is

The above reaction completes in two steps. In the first step, the electrophilic addition step, the proton added to the internal carbon, forming the the more stable carbocation intermediate, which is tertiary and resonance stabilized. The second step is the coordination step in which the nucleophile attacks the carbocation to yield the product.
The complete mechanism for the above reaction is
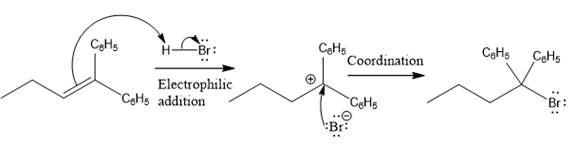
The reaction and complete, detailed mechanism for the reaction is drawn on the basis of the mechanism of electrophilic addition reaction of alkenes with strong acid.
(d)
Interpretation:
The reaction and complete, detailed mechanism for the reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Alkyl halide is the product of the electrophilic addition reaction of the alkene with a strong Bronsted acid such as
A strong Bronsted acid such as
Answer to Problem 11.27P
The overall reaction for the given compound is
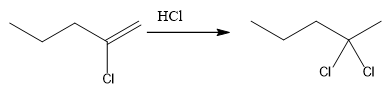
The complete mechanism for the above reaction is
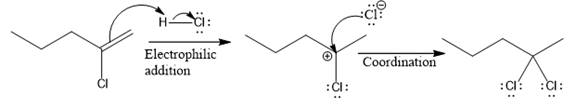
Explanation of Solution
The structure for the given compound
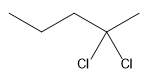
The compound shown above is the alkyl halide compound. This compound is formed by an electrophilic addition reaction of alkene with a strong Bronsted acid
The overall reaction for the given compound is

The above reaction completes in two steps. In the first step, the electrophilic addition step, the proton is added to the internal carbon, forming the the more stable carbocation intermediate, which is tertiary. The second step is the coordination step in which the nucleophile attacks the carbocation to yield the product.
The complete mechanism for the above reaction is
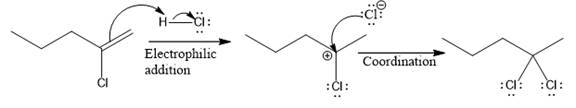
The reaction and complete, detailed mechanism for the reaction is drawn on the basis of the mechanism of electrophilic addition reaction of alkenes with strong acid.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
ORG CHEM W/ EBOOK & SW5 + STUDY GUIDE
- Draw a tetramer of this alternating copolymer.arrow_forwardH I T H HH H -H C. H- Identify and select all structures below that represent a constitutional isomer(s) of the compound shown above. H- H CIH H H H HHHH H H 0 ·H H– 冊 CH CHI HH C- H- H H- H H A. H H C H H- -H HH H B. H- -H D. H H H H • H -H E. -H H H HICH T HHH F. H-arrow_forwardPolylactic acid (shown below) is a biodegradable polymer used for food packaging. Identify the monomer(s) used in the production of this polymer using a condensation process.arrow_forward
- Draw the product of the reaction shown below. Ignore small byproducts that would evaporate pleasearrow_forwardPoly(ethylene adipate) is a biodegradable polyester (shown below). Identify the type of polymerization process used in the production of this polymer.arrow_forwardPolymers may be composed of thousands of monomers. draw two repeat units(dimer) of the polymer formed in this reaction. assume there are hydrogen atoms on the two ends of the dimer. ignore inorganic byproducts pleasearrow_forward
- Draw the product of the reaction shown below. Use a dash or wedge bond to indicate stereochemistry of substituents on asymmetric centers, Ignore inorganic byproductsarrow_forwardDraw the product of this reaction please. Ignore inorganic byproductsarrow_forwardOne of the pi molecular orbitals of 1,3-butadiene (CH2=CHCH=CH2) is shown below. Please identify the number of nodal planes perpendicular to the bonding axisarrow_forward
- Draw the monomers required to synthesize this condensation polymer please.arrow_forwardProvide the correct systematic name for the compound shown here. Please take into account the keyboard options belowarrow_forwardcurved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s)arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





