
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The product that is formed by the reaction of
Concept introduction: The replacement or substitution of one
Answer to Problem 11.20P
The product that is formed by the reaction of
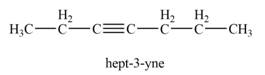
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of
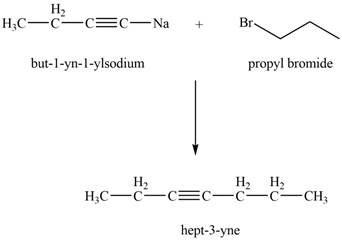
Figure 1
Thus, the product that is formed by the reaction of
The product that is formed by the reaction of
(b)
Interpretation: The product that is formed by the reaction of
Concept introduction: The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The nucleophilic reaction that consists of bimolecular as well as bond-making and bond-breaking steps is termed as
Answer to Problem 11.20P
The product that is formed by the reaction of
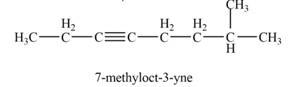
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of
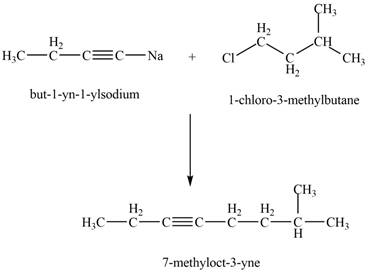
Figure 2
Thus, the product that is formed by the reaction of
The product that is formed by the reaction of
(c)
Interpretation: The product that is formed by the reaction of
Concept introduction: The bimolecular elimination reaction that favours the removal of a HX substituent from an
Answer to Problem 11.20P
The product that is formed by the reaction of
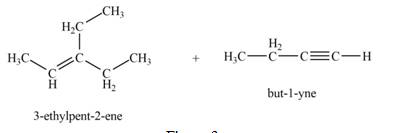
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of
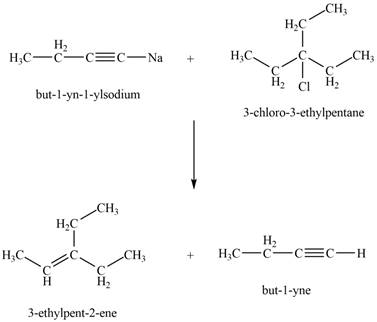
Figure 3
Thus, the products that are formed by the reaction of
The products that are formed by the reaction of
(d)
Interpretation: The product that is formed by the reaction of
Concept introduction: The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The nucleophilic reaction that consists of bimolecular as well as bond-making and bond-breaking steps is termed as
Answer to Problem 11.20P
The product that is formed by the reaction of
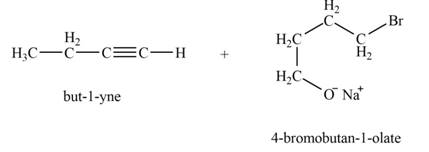
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of
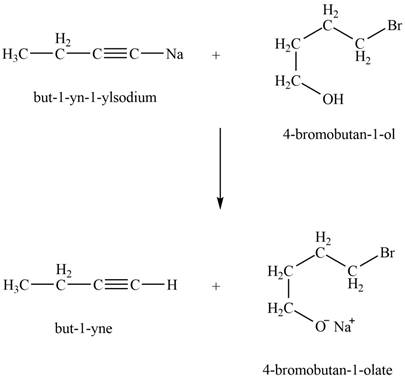
Figure 4
Thus, the major product that is formed by the reaction of
The major product that is formed by the reaction of
(e)
Interpretation: The product that is formed by the reaction of
Concept introduction: The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The nucleophilic reaction that consists of bimolecular as well as bond-making and bond-breaking steps is termed as
Answer to Problem 11.20P
The product that is formed by the reaction of
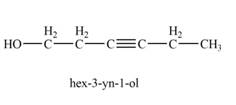
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of
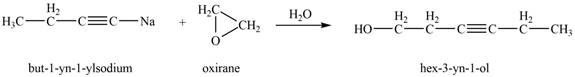
Figure 5
Thus, the major product that is formed by the reaction of
The product that is formed by the reaction of
(f)
Interpretation: The product that is formed by the reaction of
Concept introduction: The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The nucleophilic reaction that consists of bimolecular as well as bond-making and bond-breaking steps is termed as
Answer to Problem 11.20P
The product that is formed by the reaction of
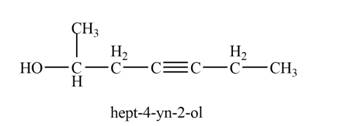
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of
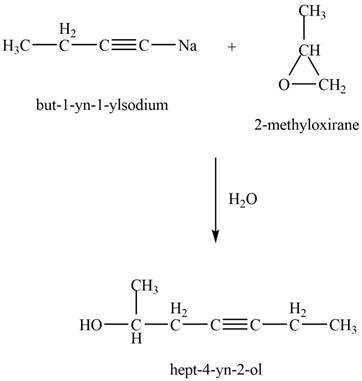
Figure 6
Thus, the major product that is formed by the reaction of
The product that is formed by the reaction of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- 36) Complete the following multi-step reactions showing applications of enolate ions arising from ketones, esters, malonic ester, and keto ester, etc. (30 pts) (1) A NaOH, H₂O+ heat A NaOEt EtO OEt (11) EOH, H+ H. B LDA, H₂O+ -78°C B (i) NaOMe, Et-Br (ii) H₂O+, heat EtOOC (III) COOEt B A (i) NaOEt LiAlH 4-bromo-2-butene H₂O+ (ii) H3O+, heat Write the mechanism for Aldol Condensation (I A or B), and Claisen Condensation (II A).arrow_forward31) Complete two sets of reactions involving (R)-4-methyl-pent-2-ol producing racemic mixture of tertiary alcohols (D) and ketone derivative (C). Illustrate the mechanism of B and C or D. (25 pts) O OH 0 K2Cr2O7 Ph-CH2-Br, Mg, H2SO4 THF, H3O* (A) (D) Racemic mixture TsCl, Py (B) KCN, DMSO Ph-CH2-Br, Mg, THF, H3O+ (C) Mechanism for reactions B and C:arrow_forwardManoharan Mariappan, Ph.D., Dept. of Natur. Sci., NFC, Tallahassee, FL 33) Synthesize the aromatic compound containing para-substituted carbonyl compound starting from benzene. Illustrate the mechanism for reaction A. 1) NU (25 pts) A FeCl B (i) HNO3, H2SO4 (II) Sn, HCl(aq) NH₂ NO₂-D NH₂ (i) MeCO2Me, heat C (ii) K2Cr2O7/H2SO4 D (ii) SOCl2 (iii) 2 Et-NH2 Mechanism for reaction for the nitration of alkyl benzene (B-i): Characterize the product compound arising from the reaction D by IR and IH NMR spectral data: IR data (cm): 'H NMR data: Draw the structure and assign the chemical shift with the spin-splitting.arrow_forward
- Write structural formulas for the major products by doing addition reactions 1. You must add H2 as Pt is catalyst it does not take part in reactions only speed up the process H₂ CH2=CH-CH3 Pt 2. Add HCI break it into H and Cl CH3 HCI 3. Add Br2 only CC14 is catalyst CH3-CH=CH2 B12 CCl4 4. Add water to this and draw major product, H2SO4 is catalyst you have add water H20 in both the reaction below H₂SO4 CH3-CH=CH2 CH3 H2SO4/H₂O CH3-C=CH2 reflux ?arrow_forwardPlan the synthesis of the following compound using the starting material provided and any other reagents needed as long as carbon based reagents have 3 carbons or less. Either the retrosynthesis or the forward synthesis (mechanisms are not required but will be graded if provided) will be accepted if all necessary reagents and intermediates are shown (solvents and temperature requirements are not needed unless specifically involved in the reaction, i.e. DMSO in the Swern oxidation or heat in the KMnO4 oxidation). H Harrow_forwardHint These are benzene substitution reactions. ALCI3 and UV light are catalyst no part in reactions and triangle A means heating. A. Add ethyl for Et in benzene ring alkylation reaction EtCl = CH3CH2CL 1) EtC1 / AlCl3 / A ? B: Add Br to benzene ring ( substitution) 2) Br₂ / uv light ? C Add (CH3)2 CHCH2 in benzene ring ( substitution) (CH3)2CHCH,C1 / AICI, ?arrow_forward
- Draw the mechanism to make the alcohol 2-hexanol. Draw the Mechanism to make the alcohol 1-hexanol.arrow_forwardDraw the mechanism for the formation of diol by starting with 1-pentanal in... basic conditions then acidic conditions then draw the mechanism for the formation of a carboxylic acid from your product.arrow_forwardIdentify each chiral carbon as either R or S. Identify the overall carbohydrates as L or Darrow_forward
- Ethers can be formed via acid-catalyzed acetal formation. Draw the mechanism for the molecule below and ethanol.arrow_forwardHOCH, H HO CH-OH OH H OH 11 CH₂OH F II OH H H 0 + H OHarrow_forwardDraw the mechanism for the formation of diol by starting with one pen and all in... basic conditions then acidic conditions then draw the mechanism for the formation of a carboxylic acid from your product.arrow_forward
- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning 
 Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax





