
Concept explainers
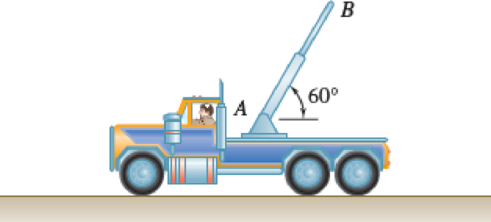
The end point B of a boom is originally 5 m from fixed point A when the driver starts to retract the boom with a constant radial acceleration of r = −1.0 m/s2 and lower it with a constant angular acceleration θ = −0.5 rad/ s2. At t = 2 s, determine (a) the velocity of point B,(b) the acceleration of point B, (c) the radius of curvature of the path.
Fig. P11.192
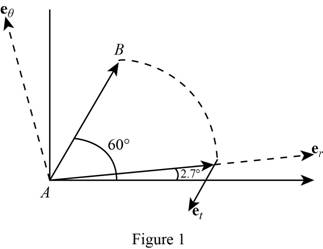
(a)
The velocity
Answer to Problem 11.192RP
The velocity
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The distance
The boom with a constant radial velocity
The boom with a constant radial acceleration
The boom with a constant angular acceleration
The time (t) is 2 sec.
Calculation:
Write the expression for rectangular position coordinate (r) of point B using equation of motion:
Here,
The radial initial velocity of point B is 0.
Calculate the radial coordinate (r) of point B:
Substitute 5m for
Calculate the radial velocity
Substitute 0 for
Calculate the angular coordinate
Here,
Angular coordinate of initial velocity of point B is 0. Thus,
Substitute
Calculate the
Substitute zero for
Calculate velocity
Here,
Rewrite Equation (2) in terms of r,
Substitute
Calculate the magnitude of
Substitute
Calculate unit vector
Substitute
Calculate angle
Substitute
Calculate the angle
Substitute
Therefore, the velocity
(b)
The acceleration
Answer to Problem 11.192RP
The acceleration
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The distance
The boom with a constant radial acceleration
The boom with a constant radial acceleration
The boom with a constant angular acceleration
The time (t) is 2 sec.
Calculation:
Show the values of
Write acceleration
Here,
Rewrite the above equation in term of r,
Substitute
Here,
Calculate the magnitude of
Substitute
Calculate the angle
Substitute
Calculate the angle
Substitute
Therefore, the acceleration
(c)
The radius of curvature
Answer to Problem 11.192RP
The radius of curvature
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The distance
The boom with a constant radial acceleration
The boom with a constant radial acceleration
The boom with a constant angular acceleration
The time (t) is 2 sec.
Calculation:
Calculate the tangential component of acceleration
Substitute
Write normal component
Substitute
Substitute
Calculate the normal acceleration
Substitute
Calculate the radius of curvature
Rewrite Equation for radius of curvature.
Substitute
Therefore, the radius of curvature
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
VECTOR MECH...,STAT.+DYN.(LL)-W/ACCESS
- Correct answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution only with fbd. I will upvote, thank you.arrow_forwardCorrect answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution only. I will upvote, thank you.arrow_forwardCorrect answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution with fbd only. I will upvote, thank you.arrow_forward
- Correct answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution only. I will upvote, thank you.arrow_forwardCorrect answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution with fbd only. I will upvote, thank you.arrow_forwardCorrect answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution only. I will upvote, thank you.arrow_forward
- Correct answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution only. I will upvote, thank you.arrow_forwardCorrect answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution only. I will upvote, thank you.arrow_forwardCorrect answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution with fbd only. I will upvote, thank you. Prefferably handwritten solution pleasearrow_forward
- Correct answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution with fbd only. I will upvote, thank you. Prefferably handwritten solution pleasearrow_forwardCorrect answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution only. I will upvote, thank you.arrow_forwardCorrect answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution with fbd only. I will upvote, thank you. Prefferably handwritten solution pleasearrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





